Abstract
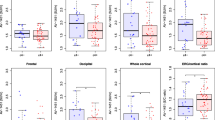
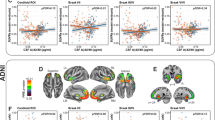
Apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 allele is the most important genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and it is thought to do so by modulating levels of its product, apolipoprotein E (Apo-E), and regulating amyloid-β (Aβ) clearance. However, information on clinical and biomarker correlates of Apo-E proteins is scarce. We examined the relationship of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma Apo-E protein levels, and APOE genotype to cognition and AD biomarker changes in 311 AD neuroimaging initiative subjects with CSF Apo-E measurements and 565 subjects with plasma Apo-E measurements. At baseline, higher CSF Apo-E levels were associated with higher total and phosphorylated CSF tau levels. CSF Apo-E levels were associated with longitudinal cognitive decline, MCI conversion to dementia, and gray matter atrophy rate in total tau/Aβ1–42 ratio and APOE genotype-adjusted analyses. In analyses stratified by APOE genotype, our results were only significant in the group without the ε4 allele. Baseline CSF Apo-E levels did not predict longitudinal CSF Aβ or tau changes. Plasma Apo-E levels show a mild correlation with CSF Apo-E levels, but were not associated with longitudinal cognitive and MRI changes. Based on our analyses, we speculate that increased CSF Apo-E2 or -E3 levels might represent a protective response to injury in AD and may have neuroprotective effects by decreasing neuronal damage independent of tau and amyloid deposition in addition to its effects on amyloid clearance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki K, Uchihara T, Sanjo N, Nakamura A, Ikeda K, Tsuchiya K, Wakayama Y (2003) Increased expression of neuronal apolipoprotein E in human brain with cerebral infarction. Stroke 34(4):875–880. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000064320.73388.C6
Baird GS, Nelson SK, Keeney TR, Stewart A, Williams S, Kraemer S, Peskind ER, Montine TJ (2012) Age-dependent changes in the cerebrospinal fluid proteome by slow off-rate modified aptamer array. Am J Pathol 180(2):446–456. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.024
Boschert U, Merlo-Pich E, Higgins G, Roses AD, Catsicas S (1999) Apolipoprotein E expression by neurons surviving excitotoxic stress. Neurobiol Dis 6(6):508–514. doi:10.1006/nbdi 1999.0251
Boyles JK, Pitas RE, Wilson E, Mahley RW, Taylor JM (1985) Apolipoprotein E associated with astrocytic glia of the central nervous system and with nonmyelinating glia of the peripheral nervous system. J Clin Invest 76(4):1501–1513. doi:10.1172/JCI112130
Bunce D, Fratiglioni L, Small BJ, Winblad B, Backman L (2004) APOE and cognitive decline in preclinical Alzheimer disease and non-demented aging. Neurology 63(5):816–821
Burnham SC, Faux NG, Wilson W, Laws SM, Ames D, Bedo J, Bush AI, Doecke JD, Ellis KA, Head R, Jones G, Kiiveri H, Martins RN, Rembach A, Rowe CC, Salvado O, Macaulay SL, Masters CL, Villemagne VL (2013) A blood-based predictor for neocortical Abeta burden in Alzheimer’s disease: results from the AIBL study. Mol Psychiatry. doi:10.1038/mp.2013.40
Castellano JM, Kim J, Stewart FR, Jiang H, DeMattos RB, Patterson BW, Fagan AM, Morris JC, Mawuenyega KG, Cruchaga C, Goate AM, Bales KR, Paul SM, Bateman RJ, Holtzman DM (2011) Human apoE isoforms differentially regulate brain amyloid-beta peptide clearance. Sci Transl Med 3(89):89ra57. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3002156
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261(5123):921–923
Cosentino S, Scarmeas N, Helzner E, Glymour MM, Brandt J, Albert M, Blacker D, Stern Y (2008) APOE epsilon 4 allele predicts faster cognitive decline in mild Alzheimer disease. Neurology 70(19 Pt 2):1842–1849. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000304038.37421.cc
Cramer PE, Cirrito JR, Wesson DW, Lee CY, Karlo JC, Zinn AE, Casali BT, Restivo JL, Goebel WD, James MJ, Brunden KR, Wilson DA, Landreth GE (2012) ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models. Science 335(6075):1503–1506. doi:10.1126/science.1217697
Cruchaga C, Kauwe JS, Nowotny P, Bales K, Pickering EH, Mayo K, Bertelsen S, Hinrichs A, Fagan AM, Holtzman DM, Morris JC, Goate AM (2012) Cerebrospinal fluid APOE levels: an endophenotype for genetic studies for Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 21(20):4558–4571. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds296
Darreh-Shori T, Modiri N, Blennow K, Baza S, Kamil C, Ahmed H, Andreasen N, Nordberg A (2011) The apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele plays pathological roles in AD through high protein expression and interaction with butyrylcholinesterase. Neurobiol Aging 32(7):1236–1248. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.07.015
Doecke JD, Laws SM, Faux NG, Wilson W, Burnham SC, Lam CP, Mondal A, Bedo J, Bush AI, Brown B, De Ruyck K, Ellis KA, Fowler C, Gupta VB, Head R, Macaulay SL, Pertile K, Rowe CC, Rembach A, Rodrigues M, Rumble R, Szoeke C, Taddei K, Taddei T, Trounson B, Ames D, Masters CL, Martins RN (2012) Blood-based protein biomarkers for diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 69(10):1318–1325. doi:10.1001/archneurol2012.1282
Donkin JJ, Stukas S, Hirsch-Reinshagen V, Namjoshi D, Wilkinson A, May S, Chan J, Fan J, Collins J, Wellington CL (2010) ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 mediates the beneficial effects of the liver X receptor agonist GW3965 on object recognition memory and amyloid burden in amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 mice. J Biol Chem 285(44):34144–34154. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.108100
Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JL, Hyman B, Kukull WA, Mayeux R, Myers RH, Pericak-Vance MA, Risch N, van Duijn CM (1997) Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA 278(16):1349–1356
Figurski MJ, Waligorska T, Toledo J, Vanderstichele H, Korecka M, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM (2012) Improved protocol for measurement of plasma beta-amyloid in longitudinal evaluation of Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative study patients. Alzheimers Dement 8(4):250–260. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2012.01.001
Fitz NF, Cronican AA, Lefterov I, Koldamova R (2013) Comment on “ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models”. Science 340(6135):924-c. doi:10.1126/science.1235809
Foster JK, Albrecht MA, Savage G, Lautenschlager NT, Ellis KA, Maruff P, Szoeke C, Taddei K, Martins R, Masters CL, Ames D (2013) Lack of reliable evidence for a distinctive {varepsilon}4-related cognitive phenotype that is independent from clinical diagnostic status: findings from the Australian imaging, biomarkers and lifestyle study. Brain 136(Pt 7):2201–2216. doi:10.1093/brain/awt127
Fukuyama R, Mizuno T, Mori S, Yanagisawa K, Nakajima K, Fushiki S (2000) Age-dependent decline in the apolipoprotein E level in cerebrospinal fluid from control subjects and its increase in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Neurol 43(3):161–169 (8157)
Gregg RE, Zech LA, Schaefer EJ, Stark D, Wilson D, Brewer HB Jr (1986) Abnormal in vivo metabolism of apolipoprotein E4 in humans. J Clin Invest 78(3):815–821. doi:10.1172/JCI112645
Gupta VB, Laws SM, Villemagne VL, Ames D, Bush AI, Ellis KA, Lui JK, Masters C, Rowe CC, Szoeke C, Taddei K, Martins RN (2011) Plasma apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease risk: the AIBL study of aging. Neurology 76(12):1091–1098. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318211c352
Haag MD, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Stricker BH, Breteler MM (2009) Statins are associated with a reduced risk of Alzheimer disease regardless of lipophilicity. The Rotterdam study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80(1):13–17. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2008.150433
Hong Z, Shi M, Chung KA, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Galasko D, Jankovic J, Zabetian CP, Leverenz JB, Baird G, Montine TJ, Hancock AM, Hwang H, Pan C, Bradner J, Kang UJ, Jensen PH, Zhang J (2010) DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 133(Pt 3):713–726. doi:10.1093/brain/awq008
Hu WT, Holtzman DM, Fagan AM, Shaw LM, Perrin R, Arnold SE, Grossman M, Xiong C, Craig-Schapiro R, Clark CM, Pickering E, Kuhn M, Chen Y, Van Deerlin VM, McCluskey L, Elman L, Karlawish J, Chen-Plotkin A, Hurtig HI, Siderowf A, Swenson F, Lee VM, Morris JC, Trojanowski JQ, Soares H (2012) Plasma multianalyte profiling in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 79(9):897–905. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318266fa70
Huang Y (2010) Abeta-independent roles of apolipoprotein E4 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med 16(6):287–294. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2010.04.004
Huang Y, Liu XQ, Wyss-Coray T, Brecht WJ, Sanan DA, Mahley RW (2001) Apolipoprotein E fragments present in Alzheimer’s disease brains induce neurofibrillary tangle-like intracellular inclusions in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(15):8838–8843. doi:10.1073/pnas.151254698
Jack CR Jr, Bernstein MA, Fox NC, Thompson P, Alexander G, Harvey D, Borowski B, Britson PJ, Whitwell JL, Ward C, Dale AM, Felmlee JP, Gunter JL, Hill DL, Killiany R, Schuff N, Fox-Bosetti S, Lin C, Studholme C, DeCarli CS, Krueger G, Ward HA, Metzger GJ, Scott KT, Mallozzi R, Blezek D, Levy J, Debbins JP, Fleisher AS, Albert M, Green R, Bartzokis G, Glover G, Mugler J, Weiner MW (2008) The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI): MRI methods. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(4):685–691. doi:10.1002/jmri.21049
Jiang Q, Lee CY, Mandrekar S, Wilkinson B, Cramer P, Zelcer N, Mann K, Lamb B, Willson TM, Collins JL, Richardson JC, Smith JD, Comery TA, Riddell D, Holtzman DM, Tontonoz P, Landreth GE (2008) ApoE promotes the proteolytic degradation of Abeta. Neuron 58(5):681–693. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2008.04.010
Kim S, Swaminathan S, Inlow M, Risacher SL, Nho K, Shen L, Foroud TM, Petersen RC, Aisen PS, Soares H, Toledo JB, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ, Weiner MW, McDonald BC, Farlow MR, Ghetti B, Saykin AJ (2013) Influence of genetic variation on plasma protein levels in older adults using a multi-analyte panel. PLoS One 8(7):e70269. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070269
Korff A, Liu C, Ginghina C, Shi M, Zhang J (2013) α-Synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 36(4):679–688. doi:10.3233/JAD-130458
LaClair KD, Manaye KF, Lee DL, Allard JS, Savonenko AV, Troncoso JC, Wong PC (2013) Treatment with bexarotene, a compound that increases apolipoprotein-E, provides no cognitive benefit in mutant APP/PS1 mice. Mol Neurodegener 8:18. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-8-18
Landreth GE, Cramer PE, Lakner MM, Cirrito JR, Wesson DW, Brunden KR, Wilson DA (2013) Response to comments on “ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models”. Science 340(6135):924-g. doi:10.1126/science.1234114
Lehtimaki T, Pirttila T, Mehta PD, Wisniewski HM, Frey H, Nikkari T (1995) Apolipoprotein E (apoE) polymorphism and its influence on ApoE concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid in Finnish patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Genet 95(1):39–42
Liu CC, Kanekiyo T, Xu H, Bu G (2013) Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat Rev Neurol 9(2):106–118. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2012.263
Liu M, Kuhel DG, Shen L, Hui DY, Woods SC (2012) Apolipoprotein E does not cross the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier, as revealed by an improved technique for sampling CSF from mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 303(9):R903–R908. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00219.2012
Poirier J, Hess M, May PC, Finch CE (1991) Astrocytic apolipoprotein E mRNA and GFAP mRNA in hippocampus after entorhinal cortex lesioning. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 11(2):97–106
Price AR, Xu G, Siemienski ZB, Smithson LA, Borchelt DR, Golde TE, Felsenstein KM (2013) Comment on “ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models”. Science 340(6135):924-d. doi:10.1126/science.1234089
Reiman EM, Chen K, Liu X, Bandy D, Yu M, Lee W, Ayutyanont N, Keppler J, Reeder SA, Langbaum JB, Alexander GE, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Price JC, Aizenstein HJ, DeKosky ST, Caselli RJ (2009) Fibrillar amyloid-beta burden in cognitively normal people at 3 levels of genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(16):6820–6825. doi:10.1073/pnas.0900345106
Reuter M, Rosas HD, Fischl B (2010) Highly accurate inverse consistent registration: a robust approach. Neuroimage 53(4):1181–1196. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.07.020
Reuter M, Schmansky NJ, Rosas HD, Fischl B (2012) Within-subject template estimation for unbiased longitudinal image analysis. Neuroimage 61(4):1402–1418. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.02.084
Riddell DR, Zhou H, Atchison K, Warwick HK, Atkinson PJ, Jefferson J, Xu L, Aschmies S, Kirksey Y, Hu Y, Wagner E, Parratt A, Xu J, Li Z, Zaleska MM, Jacobsen JS, Pangalos MN, Reinhart PH (2008) Impact of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) polymorphism on brain ApoE levels. J Neurosci 28(45):11445–11453. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1972-08.2008
Roheim PS, Carey M, Forte T, Vega GL (1979) Apolipoproteins in human cerebrospinal fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76(9):4646–4649
Shaw LM, Vanderstichele H, Knapik-Czajka M, Clark CM, Aisen PS, Petersen RC, Blennow K, Soares H, Simon A, Lewczuk P, Dean R, Siemers E, Potter W, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker signature in Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative subjects. Ann Neurol 65(4):403–413. doi:10.1002/ana.21610
Shaw LM, Vanderstichele H, Knapik-Czajka M, Figurski M, Coart E, Blennow K, Soares H, Simon AJ, Lewczuk P, Dean RA, Siemers E, Potter W, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2011) Qualification of the analytical and clinical performance of CSF biomarker analyses in ADNI. Acta Neuropathol 121(5):597–609. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0808-0
Shepardson NE, Shankar GM, Selkoe DJ (2011) Cholesterol level and statin use in Alzheimer disease: I. Review of epidemiological and preclinical studies. Arch Neurol 68(10):1239–1244. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2011.203
Shepardson NE, Shankar GM, Selkoe DJ (2011) Cholesterol level and statin use in Alzheimer disease: II. Review of human trials and recommendations. Arch Neurol 68(11):1385–1392. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2011.242
Soares HD, Potter WZ, Pickering E, Kuhn M, Immermann FW, Shera DM, Ferm M, Dean RA, Simon AJ, Swenson F, Siuciak JA, Kaplow J, Thambisetty M, Zagouras P, Koroshetz WJ, Wan HI, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM (2012) Plasma biomarkers associated with the apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 69(10):1310–1317. doi:10.1001/archneurol2012.1070
Tesseur I, Lo AC, Roberfroid A, Dietvorst S, Van Broeck B, Borgers M, Gijsen H, Moechars D, Mercken M, Kemp J, D’Hooge R, De Strooper B (2013) Comment on “ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models”. Science 340(6135):924-e. doi:10.1126/science.1233937
Toledo JB, Arnold SE, Raible K, Brettschneider J, Xie SX, Grossman M, Monsell SE, Kukull WA, Trojanowski JQ (2013) Contribution of cerebrovascular disease in autopsy confirmed neurodegenerative disease cases in the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Centre. Brain 136(Pt 9):2697–2706. doi:10.1093/brain/awt188
Toledo JB, Korff A, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ, Zhang J (2013) CSF alpha-synuclein improves diagnostic and prognostic performance of CSF tau and Abeta in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 126(5):683–697. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1148-z
Toledo JB, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ (2013) Plasma amyloid beta measurements—a desired but elusive Alzheimer’s disease biomarker. Alzheimers Res Ther 5(2):8. doi:10.1186/alzrt162
Toledo JB, Vanderstichele H, Figurski M, Aisen PS, Petersen RC, Weiner MW, Jack CR Jr, Jagust W, Decarli C, Toga AW, Toledo E, Xie SX, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM (2011) Factors affecting Abeta plasma levels and their utility as biomarkers in ADNI. Acta Neuropathol 122(4):401–413. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0861-8
Toledo JB, Xie SX, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM (2013) Longitudinal change in CSF Tau and Abeta biomarkers for up to 48 months in ADNI. Acta Neuropathol 126(5):659–670. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1151-4
Vanmierlo T, Rutten K, Dederen J, Bloks VW, van Vark-van der Zee LC, Kuipers F, Kiliaan A, Blokland A, Sijbrands EJ, Steinbusch H, Prickaerts J, Lutjohann D, Mulder M (2011) Liver X receptor activation restores memory in aged AD mice without reducing amyloid. Neurobiol Aging 32(7):1262–1272. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.07.005
Veeraraghavalu K, Zhang C, Miller S, Hefendehl JK, Rajapaksha TW, Ulrich J, Jucker M, Holtzman DM, Tanzi RE, Vassar R, Sisodia SS (2013) Comment on “ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models”. Science 340(6135):924-f. doi:10.1126/science.1235505
Vijayaraghavan S, Maetzler W, Reimold M, Lithner CU, Liepelt-Scarfone I, Berg D, Darreh-Shori T (2013) High apolipoprotein E in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Lewy body disorders is associated with dementia. Alzheimers Dement. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2013.03.010
Villemagne VL, Burnham S, Bourgeat P, Brown B, Ellis KA, Salvado O, Szoeke C, Macaulay SL, Martins R, Maruff P, Ames D, Rowe CC, Masters CL (2013) Amyloid beta deposition, neurodegeneration, and cognitive decline in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol 12(4):357–367. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70044-9
Wahrle SE, Shah AR, Fagan AM, Smemo S, Kauwe JS, Grupe A, Hinrichs A, Mayo K, Jiang H, Thal LJ, Goate AM, Holtzman DM (2007) Apolipoprotein E levels in cerebrospinal fluid and the effects of ABCA1 polymorphisms. Mol Neurodegener 2:7. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-2-7
Weiner MW, Veitch DP, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Cairns NJ, Green RC, Harvey D, Jack CR, Jagust W, Liu E, Morris JC, Petersen RC, Saykin AJ, Schmidt ME, Shaw L, Siuciak JA, Soares H, Toga AW, Trojanowski JQ (2012) The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative: a review of papers published since its inception. Alzheimers Dement 8(1 Suppl):S1–S68. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2011.09.172
Weisgraber KH, Shinto LH (1991) Identification of the disulfide-linked homodimer of apolipoprotein E3 in plasma. Impact on receptor binding activity. J Biol Chem 266(18):12029–12034
Winnock M, Letenneur L, Jacqmin-Gadda H, Dallongeville J, Amouyel P, Dartigues JF (2002) Longitudinal analysis of the effect of apolipoprotein E epsilon4 and education on cognitive performance in elderly subjects: the PAQUID study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72(6):794–797
Wolk DA, Dickerson BC (2010) Apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotype has dissociable effects on memory and attentional-executive network function in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(22):10256–10261. doi:10.1073/pnas.1001412107
Xu Q, Bernardo A, Walker D, Kanegawa T, Mahley RW, Huang Y (2006) Profile and regulation of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) expression in the CNS in mice with targeting of green fluorescent protein gene to the ApoE locus. J Neurosci 26(19):4985–4994. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5476-05.2006
Yaffe K, Cauley J, Sands L, Browner W (1997) Apolipoprotein E phenotype and cognitive decline in a prospective study of elderly community women. Arch Neurol 54(9):1110–1114
Yu L, Boyle PA, Leurgans S, Schneider JA, Bennett DA (2013) Disentangling the effects of age and APOE on neuropathology and late life cognitive decline. Neurobiol Aging. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.10.074
Acknowledgments
Data collection and sharing for this project were funded by (ADNI (National Institutes of Health Grant U01 AG024904). ADNI is funded by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, and through generous contributions from the following: Alzheimer’s Association; Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation; BioClinica, Inc.; Biogen Idec Inc.; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; Eisai Inc.; Elan Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Eli Lilly and Company; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd and its affiliated company Genentech, Inc.; GE Healthcare; Innogenetics, N·V.; IXICO Ltd.; Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy Research and Development, LLC.; Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development LLC.; Medpace, Inc.; Merck & Co., Inc.; Meso Scale Diagnostics, LLC.; NeuroRx Research; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; Pfizer Inc.; Piramal Imaging; Servier; Synarc Inc.; and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company. The Canadian Institutes of Health Research is providing funds to support ADNI clinical sites in Canada. Private sector contributions are facilitated by the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (www.fnih.org). The grantee organization is the Northern California Institute for Research and Education, and the study is coordinated by the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study at the University of California, San Diego. ADNI data are disseminated by the Laboratory for Neuro Imaging at the University of California, Los Angeles. This research was also supported by NIH grants P30 AG010129 and K01 AG030514. JQT is the William Maul Measey-Truman G. Schnabel, Jr., Professor of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology.
Conflict of interest
Dr. Arnold reports grants from NIH, the American Health Assistance Foundation and the Marian S Ware Alzheimer’s Programseveral pharmaceutical companies, other from Universities, pharmaceutical companies and advisory/speaking honoraria from Universities, pharmaceutical companies and law firms. Dr. Trojanowski reports grants from NIH, Bristol Myer Squib, Astra Zeneca and several non-profits, outside the submitted work; In addition, Dr. Trojanowski has a patent Modified avidin–biotin technique, Method of stabilizing microtubules to treat Alzheimer’s disease, Method of detecting abnormally phosphorylated tau, Method of screening for Alzheimer’s disease or disease associated with the accumulation of paired helical filaments, Compositions and methods for producing and using homogeneous neuronal cell transplants, Rat comprising straight filaments in its brain, Compositions and methods for producing and using homogeneous neuronal cell transplants to treat neurodegenerative disorders and brain and spinal cord injuries, Diagnostic methods for Alzheimer’s disease by detection of multiple MRNAs, Methods and compositions for determining lipid peroxidation levels in oxidant stress syndromes and diseases, Compositions and methods for producing and using homogenous neuronal cell transplants, Method of identifying, diagnosing and treating alpha-synuclein positive neurodegenerative disorders, Mutation-specific functional impairments in distinct tau isoforms of hereditary frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome-17: genotype predicts phenotype, Microtubule stabilizing therapies for neurodegenerative disorders, and Treatment of Alzheimer’s and related diseases with an antibody pending, and a patent Amyloid plaque aggregation inhibitors and diagnostic imaging agents sold to Avid to Eli Lily. Dr. Weiner reports stock/stock options from Elan, Synarc, travel expenses from Novartis, Tohoku University, Fundacio Ace, Travel eDreams, MCI Group, NSAS, Danone Trading, ANT Congress, NeuroVigil, CHRU-Hopital Roger Salengro, Siemens, AstraZeneca, Geneva University Hospitals, Lilly, University of California, San Diego—ADNI, Paris University, Institut Catala de Neurociencies Aplicades, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Ipsen, Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease, Pfizer, AD PD meeting, Paul Sabatier University, board membership for Lilly, Araclon, Institut Catala de Neurociencies Aplicades, Gulf War Veterans Illnesses Advisory Committee, VACO, Biogen Idec, Pfizer, consultancy from AstraZeneca, Araclon, Medivation/Pfizer, Ipsen, TauRx Therapeutics, Bayer Healthcare, Biogen Idec, ExonHit Therapeutics, Servier, Synarc, Pfizer, Janssen, honoraria from NeuroVigil, Insitut Catala de Neurociencies Aplicades, PMDA/Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare, Tohoku University, commercial research support from Merck, Avid; government research support, DOD, VA, outside the submitted work. Other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toledo, J.B., Da, X., Weiner, M.W. et al. CSF Apo-E levels associate with cognitive decline and MRI changes. Acta Neuropathol 127, 621–632 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1236-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1236-0