Abstract
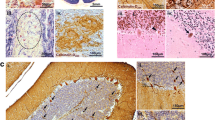
Cerebellar atrophy, consequent to the postdevelopmental degeneration and loss of Purkinje cells and granular neurons, has been identified in three patients with rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata (RCDP). Cerebellar atrophy in our two chronic patients was symmetrical, but the vermis and medial portions of both hemispheres, particularly the dorsal lobules, displayed more severe atrophy than the lateral hemispheres. The distal tips of folia showed the greatest neuronal loss. Residual Purkinje cells showed progressive degenerative changes that appeared to be due, in part, to their topography. The precise mode of death of Purkinje cells in RCDP has not been established, but it does not appear to be mediated by entrance into the cell cycle or by ubiquitination; however, alterations in intracellular calcium levels and mitochondria may be involved. Elevated serum/CSF phytanic acid, decreased levels of tissue plasmalogens and increased chronological age are believed to play synergistic pathogenetic roles in this lesion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 September 1998 / Revised, accepted: 21 December 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Powers, J., Kenjarski, T., Moser, A. et al. Cerebellar atrophy in chronic rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata: a potential role for phytanic acid and calcium in the death of its Purkinje cells. Acta Neuropathol 98, 129–134 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010051060
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010051060