Abstract
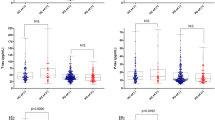
Tau gene has been consistently associated with the risk of Parkinson disease in recent genome wide association studies. In addition, alterations of the levels of total tau, phosphorylated tau [181P], and amyloid beta 1–42 in cerebrospinal fluid have been reported in patients with sporadic Parkinson disease and asymptomatic carriers of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 mutations, in patterns that clearly differ from those typically described for patients with Alzheimer disease. To further determine the potential roles of these molecules in Parkinson disease pathogenesis and/or in tracking the disease progression, especially at early stages, the current study assessed all three proteins in 403 Parkinson disease patients enrolled in the DATATOP (Deprenyl and tocopherol antioxidative therapy of parkinsonism) placebo-controlled clinical trial, the largest cohort to date with cerebrospinal fluid samples collected longitudinally. These initially drug-naive patients at early disease stages were clinically evaluated, and cerebrospinal fluid was collected at baseline and then at endpoint, defined as the time at which symptomatic anti-Parkinson disease medications were determined to be required. General linear models were used to test for associations between baseline cerebrospinal fluid biomarker levels or their rates of change and changes in the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale (total or part III motor score) over time. Robust associations among candidate markers are readily noted. Baseline levels of amyloid beta were weakly but negatively correlated with baseline Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale total scores. Baseline phosphorylated tau/total tau and phosphorylated tau/amyloid beta were significantly and negatively correlated with the rates of the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale change. While medications (deprenyl and/or tocopherol) did not appear to alter biomarkers appreciably, a weak but significant positive correlation between the rate of change in total tau or total tau/amyloid beta levels and the change of the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale was observed. Notably, these correlations did not appear to be influenced by APOE genotype. These results are one of the very first pieces of evidence suggesting that tau and amyloid beta are critically involved in early Parkinson disease progression, potentially by a different mechanism than that in Alzheimer disease, although their applications as Parkinson disease progression markers will likely require the addition of other proteins.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasly JO, Shi M, Sossi V, Stewart T, Johansen KK, Wszolek ZK, Uitti RJ, Hasegawa K, Yokoyama T, Zabetian CP, Kim HM, Leverenz JB, Ginghina C, Armaly J, Edwards KL, Snapinn KW, Stoessl AJ, Zhang J (2012) Cerebrospinal fluid amyloid beta and tau in LRRK2 mutation carriers. Neurology 78:55–61
Alcalay RN, Caccappolo E, Mejia-Santana H, Tang MX, Rosado L, Ross BM, Verbitsky M, Kisselev S, Louis ED, Comella C, Colcher A, Jennings D, Nance MA, Bressman SB, Scott WK, Tanner C, Mickel S, Andrews H, Waters C, Fahn S, Cote L, Frucht S, Ford B, Rezak M, Novak K, Friedman JH, Pfeiffer R, Marsh L, Hiner B, Siderowf A, Ottman R, Marder K, Clark LN (2010) Frequency of known mutations in early-onset Parkinson disease: implication for genetic counseling: the consortium on risk for early onset Parkinson disease study. Arch Neurol 67:1116–1122
Alves G, Bronnick K, Aarsland D, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Ballard C, Kurz MW, Andreasson U, Tysnes OB, Larsen JP, Mulugeta E (2010) CSF amyloid-beta and tau proteins, and cognitive performance, in early and untreated Parkinson’s disease: the Norwegian ParkWest study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:1080–1086
Andreasen N, Minthon L, Davidsson P, Vanmechelen E, Vanderstichele H, Winblad B, Blennow K (2001) Evaluation of CSF-tau and CSF-Abeta42 as diagnostic markers for Alzheimer disease in clinical practice. Arch Neurol 58:373–379
Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:663–672
Clinton LK, Blurton-Jones M, Myczek K, Trojanowski JQ, LaFerla FM (2010) Synergistic Interactions between Abeta, tau, and alpha-synuclein: acceleration of neuropathology and cognitive decline. J Neurosci 30:7281–7289
Compta Y, Marti MJ, Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Junque C, Valldeoriola F, Munoz E, Ezquerra M, Rios J, Tolosa E (2009) Cerebrospinal tau, phospho-tau, and beta-amyloid and neuropsychological functions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 24:2203–2210
Dickson DW, Crystal HA, Mattiace LA, Masur DM, Blau AD, Davies P, Yen SH, Aronson MK (1992) Identification of normal and pathological aging in prospectively studied nondemented elderly humans. Neurobiol Aging 13:179–189
Drechsel DN, Hyman AA, Cobb MH, Kirschner MW (1992) Modulation of the dynamic instability of tubulin assembly by the microtubule-associated protein tau. Mol Biol Cell 3:1141–1154
Edwards TL, Scott WK, Almonte C, Burt A, Powell EH, Beecham GW, Wang L, Zuchner S, Konidari I, Wang G, Singer C, Nahab F, Scott B, Stajich JM, Pericak-Vance M, Haines J, Vance JM, Martin ER (2010) Genome-wide association study confirms SNPs in SNCA and the MAPT region as common risk factors for Parkinson disease. Ann Hum Genet 74:97–109
Esposito A, Dohm CP, Kermer P, Bahr M, Wouters FS (2007) alpha-Synuclein and its disease-related mutants interact differentially with the microtubule protein tau and associate with the actin cytoskeleton. Neurobiol Dis 26:521–531
Fagan AM, Roe CM, Xiong C, Mintun MA, Morris JC, Holtzman DM (2007) Cerebrospinal fluid tau/beta-amyloid(42) ratio as a prediction of cognitive decline in nondemented older adults. Arch Neurol 64:343–349
Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JL, Hyman B, Kukull WA, Mayeux R, Myers RH, Pericak-Vance MA, Risch N, van Duijn CM (1997) Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA 278:1349–1356
Foster ER, Campbell MC, Burack MA, Hartlein J, Flores HP, Cairns NJ, Hershey T, Perlmutter JS (2010) Amyloid imaging of Lewy body-associated disorders. Mov Disord 25:2516–2523
Haass C, Selkoe DJ (2007) Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:101–112
Hansson O, Zetterberg H, Buchhave P, Londos E, Blennow K, Minthon L (2006) Association between CSF biomarkers and incipient Alzheimer’s disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment: a follow-up study. Lancet Neurol 5:228–234
Hong Z, Shi M, Chung KA, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Galasko D, Jankovic J, Zabetian CP, Leverenz JB, Baird G, Montine TJ, Hancock AM, Hwang H, Pan C, Bradner J, Kang UJ, Jensen PH, Zhang J (2010) DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 133:713–726
Hulstaert F, Blennow K, Ivanoiu A, Schoonderwaldt HC, Riemenschneider M, De Deyn PP, Bancher C, Cras P, Wiltfang J, Mehta PD, Iqbal K, Pottel H, Vanmechelen E, Vanderstichele H (1999) Improved discrimination of AD patients using beta-amyloid(1–42) and tau levels in CSF. Neurology 52:1555–1562
Jankovic J (2008) Parkinson’s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:368–376
Jankovic J, McDermott M, Carter J, Gauthier S, Goetz C, Golbe L, Huber S, Koller W, Olanow C, Shoulson I, Stern M, Tanner C, Weiner W, Parkinson Study Group (1990) Variable expression of Parkinson’s disease: a base-line analysis of the DATATOP cohort. Neurology 40:1529–1534
Johansson A, Savitcheva I, Forsberg A, Engler H, Langstrom B, Nordberg A, Askmark H (2008) [(11)C]-PIB imaging in patients with Parkinson’s disease: preliminary results. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14:345–347
Kang JH, Caspell C, Coffey C, Taylor P, Frasier M, Marek K, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM (2012) Association between CSF biomarkers and clinical phenotype of early Parkinson’s disease in the Parkinson’s Progression Marker Initiative (PPMI). Mov Disord 27:S34–S35
Kauwe JS, Cruchaga C, Mayo K, Fenoglio C, Bertelsen S, Nowotny P, Galimberti D, Scarpini E, Morris JC, Fagan AM, Holtzman DM, Goate AM (2008) Variation in MAPT is associated with cerebrospinal fluid tau levels in the presence of amyloid-beta deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:8050–8054
Kieburtz K, McDermott M, Como P, Growdon J, Brady J, Carter J, Huber S, Kanigan B, Landow E, Rudolph A, Saint-Cyr J, Stern Y, Tennis M, Thelen J, Shoulson I, Parkinson Study Group (1994) The effect of deprenyl and tocopherol on cognitive performance in early untreated Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 44:1756–1759
Kim S, Swaminathan S, Shen L, Risacher SL, Nho K, Foroud T, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ, Potkin SG, Huentelman MJ, Craig DW, DeChairo BM, Aisen PS, Petersen RC, Weiner MW, Saykin AJ (2011) Genome-wide association study of CSF biomarkers Abeta1-42, t-tau, and p-tau181p in the ADNI cohort. Neurology 76:69–79
Kronmal RA (1993) Spurious correlation and the fallacy of the ratio standard revisited. J R Stat Soc Ser A (Stat Soc) 156:379–392
Laws SM, Friedrich P, Diehl-Schmid J, Muller J, Eisele T, Bauml J, Forstl H, Kurz A, Riemenschneider M (2007) Fine mapping of the MAPT locus using quantitative trait analysis identifies possible causal variants in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 12:510–517
Lei P, Ayton S, Finkelstein DI, Spoerri L, Ciccotosto GD, Wright DK, Wong BX, Adlard PA, Cherny RA, Lam LQ, Roberts BR, Volitakis I, Egan GF, McLean CA, Cappai R, Duce JA, Bush AI (2012) Tau deficiency induces parkinsonism with dementia by impairing APP-mediated iron export. Nat Med 18:291–295
Li G, Sokal I, Quinn JF, Leverenz JB, Brodey M, Schellenberg GD, Kaye JA, Raskind MA, Zhang J, Peskind ER, Montine TJ (2007) CSF tau/Abeta42 ratio for increased risk of mild cognitive impairment: a follow-up study. Neurology 69:631–639
Marder KS, Clark LN, McDermott M, Uc E, PSG DATATOP Investigators (2010) Genetic risk factors for cognitive impairment in the DATATOP cohort. Neurology 74:A254
Marek K, Jennings D, Lasch S, Siderowf A, Tanner C, Simuni T, Coffey C, Kieburtz K, Flagg E, Chowdhury S, Poewe W, Mollenhauer B, Klinik P-E, Sherer T, Frasier M, Meunier C, Rudolph A, Casaceli C, Seibyl J, Mendick S, Schuff N, Zhang Y, Toga A, Crawford K, Ansbach A, De Blasio P, Piovella M, Trojanowski J, Shaw L, Singleton A, Hawkins K, Eberling J, Brooks D, Russell D, Leary L, Factor S, Sommerfeld B, Hogarth P, Pighetti E, Williams K, Standaert D, Guthrie S, Hauser R, Delgado H, Jankovic J, Hunter C, Stern M, Tran B, Leverenz J, Baca M, Frank S, Thomas C-A, Richard I, Deeley C, Rees L, Sprenger F, Lang E, Shill H, Obradov S, Fernandez H, Winters A, Berg D, Gauss K, Galasko D, Fontaine D, Mari Z, Gerstenhaber M, Brooks D, Malloy S, Barone P, Longo K, Comery T, Ravina B, Grachev I, Gallagher K, Collins M, Widnell KL, Ostrowizki S, Fontoura P, Ho T, Luthman J, Brug Mvd, Reith AD, Taylor P (2011) The Parkinson Progression Marker Initiative (PPMI). Prog Neurobiol 95:629–635
Mattsson N, Zetterberg H, Hansson O, Andreasen N, Parnetti L, Jonsson M, Herukka SK, van der Flier WM, Blankenstein MA, Ewers M, Rich K, Kaiser E, Verbeek M, Tsolaki M, Mulugeta E, Rosen E, Aarsland D, Visser PJ, Schroder J, Marcusson J, de Leon M, Hampel H, Scheltens P, Pirttila T, Wallin A, Jonhagen ME, Minthon L, Winblad B, Blennow K (2009) CSF biomarkers and incipient Alzheimer disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment. JAMA 302:385–393
Mazanetz MP, Fischer PM (2007) Untangling tau hyperphosphorylation in drug design for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:464–479
McDermott MP, Jankovic J, Carter J, Fahn S, Gauthier S, Goetz CG, Golbe LI, Koller W, Lang AE, Olanow CW, Shoulson I, Stern MB, Tanner CM, Weiner WJ, Parkinson Study Group (1995) Factors predictive of the need for levodopa therapy in early, untreated Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 52:565–570
Mollenhauer B, Bibl M, Esselmann H, Steinacker P, Trenkwalder C, Wiltfang J, Otto M (2007) Tauopathies and synucleinopathies: do cerebrospinal fluid beta-amyloid peptides reflect disease-specific pathogenesis? J Neural Transm 114:919–927
Montine TJ, Shi M, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Craft S, Ginghina C, Chung KA, Kim H, Galasko DR, Jankovic J, Zabetian CP, Leverenz JB, Zhang J (2010) CSF Abeta(42) and tau in Parkinson’s disease with cognitive impairment. Mov Disord 25:2682–2685
Murphy MP, LeVine H 3rd (2010) Alzheimer’s disease and the amyloid-beta peptide. J Alzheimers Dis 19:311–323
Olanow CW, Rascol O, Hauser R, Feigin PD, Jankovic J, Lang A, Langston W, Melamed E, Poewe W, Stocchi F, Tolosa E (2009) A double-blind, delayed-start trial of rasagiline in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 361:1268–1278
Olanow CW, Wunderle KB, Kieburtz K (2011) Milestones in movement disorders clinical trials: advances and landmark studies. Mov Disord 26:1003–1014
Parkinson Study Group (1989) DATATOP: a multicenter controlled clinical trial in early Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 46:1052–1060
Parkinson Study Group (1989) Effect of deprenyl on the progression of disability in early Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 321:1364–1371
Parkinson Study Group (1995) Cerebrospinal fluid homovanillic acid in the DATATOP study on Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 52:237–245
Parkinson Study Group (2004) A controlled, randomized, delayed-start study of rasagiline in early Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 61:561–566
Parnetti L, Tiraboschi P, Lanari A, Peducci M, Padiglioni C, D’Amore C, Pierguidi L, Tambasco N, Rossi A, Calabresi P (2008) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease with dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies. Biol Psychiatry 64:850–855
Petrou M, Bohnen NI, Muller ML, Koeppe RA, Albin RL, Frey KA (2012) Abeta-amyloid deposition in patients with Parkinson disease at risk for development of dementia. Neurology 79:1161–1167
Prince JA, Zetterberg H, Andreasen N, Marcusson J, Blennow K (2004) APOE epsilon4 allele is associated with reduced cerebrospinal fluid levels of Abeta42. Neurology 62:2116–2118
Qureshi HY, Paudel HK (2011) Parkinsonian neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and alpha-synuclein mutations promote Tau protein phosphorylation at Ser262 and destabilize microtubule cytoskeleton in vitro. J Biol Chem 286:5055–5068
Rajendran L, Honsho M, Zahn TR, Keller P, Geiger KD, Verkade P, Simons K (2006) Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid peptides are released in association with exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:11172–11177
Rascol O, Fitzer-Attas CJ, Hauser R, Jankovic J, Lang A, Langston JW, Melamed E, Poewe W, Stocchi F, Tolosa E, Eyal E, Weiss YM, Olanow CW (2011) A double-blind, delayed-start trial of rasagiline in Parkinson’s disease (the ADAGIO study): prespecified and post hoc analyses of the need for additional therapies, changes in UPDRS scores, and non-motor outcomes. Lancet Neurol 10:415–423
Saman S, Kim W, Raya M, Visnick Y, Miro S, Saman S, Jackson B, McKee AC, Alvarez VE, Lee NC, Hall GF (2012) Exosome-associated tau is secreted in tauopathy models and is selectively phosphorylated in cerebrospinal fluid in early Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 287:3842–3849
Satake W, Nakabayashi Y, Mizuta I, Hirota Y, Ito C, Kubo M, Kawaguchi T, Tsunoda T, Watanabe M, Takeda A, Tomiyama H, Nakashima K, Hasegawa K, Obata F, Yoshikawa T, Kawakami H, Sakoda S, Yamamoto M, Hattori N, Murata M, Nakamura Y, Toda T (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1303–1307
Schulz KL, Eckert A, Rhein V, Mai S, Haase W, Reichert AS, Jendrach M, Muller WE, Leuner K (2012) A new link to mitochondrial impairment in tauopathies. Mol Neurobiol 46:205–216
Shaw LM, Vanderstichele H, Knapik-Czajka M, Clark CM, Aisen PS, Petersen RC, Blennow K, Soares H, Simon A, Lewczuk P, Dean R, Siemers E, Potter W, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker signature in Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative subjects. Ann Neurol 65:403–413
Shi M, Bradner J, Hancock AM, Chung KA, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Galasko D, Jankovic J, Zabetian CP, Kim HM, Leverenz JB, Montine TJ, Ginghina C, Kang UJ, Cain KC, Wang Y, Aasly J, Goldstein D, Zhang J (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Parkinson disease diagnosis and progression. Ann Neurol 69:570–580
Shi M, Zhang J (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein, tau and amyloid β in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 10:681
Shoulson I, Parkinson Study Group (1992) An interim report of the effect of selegiline (L-deprenyl) on the progression of disability in early Parkinson’s disease. Eur Neurol 32(Suppl 1):46–53
Shoulson I, Oakes D, Fahn S, Lang A, Langston JW, LeWitt P, Olanow CW, Penney JB, Tanner C, Kieburtz K, Rudolph A (2002) Impact of sustained deprenyl (selegiline) in levodopa-treated Parkinson’s disease: a randomized placebo-controlled extension of the deprenyl and tocopherol antioxidative therapy of parkinsonism trial. Ann Neurol 51:604–612
Siderowf A, Xie SX, Hurtig H, Weintraub D, Duda J, Chen-Plotkin A, Shaw LM, Van Deerlin V, Trojanowski JQ, Clark C (2010) CSF amyloid beta 1–42 predicts cognitive decline in Parkinson disease. Neurology 75:1055–1061
Simon-Sanchez J, Schulte C, Bras JM, Sharma M, Gibbs JR, Berg D, Paisan-Ruiz C, Lichtner P, Scholz SW, Hernandez DG, Kruger R, Federoff M, Klein C, Goate A, Perlmutter J, Bonin M, Nalls MA, Illig T, Gieger C, Houlden H, Steffens M, Okun MS, Racette BA, Cookson MR, Foote KD, Fernandez HH, Traynor BJ, Schreiber S, Arepalli S, Zonozi R, Gwinn K, van der Brug M, Lopez G, Chanock SJ, Schatzkin A, Park Y, Hollenbeck A, Gao J, Huang X, Wood NW, Lorenz D, Deuschl G, Chen H, Riess O, Hardy JA, Singleton AB, Gasser T (2009) Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1308–1312
Sjogren M, Davidsson P, Tullberg M, Minthon L, Wallin A, Wikkelso C, Granerus AK, Vanderstichele H, Vanmechelen E, Blennow K (2001) Both total and phosphorylated tau are increased in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70:624–630
Sunderland T, Linker G, Mirza N, Putnam KT, Friedman DL, Kimmel LH, Bergeson J, Manetti GJ, Zimmermann M, Tang B, Bartko JJ, Cohen RM (2003) Decreased beta-amyloid1-42 and increased tau levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer disease. JAMA 289:2094–2103
Takashima A (2006) GSK-3 is essential in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 9:309–317
Wang J, Dickson DW, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (1999) The levels of soluble versus insoluble brain Abeta distinguish Alzheimer’s disease from normal and pathologic aging. Exp Neurol 158:328–337
Wang Y, Shi M, Chung KA, Zabetian CP, Leverenz JB, Berg D, Srulijes K, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Siderowf AD, Hurtig H, Litvan I, Schiess MC, Peskind ER, Masuda M, Hasegawa M, Lin X, Pan C, Galasko D, Goldstein DS, Jensen PH, Yang H, Cain KC, Zhang J (2012) Phosphorylated alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Sci Transl Med 4:121ra120
Wills J, Jones J, Haggerty T, Duka V, Joyce JN, Sidhu A (2010) Elevated tauopathy and alpha-synuclein pathology in postmortem Parkinson’s disease brains with and without dementia. Exp Neurol 225:210–218
Wray S, Noble W (2009) Linking amyloid and tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease: the role of membrane cholesterol in Abeta-mediated tau toxicity. J Neurosci 29:9665–9667
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Michael J. Fox Foundation, the Parkinson Study Group; and the National Institutes of Health [AG033398, ES004696-5897, ES007033-6364, ES016873, ES019277, NS057567, NS060252, NS062684-6221, and NS082137 to J.Z.]. We thank Dr. Hunter R. Underhill for his kind assistance in the initial data analysis, Dr. Karen Marder, Dr. Lorraine N. Clark, and the Parkinson’s Disease Foundation Weill Family Fund for providing the APOE data for this study. We also deeply appreciate the patients for their generous participation and sample donations.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Mattison, H.A., Liu, C. et al. Longitudinal assessment of tau and amyloid beta in cerebrospinal fluid of Parkinson disease. Acta Neuropathol 126, 671–682 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1121-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1121-x