Abstract
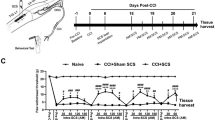
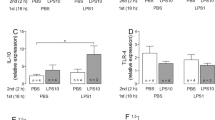
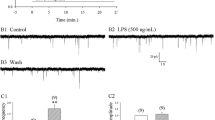
We have analyzed development of mechanical hyperalgesia after repeated systemic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injections and correlated these findings with stimulation of astrocytes and microglia in spinal cord. Male Lewis rats received a single or seven intraperitoneal injections of LPS. Mechanical hyperalgesia was measured as rat hindpaw withdrawal thresholds (PWTs). We observed that a single LPS injection elicited a specific change of PWTs while stimulated spinal glial activation was identified by immunoreactivities of specific markers, ED1, P2X4 receptor, endothelial monocyte activating polypeptide II (EMAP II) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), respectively; multiple LPS treatments induced tolerance to mechanical hyperalgesia, whereas expression of ED1 and GFAP were further increased. In conclusion, we have demonstrated that the number of activated spinal glial cells was increased as an acute effect of LPS correlating with increased sensitivity to mechanical stimulation. However chronic exposure to LPS can develop a tolerance to mechanical hyperalgesia despite ongoing signs of CNS glial activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmone-Cat MA, Nicolini A, Minghetti L (2003) Prolonged exposure of microglia to lipopolysaccharide modifies the intracellular signaling pathways and selectively promotes prostaglandin E2 synthesis. J Neurochem 87:1193–1203
Aschner M (1998) Immune and inflammatory responses in the CNS: modulation by astrocytes. Toxicol Lett 102–103:283–287
Cavaillon JM (1995) The nonspecific nature of endotoxin tolerance. Trends Microbiol 3:320–324
Cavaillon JM, Adrie C, Fitting C, Adib-Conquy M (2003) Endotoxin tolerance: is there a clinical relevance? J Endotoxin Res 9:101–107
Chu SJ, Perng WC, Hung CM, Chang DM, Lin SH, Huang KL (2005) Effects of various body temperatures after lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in rats. Chest 128:327–336
Coull JA, Beggs S, Boudreau D, Boivin D, Tsuda M, Inoue K, Gravel C, Salter MW, De Koninck Y (2005) BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 438:1017–1021
Damoiseaux JG, Dopp EA, Calame W, Chao D, MacPherson GG, Dijkstra CD (1994) Rat macrophage lysosomal membrane antigen recognized by monoclonal antibody ED1. Immunology 83:140–147
DeLeo JA, Tanga FY, Tawfik V (2004) Neuroimmune activation and neuroinflammation in chronic pain and opioid tolerance/hyperalgesia. The Neuroscientist 10:40–52
DeLeo JA, Yezierski RPB (2001) The role of neuroinflammation and neuroimmune activation in persistent pain. Pain 90:1–6
Devor M, Gilad A, Arbilly M, Yakir B, Raber P, Pisante A, Darvasi A (2005) pain1: a neuropathic pain QTL on mouse chromosome 15 in a C3HxC58 backcross. Pain 116:289–293
Fan H, Cook JA (2004) Molecular mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance. J Endotoxin Res 10:71–84
Ferreira SH, Lorenzetti BB, Bristow AF, Pooles S (1988) Interleukin-1 beta as a potent hyperalgesic agent antagonized by a tripeptide analogue. Nature 334:698–700
Fu KY, Light AR, Maixner W (2000) Relationship between nociceptor activity, peripheral edema, spinal microglial activation and long-term hyperalgesia induced by formalin. Neuroscience 101:1127–1135
Furuse T, Miura Y, Yagasaki K, Shiroishi T, Koide T (2003) Identification of QTLs for differential capsaicin sensitivity between mouse strains KJR and C57BL/6. Pain 105:169–175
Gong JP, Dai LL, Liu CA, Wu CX, Shi YJ, Li SW, Li XH (2002) Expression of CD14 protein and its gene in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells during endotoxemia. World J Gastroenterol 8:551–554
Guo LH, Trautmann K, Schluesener HJ (2004) Expression of P2X4 receptor in rat C6 glioma by tumor-associated macrophages and activated microglia. J Neuroimmunol 152(1–2):67–72
Guo LH, Trautmann K, Schluesener HJ (2005) Expression of P2X4 receptor by lesional activated microglia during formalin-induced inflammatory pain. J Neuroimmunol 163:120–127
Hanisch UK (2002) Microglia as a source and target of cytokines. Glia 40:140–55
Ignatowski TA, Covey WC, Knight PR, Severin CM, Nickola TJ, Spengler RN (1999) Brain-derived TNFalpha mediates neuropathic pain. Brain Res 841:70–77
Jiang-Shieh YF, Wu CH, Chien HF, Wei IH, Chang ML, Shieh JY, Wen CY (2005) Reactive changes of interstitial glia and pinealocytes in the rat pineal gland challenged with cell wall components from gram-positive and -negative bacteria. J Pineal Res 38:17–26
Kao J, Houck K, Fan Y, Haehnel I, Libutti SK, Kayton ML, Grikscheit T, Chabot J, Nowygrod R, Greenberg S, Kuang WJ, Leung DW, Hayward JR, Kisielll W, Heath M, Brett J, Stern DM (1994) Characterization of a novel tumor-derived cytokine. Endothelial-monocyte activating polypeptide II. J Biol Chem 269:25106–25119
Kehl LJ, Kovacs KJ, Larson AA (2004) Tolerance develops to the effect of lipopolysaccharides on movement-evoked hyperalgesia when administered chronically by a systemic but not an intrathecal route. Pain 111:104–115
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19:312–318
Lariviere WR, Sattar MA, Melzack R (2006) Inflammation-susceptible Lewis rats show less sensitivity than resistant Fischer rats in the formalin inflammatory pain test and with repeated thermal testing. J Neurophysiol 95:2889–2897
Liebert UG, Linington C, ter Meulen V (1988) Induction of autoimmune reactions to myelin basic protein in measles virus encephalitis in Lewis rats. J Neuroimmunol 17:103–118
Maier SF, Wiertelak EP, Martin D, Watkins LR (1993) Interleukin-1 mediates the behavioral hyperalgesia produced by lithium chloride and endotoxin. Brain Res 623:321–324
Mathison JC, Virca GD, Wolfson E, Tobias PS, Glaser K, Ulevitch RJ (1990) Adaptation to bacterial lipopolysaccharide controls lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor production in rabbit macrophages. J Clin Invest 85:1108–1118
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Kopp E, Stadlen A, Chen C, Ghosh S, Janeway CA Jr (1998) MyD88 is an adaptor protein in the hToll/IL-1 receptor family signaling pathways. Mol Cell 2:253–258
Miller G (2005) Neuroscience. The dark side of glia. Science 308:778–781
Milligan ED, O’Connor KA, Nguyen KT, Armstrong CB, Twining C, Gaykema RP, Holguin A, Martin D, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2001) Intrathecal HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 induces enhanced pain states mediated by spinal cord proinflammatory cytokines. J Neurosci 21:2808–2819
Morrison DC (1987) Endotoxin and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med 38:417–432
Mueller CA, Schluesener HJ, Conrad S, Meyermann R, Schwab JM (2003) Spinal cord injury induces lesional expression of the proinflammatory and antiangiogenic cytokine EMAP II. J Neurotrauma 20:1007–1015
Nakajima K, Kohsaka S (2004) Microglia: neuroprotective and neurotrophic cells in the central nervous system. Curr. Drug Targets Cardiovasc. Haematol. Disord. 4:65–84
Nava F, Calapai G, Facciola G, Cuzzocrea S, Giuliani G, DeSarro A, Caputi AP (1997) Melatonin effects on inhibition of thirst and fever induced by lipopolysaccharide in rat. Eur J Pharmacol 331:267–274
Nava F, Calapai G, Facciola G, Cuzzocrea S, Marciano MC, DeSarro A, Caputi AP (1997) Effects of interleukin-10 on water intake, locomotory activity, and rectal temperature in rat treated with endotoxin. Int J Immunopharmacol 19:31–38
Nava F, Carta G (2000) Repeated lipopolysaccharide administration produces tolerance to anorexia and fever but not to inhibition of thirst in rat. Int J Immunopharmacol 22:943–953
Nguyen MD, D’Aigle T, Gowing G, Julien JP, Rivest S (2004) Exacerbation of motor neuron disease by chronic stimulation of innate immunity in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci 24:1340–1349
North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82:1013–1067
Prat A, Biernacki K, Wosik K, Antel JP (2001) Glial cell influence on the human blood-brain barrier. Glia 36:145–55
Reddy MM, Mahipal SV, Subhashini J, Reddy MC, Roy KR, Reddy GV, Reddy PR, Reddanna P (2006) Bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in the impairment of steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis in rats. Reprod Toxicol (in press)
Ribeiro ML, Cella M, Farina M, Franchi A (2003) Crosstalk between nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase metabolites in the estrogenized rat uterus. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 68:285–290
Schluesener HJ, Seid K, Zhao Y, Meyermann R (1997) Localization of endothelial-monocyte-activating polypeptide II (EMAP II), a novel proinflammatory cytokine, to lesions of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, neuritis and uveitis: expression by monocytes and activated microglial cells. Glia 20:365–372
Schwab JM, Guo L, Schluesener HJ (2005) Spinal cord injury induces early and persistent lesional P2X(4) receptor expression. J Neuroimmunol 163:185–189
Shi SR, Chaiwun B, Young L, Cote RJ, Taylor CR (1993) Antigen retrieval technique utilizing citrate buffer or urea solution for immunohistochemical demonstration of androgen receptor in formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Histochem Cytochem 41:1599–1604
Streit WJ, Walter SA, Pennell NA (1999) Reactive microgliosis. Prog Neurobiol 57:563–581
Sweitzer SM, Colburn RW, Rutkowski M, DeLeo JA (1999) Acute peripheral inflammation induces moderate glial activation and spinal IL-1beta expression that correlates with pain behavior in the rat. Brain Res 829:209–221
Tsuda M, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Koizumi S, Mizokoshi A, Kohsaka S, Salter MW, Inoue K (2003) P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 424:778–783
Vincent D, Lefort J, Bureau M, Dry J, Vazgaftig BB (1991) Dissociation between LPS-induced bronchial hyperreactivity and airway edema in the guinea-pig. Agents Actions 34:203–204
Watkins LR, Maier SF (2003) Glia: a novel drug discovery target for clinical pain. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2:973–985
Watkins LR, Maier SF (2004) Targeting glia to control clinical pain: an idea whose time has come. Drug discovery today Therapeutic Strategies 1:83–88
Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF (2001) Glial activation: a driving force for pathological pain. Trends Neurosci 24:450–455
Watkins LR, Wiertelak EP, Goehler LE, Smith KP, Martin D, Maier SF (1994) Characterization of cytokine-induced hyperalgesia. Brain Res 654:15–26
Wekerle H, Bradl M, Linington C, Kaab G, Kojima K (1996) The shaping of the brain-specific T lymphocyte repertoire in the thymus. Immunol Rev 149:231–243
West MA, Heagy W (2002) Endotoxin tolerance: a review. Crit Care Med 30:S64–73
Wieseler-Frank J, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2004) Glial activation and pathological pain. Neurochem Int 45:389–395
Wilson SG, Chesler EJ, Hain H, Rankin AJ, Schwarz JZ, Call SB, Murray MR, West EE, Teuscher C, Rodriguez-Zas S, Belknap JK, Mogil JS (2002) Identification of quantitative trait loci for chemical/inflammatory nociception in mice. Pain 96:385–391
Wright SD (1999) Toll, a new piece in the puzzle of innate immunity. J Exp Med 189:605–609
Yirmiya R, Rosen H, Donchin O, Ovadia H (1994) Behavioral effects of lipopolysaccharide in rats: involvement of endogenous opioids. Brain Res 648:80–86
Ziegler-Heitbrock HW (1994) Molecular mechanism in tolerance to lipopolysaccharide. J Inflamm 45:13–26
Zimmermann M (2001) Pathobiology of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 429:23–37
Zweigner J, Gramm HJ, Singer OC, Wegscheider K, Schumann RR (2001) High concentrations of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in serum of patients with severe sepsis or septic shock inhibit the lipopolysaccharide response in human monocytes. Blood 98:3800–3808
Acknowledgment
We wish to thank Mrs. Trautmann for expert technical support. Mrs. Guo is a member of the Graduate College “Cellular mechanisms of immune-associated process” (DFG: GK 794).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, LH., Schluesener, H.J. Acute but not chronic stimulation of glial cells in rat spinal cord by systemic injection of lipopolysaccharide is associated with hyperalgesia. Acta Neuropathol 112, 703–713 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0135-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0135-z