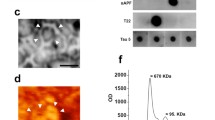
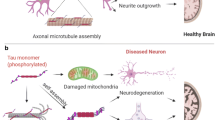
Abstract
Tauopathies like the “frontotemporal dementia with Parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17” (FTDP-17) are characterized by an aberrant accumulation of intracellular neurofibrillary tangles composed of hyperphosphorylated tau. For FTDP-17, a pathogenic tau mutation P301L was identified. Impaired mitochondrial function including disturbed dynamics such as fission and fusion are most likely major pathomechanisms of most neurodegenerative diseases. However, very little is known if tau itself affects mitochondrial function and dynamics. We addressed this question using SY5Y cells stably overexpressing wild-type (wt) and P301L mutant tau. P301L overexpression resulted in a substantial complex I deficit accompanied by decreased ATP levels and increased susceptibility to oxidative stress. This was paralleled by pronounced changes in mitochondrial morphology, decreased fusion and fission rates accompanied by reduced expression of several fission and fusion factors like OPA-1 or DRP-1. In contrast, overexpression of wt tau exhibits protective effects on mitochondrial function and dynamics including enhanced complex I activity. Our findings clearly link tau bidirectional to mitochondrial function and dynamics, identifying a novel aspect of the physiological role of tau and the pathomechanism of tauopathies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spires-Jones TL, Stoothoff WH, de Calignon A, Jones PB, Hyman BT (2009) Tau pathophysiology in neurodegeneration: a tangled issue. Trends Neurosci 3:150–159
Goedert M, Wischik CM, Crowther RA, Walker JE, Klug A (1988) Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: identification as the microtubule-associated protein tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 11:4051–4055
Dixit R, Ross JL, Goldman YE, Holzbaur EL (2008) Differential regulation of dynein and kinesin motor proteins by tau. Science 5866:1086–1089
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, Pickering-Brown S, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A et al (1998) Association of missense and 5′-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 6686:702–705
Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Wijsman E, Nemens E, Garruto RM, Anderson L, Andreadis A, Wiederholt WC, Raskind M, Schellenberg GD (1998) Tau is a candidate gene for chromosome 17 frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 6:815–825
Spillantini MG, Murrell JR, Goedert M, Farlow MR, Klug A, Ghetti B (1998) Mutation in the tau gene in familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 13:7737–7741
von Bergen M, Barghorn S, Li L, Marx A, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (2001) Mutations of tau protein in frontotemporal dementia promote aggregation of paired helical filaments by enhancing local beta-structure. J Biol Chem 51:48165–48174
David DC, Hauptmann S, Scherping I, Schuessel K, Keil U, Rizzu P, Ravid R, Drose S, Brandt U, Muller WE et al (2005) Proteomic and functional analyses reveal a mitochondrial dysfunction in P301L Tau transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 25:23802–23814
Kuhla B, Loske C, Garcia DA, Schinzel R, Huber J, Munch G (2004) Differential effects of ”Advanced glycation endproducts” and beta-amyloid peptide on glucose utilization and ATP levels in the neuronal cell line SH-SY5Y. J Neural Transm 3:427–439
Srikanth V, Maczurek A, Phan T, Steele M, Westcott B, Juskiw D, Munch G (2011) Advanced glycation endproducts and their receptor RAGE in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 5:763–777
Busch KB, Bereiter-Hahn J, Wittig I, Schagger H, Jendrach M (2006) Mitochondrial dynamics generate equal distribution but patchwork localization of respiratory complex I. Mol Membr Biol 6:509–520
Ishihara N, Jofuku A, Eura Y, Mihara K (2003) Regulation of mitochondrial morphology by membrane potential, and DRP1-dependent division and FZO1-dependent fusion reaction in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 4:891–898
Ono T, Isobe K, Nakada K, Hayashi JI (2001) Human cells are protected from mitochondrial dysfunction by complementation of DNA products in fused mitochondria. Nat Genet 3:272–275
Suen DF, Norris KL, Youle RJ (2008) Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev 12:1577–1590
Detmer SA, Chan DC (2007) Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:870–879
Westermann B (2008) Molecular machinery of mitochondrial fusion and fission. J Biol Chem 20:13501–13505
Knott AB, Perkins G, Schwarzenbacher R, Bossy-Wetzel E (2008) Mitochondrial fragmentation in neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:505–518
Wang X, Su B, Fujioka H, Zhu X (2008) Dynamin-like protein 1 reduction underlies mitochondrial morphology and distribution abnormalities in fibroblasts from sporadic Alzheimer’s disease patients. Am J Pathol 2:470–482
Wang X, Su B, Siedlak SL, Moreira PI, Fujioka H, Wang Y, Casadesus G, Zhu X (2008) Amyloid-beta overproduction causes abnormal mitochondrial dynamics via differential modulation of mitochondrial fission/fusion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 49:19318–19323
Ferrari A, Hoerndli F, Baechi T, Nitsch RM, Gotz J (2003) beta-Amyloid induces paired helical filament-like tau filaments in tissue culture. J Biol Chem 41:40162–40168
Schaeffer V, Patte-Mensah C, Eckert A, Mensah-Nyagan AG (2006) Modulation of neurosteroid production in human neuroblastoma cells by Alzheimer’s disease key proteins. J Neurobiol 8:868–881
Letellier T, Durrieu G, Malgat M, Rossignol R, Antoch J, Deshouillers JM, Coquet M, Lacombe D, Netter JC, Pedespan JM et al (2000) Statistical analysis of mitochondrial pathologies in childhood: identification of deficiencies using principal component analysis. Lab Invest 7:1019–1030
Leuner K, Hauptmann S, Abdel-Kader R, Scherping I, Keil U, Strosznajder JB, Eckert A, Muller WE (2007) Mitochondrial dysfunction: the first domino in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease? Antioxid Redox Signal 10:1659–1675
Bai RK, Perng CL, Hsu CH, Wong LJ (2004) Quantitative PCR analysis of mitochondrial DNA content in patients with mitochondrial disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 304–309
Schneider WC, Hogeboom GH (1951) Cytochemical studies of mammalian tissues; the isolation of cell components by differential centrifugation: a review. Cancer Res 1:1–22
Baloyannis SJ (2006) Mitochondrial alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2:119–126
Bunker JM, Kamath K, Wilson L, Jordan MA, Feinstein SC (2006) FTDP-17 mutations compromise the ability of tau to regulate microtubule dynamics in cells. J Biol Chem 17:11856–11863
Ebneth A, Godemann R, Stamer K, Illenberger S, Trinczek B, Mandelkow E (1998) Overexpression of tau protein inhibits kinesin-dependent trafficking of vesicles, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Biol 3:777–794
Roy S, Zhang B, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2005) Axonal transport defects: a common theme in neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Neuropathol 1:5–13
Karbowski M, Arnoult D, Chen H, Chan DC, Smith CL, Youle RJ (2004) Quantitation of mitochondrial dynamics by photolabeling of individual organelles shows that mitochondrial fusion is blocked during the Bax activation phase of apoptosis. J Cell Biol 4:493–499
Honda S, Hirose S (2003) Stage-specific enhanced expression of mitochondrial fusion and fission factors during spermatogenesis in rat testis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2:424–432
Jendrach M, Mai S, Pohl S, Voth M, Bereiter-Hahn J (2008) Short- and long-term alterations of mitochondrial morphology, dynamics and mtDNA after transient oxidative stress. Mitochondrion 4:293–304
Alonso AC, Mederlyova A, Novak M, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2004) Promotion of hyperphosphorylation by frontotemporal dementia tau mutations. J Biol Chem 279:34873–34881
Hasegawa M, Smith MJ, Goedert M (1998) Tau proteins with FTDP-17 mutations have a reduced ability to promote microtubule assembly. FEBS Lett 3:207–210
Hong M, Zhukareva V, Vogelsberg-Ragaglia V, Wszolek Z, Reed L, Miller BI, Geschwind DH, Bird TD, McKeel D, Goate A et al (1998) Mutation-specific functional impairments in distinct tau isoforms of hereditary FTDP-17. Science 5395:1914–1917
Sumpter PQ, Mann DM, Davies CA, Yates PO, Snowden JS, Neary D (1986) An ultrastructural analysis of the effects of accumulation of neurofibrillary tangle in pyramidal neurons of the cerebral cortex in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 3:305–319
Bonda DJ, Castellani RJ, Zhu X, Nunomura A, Lee HG, Perry G, Smith MA (2011) A novel perspective on tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 6:639–642
Su B, Wang X, Lee HG, Tabaton M, Perry G, Smith MA, Zhu X (2010) Chronic oxidative stress causes increased tau phosphorylation in M17 neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci Lett 3:267–271
Palade GE (1953) An electron microscope study of the mitochondrial structure. J Histochem Cytochem 4:188–211
Demongeot J, Glade N, Hansen O, Moreira A (2007) An open issue: the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) as a free boundary problem. Biochimie 9:1049–1057
Hackenbrock CR (1968) Chemical and physical fixation of isolated mitochondria in low-energy and high-energy states. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2:598–605
Bereiter-Hahn J, Voeth M. (1983) Metabolic control of shape and structure of mitochondria in situ. Biol Cell 1042:304–309
Knott AB, Bossy-Wetzel E (2008) Impairing the mitochondrial fission and fusion balance: a new mechanism of neurodegeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1147:283–292
Lee YJ, Jeong SY, Karbowski M, Smith CL, Youle RJ (2004) Roles of the mammalian mitochondrial fission and fusion mediators Fis1, Drp1, and Opa1 in apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 11:5001–5011
Sugioka R, Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y (2004) Fzo1, a protein involved in mitochondrial fusion, inhibits apoptosis. J Biol Chem 50:52726–52734
Moreira PI, Siedlak SL, Wang X, Santos MS, Oliveira CR, Tabaton M, Nunomura A, Szweda LI, Aliev G, Smith MA et al (2007) Increased autophagic degradation of mitochondria in Alzheimer disease. Autophagy 6:614–615
Moreira PI, Siedlak SL, Wang X, Santos MS, Oliveira CR, Tabaton M, Nunomura A, Szweda LI, Aliev G, Smith MA et al (2007) Autophagocytosis of mitochondria is prominent in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 6:525–532
Schaeffer V, Lavenir I, Ozcelik S, Tolnay M, Winkler DT, Goedert M (2012) Stimulation of autophagy reduces neurodegeneration in a mouse model of human tauopathy. Brain Pt 7:2169–2177
Brandt R, Leger J, Lee G (1995) Interaction of tau with the neural plasma membrane mediated by tau’s amino-terminal projection domain. J Cell Biol 5:1327–1340
Magnani E, Fan J, Gasparini L, Golding M, Williams M, Schiavo G, Goedert M, Amos LA, Spillantini MG (2007) Interaction of tau protein with the dynactin complex. EMBO J 21:4546–4554
Liot G, Bossy B, Lubitz S, Kushnareva Y, Sejbuk N, Bossy-Wetzel E (2009) Complex II inhibition by 3-NP causes mitochondrial fragmentation and neuronal cell death via an. Cell Death Differ 16:899–909
Chen H, McCaffery JM, Chan DC (2007) Mitochondrial fusion protects against neurodegeneration in the cerebellum. Cell 3:548–562
Hansen MB, Nielsen SE, Berg K (1989) Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods 2:203–210
Crouch SP, Kozlowski R, Slater KJ, Fletcher J (1993) The use of ATP bioluminescence as a measure of cell proliferation and cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods 1:81–88
Baracca A, Sgarbi G, Solaini G, Lenaz G (2003) Rhodamine 123 as a probe of mitochondrial membrane potential: evaluation of proton flux through F(0) during ATP synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1–3:137–146
Djafarzadeh R, Kerscher S, Zwicker K, Radermacher M, Lindahl M, Schagger H, Brandt U (2000) Biophysical and structural characterization of proton-translocating NADH–dehydrogenase (complex I) from the strictly aerobic yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Biochim Biophys Acta 1:230–238
Aleardi AM, Benard G, Augereau O, Malgat M, Talbot JC, Mazat JP, Letellier T, Dachary-Prigent J, Solaini GC, Rossignol R (2005) Gradual alteration of mitochondrial structure and function by beta-amyloids: importance of membrane viscosity changes, energy deprivation, reactive oxygen species production, and cytochrome c release. J Bioenerg Biomembr 4:207–225
Krahenbuhl S, Chang M, Brass EP, Hoppel CL (1991) Decreased activities of ubiquinol:ferricytochrome c oxidoreductase (complex III) and ferrocytochrome c:oxygen oxidoreductase (complex IV) in liver mitochondria from rats with hydroxycobalamin[c-lactam]-induced methylmalonic aciduria. J Biol Chem 31:20998–21003
Rasmussen UF, Rasmussen HN (2000) Human quadriceps muscle mitochondria: a functional characterization. Mol Cell Biochem 1–2:37–44
Patterson GH, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2002) A photoactivatable GFP for selective photolabeling of proteins and cells. Science 5588:1873–1877
Bai RK, Perng CL, Hsu CH, Wong LJ (2004) Quantitative PCR analysis of mitochondrial DNA content in patients with mitochondrial disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci
Cote HC, Brumme ZL, Craib KJ, Alexander CS, Wynhoven B, Ting L, Wong H, Harris M, Harrigan PR, O’Shaughnessy MV et al (2002) Changes in mitochondrial DNA as a marker of nucleoside toxicity in HIV-infected patients. N Engl J Med 11:811–820
Acknowledgements
The authors thank M. Vöth for support with the mitochondrial movement data analysis, F. Haas for experimental support with the real-time PCR and F. Meier with regard to Western blotting. This work was supported in part by grants from the Swiss National Research Foundation (SNF # 31000_122572) and Synapsis Foundation to AE, by the DFG grant REI1575-1/1 (AR), he Cluster of Excellence Frankfurt Macromolecular Complexes at the University of Frankfurt DFG project EXC 115 (AR), and the BMBF, Germany, GerontoMitoSys project (AR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulz, K.L., Eckert, A., Rhein, V. et al. A New Link to Mitochondrial Impairment in Tauopathies. Mol Neurobiol 46, 205–216 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8308-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8308-3