Abstract
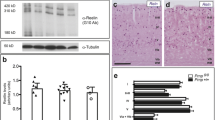
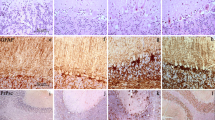
Spongiform change is a cardinal feature in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, including Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE). It is characterized by swelling of the neuronal processes and vacuolization of the neuropil, leading to increased intraneuronal water content. The present study examines, by gel electrophoresis and Western blotting, the expression levels of the water channels aquaporin 1 (AQP1) and aquaporin 4 (AQP4) in the frontal cortex (area 8) homogenates of sporadic CJD cases (six men, four women; seven cases with methionine/methionine at codon 129 and PrP type 1; two cases with valine/valine at codon 129 and PrP type 2, and one case methionine/valine at codon 129 and PrP type 1) compared with age-matched controls, and cases with Alzheimer’s disease (AD, stage VI of Braak and Braak) and diffuse Lewy body disease (DLB). AQP1 and AQP4 protein levels were also studied in the cerebral cortex of BSE-infected bovine-PrP transgenic mice (BoPrP-Tg110 mice) examined at 60, 150, 210 and 270 days post-inoculation (dpi) compared with healthy brain-inoculated control mice. Quantitative densitometry of AQP bands normalized for β-actin was analyzed using Statgraphics plus 5.0 software from ANOVA and LSD statistical tests. Significant increased expression levels of AQP1 (as revealed with two different antibodies) and AQP4 were seen in CJD, but not in advanced AD and DLB cases when compared with controls. Immunohistochemistry revealed that AQP1 and AQP4 were expressed in astrocytes in diseased cases. No modifications in the expression levels of AQP1 and AQP4 were observed in BSE-infected bovine-PrP transgenic mice at 60, 150 and 210 dpi. However, a significant increase in the expression levels of AQP1 and AQP4 was found in mice at 270 dpi, the time corresponding with the appearance of PrPres immunoreactivity in Western blots and typical spongiform lesions in the brain. Together, these findings show increased expression of water channels in the brain in human and animal prion diseases. These modifications may have implications in the regulation of water transport in astrocytes and may account for an imbalance in water and ion homeostasis in prion diseases.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agre P, Kozono D (2003) Aquaporin water channels: molecular mechanisms for human diseases. FEBS Lett 555:72–78
Aguzzi A (2003) Introduction to prion diseases. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 282–286
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP (2003) The molecular basis of water transport in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:991–1001
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Williamson A, Palomba M, Eid T, de Lanerolle NC, Naglehus EA, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Agre P, Ottersen OP (2003) Delayed K+ clearance associated with aquaporin-4 mislocalization: phenotypic defects in brains of alpha-syntrophin-null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13615–13620
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Xue R, Haug FM, Neely JD, Bhardwaj A, Agre P, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Mori S, Ottersen OP (2004) Alpha-syntrophin deletion removes the perivascular but endothelial pool of aquaporin-4 at the blood-brain barrier and delays the development of brain edema in an experimental model of acute hyponatremia. FASEB J 18:542–544
Aoki-Yoshimo K, Uchihara T, Duyckaerts C, Nakamura A, Haw JJ, Wakayama Y (2005) Enhanced expression of aquaporin 4 in human brain with inflammatory diseases. Acta Neuropathol 110:281–288
Aoki K, Uchihara T, Tsuchiya K, Nakamura A, Ikeda K, Wakayama Y (2003) Enhanced expression of aquaporin 4 in human brain with infarction. Acta Neuropathol 106:121–124
Badaut J, Lasbennes F, Magistretti PJ, Regli L (2002) Aquaporins in brain: distribution, physiology, and pathophysiology. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:367–378
Braak H, Braak E (1999) Temporal sequence of Alzheimer’s disease related pathology. In: Peters A, Morrison JH (eds) Cerebral cortex. Neurodegenerative and age-related changes in structure and function of cerebral cortex, vol 14. Kluwer/Plenum, New York, Dordrecht, pp 475–512
Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rub U, Bratzke H, del Tredici K (2004) Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tiss Res 318:121–34
Bratosiewicz-Wasik J, Wasik TJ, Liberski PP (2004) Molecular approaches to mechanisms of prion diseases. Folia Neuropathol 42:S33–S46
Brun A, Castilla J, Ramirez MA, Prager K, Parra B, Salguero FJ, Shiveral D, Sanchez C, Sanchez-Vizcaino JM, Douglas A, Torres JM (2004) Proteinase K enhanced immunoreactivity of the prion protein-specific monoclonal antibody 2A11. Neurosci Res 48:75–83
Budka H, Head MW, Ironside JW, Gambetti P, Parchi P, Zeidler M, Tagliavini F (2003) Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 287–297
Castilla J, Gutierrez-Adan A, Brun A, Pintado B, Ramirez MA, Parra B, Doyle D, Rogers M, Salguero FJ, Sanchez C, Sanchez-Vizcaino JM, Torres JM (2003) Early detection of PrP(res) in BSE-infected bovine PrP transgenic mice. Arch Virol 148:677–691
Collie DA, Summers DM, Sellar RJ, Ironside JW, Cooper S, Zeidler M, Knight R, Will RG (2003) Diagnosing variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with the pulvinar sign: MR imaging findings in 86 neuropathologically-verified cases. Am J Neuroradiol 24:1560–1569
Collinge J (2001) Prion diseases of human and animals: their causes and molecular basis. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:519–550
DeArmond SJ, Kretzschmar HA, Prusiner SB (2003) Prion diseases. In: Graham DI, Lantos PL (eds) Greenfield’s neuropathology, vol II. Arnold, London, pp 273–323
Duyckaerts C, Dickson DW (2003) Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 47–65
Ferrer I (2005) Pathology of brain edema and brain swelling. In: Kalimo H (ed) Pathology and genetics of cerebrovascular diseases. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 32–38
Freixes M, Rodríguez A, Dalfó E, Ferrer I (2006) Oxidation, glycoxidation, lipoxidation, nitration, and responses to oxidative stress in the cerebral cortex in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurobiol Aging (in press)
Frigeri A, Gropper MA, Turck CW, Verkman AS (1995) Immunolocalization of the mercurial-insensitive water channel and glycerol intrinsic protein in epithelial cell plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4328–4331
Gambetti P, Parchi P, Chen SG, Cortelli P, Lugaresi E, Montagna P (2003) Fatal insomnia: familial and sporadic. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 326–332
Ghetti B, Bugiani O, Tagliavini F, Piccardo P (2003) Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 318–325
Giese A, Kretzschmar HA (2001) Prion-induced neuronal damage: the mechanisms of neuronal destruction in the subacute spongiform encephalopathies. Curr Topics Microbiol Immunol 253:203–217
Gunnarson E, Zelenina M, Aperia A (2004) Regulation of brain aquaporins. Neuroscience 129:947–955
Ince PG, McKeith IG (2003) Dementia with Lewy bodies. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 188–197
Ironside JW (1998) Prion diseases in man. J Pathol 86:27–34
Kiening KL, van Landeghem FK, Schreiber S, Thomale UW, von Deimling A, Unterberg AW, Stover JF (2002) Decreased hemispheric aquaporin-4 is linked to evolving brain edema following controlled cortical impact injury in rats. Neurosci Lett 324:105–108
Kim JH, Manuelidis EE (1986) Serial ultrastructural study of experimental Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in guinea pigs. Acta Neuropathol 69:81–90
Kimelberg HK (2004) Water homeostasis in the brain: basic concepts. Neuroscience 129:851–860
Knight RSG, Will RG (2004) Prion diseases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 75:S136–S42
Landis DMD, Williams RS, Masters CL (1981) Golgi and electron microscopic studies of spongiform encephalopathies. Neurology 31:538–549
Lee TS, Eid T, Mane S, Kim JH, Spencer DD, Ottersen OP, de Lanerolle NC (2004) Aquaporin-4 is increased in the sclerotic hippocampus in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol 108:493–502
Liberski PP, Streichenberger N, Giraud P, Sotrenon M, Meyronnet D, Sikorska B, Kopp N (2005) Ultrastructural pathology of prion diseases revisited: brain biopsy studies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 31:88–96
Manley GT, Binder DK, Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS (2004) New insights into water transport and edema in the central nervous system from phenotype analysis of aquaporin-4 null mice. Neuroscience 129:983–991
Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS (2000) Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med 6:159–163
Miyakawa T, Katsuragi S, Koga Y, Moriyama S (1986) Status spongiosus in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Clin Neuropathol 5:146–152
Murata T, Shiga Y, Higano S, Takahashi S, Mugikura S (2002) Conspicuity and evolution of lesions in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease at diffusion-weighted imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 23:1164–1172
Neely JD, Christensen BM, Nilesen S, Agre P (1999) Heterotetrameric composition of aquaporin-4 water channels. Biochemistry 38:11156–11163
Nielsen S, Nagelhus EA, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Bourque C, Agre P, Ottersen OP (1997) Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells: high-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J Neurosci 17:171–180
Nielsen S, Smith BL, Christensen EI, Agre P (1993) Distribution of the aquaporin CHIP in secretory and resorptive epithelia and capillary endothelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7275–7279
Oshio K, Binder DK, Liang Y, Bollen A, Feuerstein B, Berger MS, Manley GT (2005) Expression of the aquaporin-1 water channel in human glial tumors. Neurosurgery 56:375–381
Parchi P, Giese A, Capellari S, Brown P, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Windl O, Zerr I, Budka H, Kopp N, Piccardo P, Poser S, Rojiani A, Streichemberger N, Julien J, Vital C, Ghetti B, Gambetti P, Kretzschmar H (1999) Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann Neurol 46:224–233
Prusiner SB (1997) The prion diseases of humans and animals. In: Rosenber RN, Prusiner SB, DiMauro S, Barchi RL (eds) The molecular and genetic basis of neurological diseases. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, pp 165–186
Riemer C, Neidhold S, Burwinkel M, Schwartz A, Schultz J, Krätzschmar J, Mönning U, Baier M (2004) Gene expression profiling of scrapie-infected brain tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323:556–564
Riemer C, Queck I, Simon D, Kurth R, Baier M (2000) Identification of upregulated genes in scrapie-infected brain tissue. J Virol 74:10245–10248
Saadoun S, Papadopuolos MC, Davies DC, Bell BA, Krishna S (2002) Increased aquaporin 1 water channel expression in human brain tumours. Br J Cancer 87:621–623
Saadoun S, Papadopuolos MC, Davies DC, Krishna S, Bell BA (2002) Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in oedematous human brain tumours. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 72:262–265
Sato S, Umenishi F, Inamasu G, Sato M, Ishikawa M, Nishizawa M, Oizumi T (2000) Expression of water channel mRNA following cerebral ischemia. Acta Neurochir Suppl 76:239–241
Scott M, Foster D, Mirenda C, Serban D, Coufal F, Walchli M, Torchia M, Groth D, Carlson G, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB (1989) Transgenic mice expressing hamster prion protein produce species-specific scrapie infectivity and amyloid plaques. Cell 59:847–857
Scott MD. Groth D, Foster D, Torchia M, Yang SL, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB (1993) Propagation of prions with artificial properties in transgenic mice expressing chimeric PrP genes. Cell 73:979–988
Solenov EI, Vetrivel L, Oshio K, Manley GT, Verkman AS (2002) Optical measurement of swelling and water transport in spinal cord slices from aquaporin null mice. J Neurosci Meth 113:85–90
Sun MC, Honey CR, Berk C, Wong NL, Tsui JK (2003) Regulation of aquaporin-4 in a traumatic brain injury model in rats. J Neurosurg 98:565–569
Taniguchi M, Yamashita T, Kumura E, Tamatani M, Kobayashi A, Yokawa T, Maruno M, Kato A, Ohnishi T, Kohmura E, Tohyama M, Yoshimine T (2000) Induction of aquaporin-4 water channel mRNA after focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Mol Brain Res 78:131–137
Tsuboi Y, Baba Y, Don-ura K, Imamura A, Fujioka S, Yamada T (2005) Diffusion-weighted MRI in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with the codon 200 mutation in the prion protein gene. J Neurol Sci 232:45–49
Ukisu R, Kushihashi T, Kitanosono T, Fujisawa H, Takenaka H, Ohgiya Y, Gokan T, Munechika H (2005) Serial diffusion-weighted MRI of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Am J Roentgenol 184:560–566
Vajda Z, Pedersen M, Fuchtbauer EM, Wertz K, Stodkilde-Jorgensen H, Sulyok E, Dóczi T, Neely JD, Agre P, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S (2002) Delayed onset of brain edema and mislocalization of aquaporin-4 in dystrophin-null transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13131–13136
Vajda Z, Promeneur D, Dóczi T, Sulyok E, Frokiaer J, Ottersen OP, Nielsen S (2000) Increased aquaporin immunoreactivity in rat brain in response to systemic hyponatremia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:495–503
Venero JL, Machado A, Cano J (2004) Importance of aquaporins in the physiopathology of brain edema. Curr Phar Des 10:2153–2161
Verkman AS (2002) Physiological importance of aquaporin water channels. Ann Med 34:192–200
Warth A, Mittelbronn M, Wolburg H (2005) Redistribution of the water channel protein aquaporin-4 and the K+ channel protein Kir4.1 differs in low- and high-grade human brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol 109:418–426
Xiang W, Windl O, Westner IM, Neumann M, Zerr I, Lederer RM, Kretzschmar HA (2005) Cerebral gene expression profiles in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol 58:242–257
Xiang W, Windl O, Wünsch, Dugas M, Kohlmann A, Dierkes N, Westner IM, Kretzschmar HA (2004) Identification of differentially expressed genes in scrapie-infected mouse brains by using global gene expression technology. J Virol 78:11051–11060
Xiao F, Arnold TC, Zhang S, Brown C, Alexander JS, Carden DL, Conrad SA (2004) Cerebral cortical aquaporin-4 expression in brain edema following cardiac arrest in rats. Acad Emerg Med 11:1001–1007
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología: EET 2001-3724 and EET2002-05168, and CAL01-018 NoE Neuroprion CT-2004-506579. We wish to thank T. Yohannan for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, A., Pérez-Gracia, E., Espinosa, J.C. et al. Increased expression of water channel aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and in bovine spongiform encephalopathy-infected bovine-PrP transgenic mice. Acta Neuropathol 112, 573–585 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0117-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0117-1