Abstract
Introduction
The early development of progressive scoliosis with pelvic obliquity is the most significant orthopaedic problem for non-ambulatory children with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
Patients
24 SMA patients were operated on for scoliosis using the ISOLA® system and 17 patients using a telescopic rod. The average age at spinal surgery was 12.3 years (6.5–22.7) in the ISOLA® group and 6.7 years (4.8–10.9) in the telescopic rod group.
Results
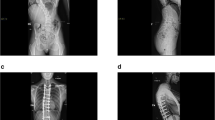
The Cobb angle was corrected on average from pre-operative 83°(54°–120°) to post-operative 39°(5°–70°) in the ISOLA® group and, respectively, from 62°(28°–86°) to 18°(0°–34°) in the telescopic rod group. Mean loss of correction at mean follow-up of 6 years (3–10) was 6°(0°–33°) in the ISOLA® group and at mean follow-up of 8.6 years (3–12) 13°(0°–49°) in the telescopic rod group excluding the patients with rod failure. The vital capacity is not worsened by these operations in comparison to the natural course. After telescopic rods were implanted, there were some unsatisfactory results due to crankshaft phenomenon and an increase of pelvic obliquity.
Conclusion
Our recommendation for non-ambulatory SMA patients is to have definitive stabilisation using multisegmental instrumentation, starting from the age of 10 to 12 years.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudnik-Schöneborn S, de Visser M, Zerres K (2004) Spinal Muscular Atrophies. In: Engel A, Franzini-Armstrong C (eds) Myology, McGraw-Hill, New York, p 1845–1864
Forst R, Ingenhorst A, Mortier W (2003) Neuromusculäre Systemerkrankungen. In: Zichner L (ed) Orthopädie und Orthopädische Chirurgie Systemerkrankungen, Thieme,Stuttgart, p 243–254
Fujak A, Forst R, Forst J (2010) Current strategies of conservative and operative treatment of the most frequent muscular disorders. Orthopade 39:38–52
Fujak A, Wollinsky KH, Forst R (2007) Proximal spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Z Orthop Unfallchir 145:1–20
Fujak A, Kopschina C, Forst R, Mueller LA, Forst J (2011) Use of orthoses and orthopaedic technical devices in proximal spinal muscular atrophy. Results of survey in 194 SMA patients. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol 6:305–311
Fujak A, Ingenhorst A, Heuser K, Forst R, Forst J (2005) Treatment of scoliosis in intermediate spinal muscular atrophy (SMA type II) in childhood. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil 7:175–179
Fujak A, Kopschina C, Gras F, Forst R, Forst J (2010) Contractures of the upper extremities in spinal muscular atrophy type II. Descriptive clinical study with retrospective data collection. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil 12:410–419
Fujak A, Kopschina C, Gras F, Forst R, Forst J (2011) Contractures of the lower extremities in spinal muscular atrophy type II. Descriptive clinical study with retrospective data collection. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil 13:27–36
Fujak A, Kopschina C, Forst R, Gras F, Mueller LA, Forst J (2010) Fractures in proximal spinal muscular atrophy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130:775–780
Granata C, Merlini L, Magni E, Marini ML, Stagni SB (1989) Spinal muscular atrophy: natural history and orthopaedic treatment of scoliosis. Spine 14:760–762
Schwentker EP, Gibson DA (1976) The orthopaedic aspects of spinal muscular atrophy. J Bone Joint Surg Am A 58:32–38
Hensinger RN, MacEwen DG (1976) Spinal deformity associated with heritable neurological conditions: Spinal muscular atrophy, friedreich′s ataxia, familial dysautonomia and charcot-marie-tooth disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am A 58:13–24
Evans GA, Drennan JC, Russman BS (1981) Functional Classification and orthopaedic management of spinal muscular atrophy. J Bone Joint Surg Br B 63:516–522
Riddick MF, Winter RB, Lutter LD (1982) Spinal deformities in patients with spinal muscular atrophy. Spine 7:476–483
Aprin H, Bowen JR, MacEwen GD, Hall JE (1982) Spine fusion in patients with spinal muscular atrophy. J Bone Joint Surg Am A 64:1179–1187
Daher YH, Lonstein JE, Winter RB, Bradford DS (1985) Spinal surgery in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J Pedriatr Orthop 5:391–395
Piasecki JO, Mahinpuor S, Levine DB (1986) Long-term follow-up of spinal fusion in spinal muscular atrophy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 207:44–54
Rodillo E, Marini ML, Heckmatt JZ, Dubowitz V (1989) Scoliosis in spinal muscular atrophy: review of 63 cases. J Child Neurol 4:118–123
Brown JC, Zeller JL, Swank SM, Furumasu J, Warath SL (1989) Surgical and functional results of spine fusion in spinal muscular atrophy. Spine 14:763–770
Broom MJ, Banta JV, Renshaw TS (1989) Spinal fusion augmented by luque-rod segmental instrumentation for neuromuscular scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am A 71:32–44
Furumasu J, Swank SM, Brown JC, Gilgoff I, Warath S, Zeller J (1989) Functional activities in spinal muscular atrophy patients after spinal fusion. Spine 14:771–775
Merlini L, Granata C, Bonfiglioli S, Marini ML, Cervellati S, Savini R (1989) Scoliosis in spinal muscular atrophy: natural history and management. Dev Med Child Neurol 31:501–508
Bell DF, Moseley CF, Koreska J, Eng P (1989) Unit rod segmental spinal instrumentation in the management of patients with progressive neuromuscular spinal deformity. Spine 14:1301–1307
Phillips DP, Roye DP, Farcy JP, Leet A, Shelton YA (1990) Surgical treatment of scoliosis in spinal muscular atrophy population. Spine 15:942–945
Granata C, Cervellati S, Ballestrazzi A, Corbascio M, Merlini L (1993) Spine surgery in spinal muscular atrophy: long term results. Neuromuscul Disord 3:207–215
Robinson D, Galasko CS, Delaney C, Williamson JB, Barrie JL (1995) Scoliosis and lung function in spinal muscular atrophy. Eur Spine J 4:268–273
Bridwell KH, Baldus C, Iffrig TM, Lenke LG, Blanke K (1999) Process measures and patient/parent evaluation of surgical management of spinal deformities in patients with progressive flaccid neuromuscular scoliosis (Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy). Spine 24:1300–1309
Bentley G, Haddad F, Bull TM, Seingry D (2001) The treatment of scoliosis in muscular dystrophy using modified Luque and Harrington-Luque instrumentation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83:22–28
Thacker M, Hui JHP, Wong HK, Chatterjee A, Lee EH (2002) Spinal fusion and instrumentation for paediatric neuromuscular scoliosis: retrospective review. J Orthop Surg 10:144–151
Chng SY, Wong YQ, Hui JH, Wong HK, Ong HT, Goh DY (2003) Pulmonary function and scoliosis in children with spinal muscular atrophy types II and III. J Paediatr Child Health 39:673–676
Roso V, Bitu Sde O, Zanoteli E, etta JT, de Castro RC, Fernandes AC (2003) Surgical treatment of scoliosis in spinal muscular atrophy. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 61:631–638
Modi HN, Suh SW, Hong JY, Cho JW, Park JH, Yang JH (2010) Treatment and complications in flaccid neuromuscular scoliosis (Duchenne muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy) with posterior-only pedicle screw instrumentation. Eur Spine J 19:384–393
Chandran S, McCarthy J, Noonan K, Mann D, Nemeth B, Guiliani T (2011) Early treatment of scoliosis with growing rods in children with severe spinal muscular atrophy: a preliminary report. J Pediatr Orthop 31:450–454
McElroy MJ, Shaner AC, Crawford TO, Thompson GH, Kadakia RV, Akbarnia BA, Skaggs DL, Emans JB, Sponseller PD (2011) Growing rods for scoliosis in spinal muscular atrophy: structural effects, complications, and hospital stays. Spine 36:1305–1311
Zebala LP, Bridwell KH, Baldus C, Richards SB, Dormans JP, Lenke LG, Auerbach JD, Lovejoy J (2011) Minimum 5-year radiographic results of long scoliosis fusion in juvenile spinal muscular atrophy patients: major curve progression after instrumented fusion. J Pediatr Orthop 31:480–488
Lohnstein JE (1989) Mangement of spinal deformity in spinal muscular atrophy. In: Merlini L, Granata C, Dubowitz V (eds) Current conepts in childhood spinal muscular atrophy, Springer, Wien, p 165–172
Noordeen MH, Lee J, Gibbons CE, Taylor BA, Bentley G (1997) Spinal cord monitoring in operations for neuromuscular scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:53–57
Shapiro F, Specht L (1993) The Diagnosis and Orthopaedic Treatment of Childhood Spinal Muscular Atrophy, Peripheral Neuropathy, Friedreich Ataxia, and Arthrogyposis. J Bone Joint Surg Am A 75:1699–1714
Miladi LT, Ghanem IB, Draoui MM, Zeller RD, Dubousset JF (1997) Iliosacral screw fixation for pelvic obliquity in neuromuscular scoliosis. A long-term follow-up study. Spine 22:1722–1729
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujak, A., Raab, W., Schuh, A. et al. Operative treatment of scoliosis in proximal spinal muscular atrophy: results of 41 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132, 1697–1706 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-012-1610-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-012-1610-8