Abstract
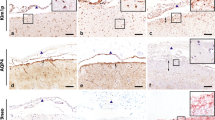
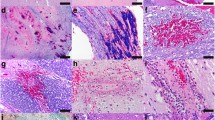
Aquaporin 4 (AQP4), one of the water channel proteins on the plasma membrane of astrocytes, is up-regulated in various conditions with brain edema. Possible participation of AQP4 in various inflammatory lesions, more or less associated with edema, was examined in human autopsied brains. Immunohistochemistry was used to investigate AQP4 expression in autopsied brains with multiple sclerosis (MS), human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis (HIVE) or progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). The cellular localization of AQP4 and its relation to inflammatory lesions were then examined with double-labeling immunohistochemistry. AQP4 immunoreactivity (IR) was restricted to astrocytes and localized to their entire processes, including their endfeet facing the abluminal surface of capillaries. In MS brains, AQP4-positive astrocytes were more abundant at the periphery of plaques than in their center, as seen in ischemic foci. Quantification of fluorescent signal demonstrated that AQP4 IR was greatly increased around plaques relative to that in unaffected area. Although the white matter was severely involved in HIVE and PML, AQP4-positive astrocytes were rare in the white matter even around perivascular active inflammatory foci. They were abundant in the gray matter and most prominent in the boundary between the gray and white matter, without apparent relation to inflammatory foci. Some bizarre astrocytes in PML exhibited AQP4 IR. Up-regulation of AQP4 was consistently found in astrocytes in various inflammatory lesions. However, the distribution of AQP4-positve astrocytes differed markedly according to disease and was not necessarily related to brain edema, indicating that functions and regulation of AQP4 in human brains are multiple.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams ME, Mueller HA, Froehner SC (2001) In vivo requirement of the α-syntrophin PDZ domain for the sarcolemmal localization of nNOS and aquaporin-4. J Cell Biol 155:113–122
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Williamson A, Palomba M, Edi T, Lanerolle NC de, Nagelhus EA, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Agre P, Ottersen OP (2003) Delayed K+ clearance associated with aquaporin-4 mislocalization: Phenotypic defects in brains of α-syntrophin-null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13615–13620
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Otsuka T, Hurn PD, Traysteman RJ, Hang FM, Froehner SC, Adams ME, Neely JD, Agre P, Ottersen OP, Bhardwaj A (2003) An α-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bi-directional water flow between blood and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2106–2111
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Xue R, Haug FM, Neely JD, Bhardwaj A, Agre P, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Mori S, Ottersen OP (2004) Alpha-syntrophin deletion remove the perivascular but not endothelial pool of aquaporin-4 at the blood-brain barrier and delays the development of brain edema in an experimental model of acute hyponatremia. FASEB J 18:542–544
Aoki K, Uchihara T, Tsuchiya K, Nakamura A, Ikeda K, Wakayama Y (2003) Enhanced expression of aquaporin 4 in human brain with infarction. Acta Neuropathol 106:121–124
Arima H, Yamamoto N, Sobue K, Umenishi F, Toda T, Katsuya H, Asai K (2003) Hyperosmolar mannitol stimulates expression of Aquaporin-4 and 9 through a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway in rat astrocytes. J Biol Chem 278:44525–44534
Frigeri A, Gropper MA, Turck CW, Verkman AS (1995) Immunolocalization of the mercurial-insensitive water channel and glycerol intrinsic protein in epithelial cell plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4328–4331
Frigeri A, Nicchia GP, Nico B, Quondamatteo F, Herken R, Rongali L, Svelto M (2001) Aquaporin-4 deficiency in skeletal muscle and brain of dystrophic mdx mice. FASEB J 15:90–98
Furman CS, Gorelick-Feldman DA, Davidson KGV, Yasumura T, Neely JD, Agre P, Rash JE (2003) Aquaporin-4 square array assembly: opposing actions of M1 and M23 isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13609–13614
Gu F, Hata R, Toku K, Yang L, Ma Y, Maeda N, Sakanaka M, Tanaka J (2003) Testosterone up-regulates aquaporin-4 expression in cultured astrocytes. J Neurosci Res 72:709–715
Guadagno E, Moukhles H (2004) Laminin-induced aggregation of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel, Kir4.1, and water-permeable channel, AQP4, via a dystroglycan-containing complex in astrocytes. Glia 47:138–149
Han Z, Wax MB, Patil RV (1998) Regulation of Aquaporin-4 water channels by phorbol ester-dependent protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 273:6001–6004
Hasegawa H, Ma T, Skach W, Matthay MA, Verkman AS (1994) Molecular cloning of a mercurial-insensitive water channel expressed in selected water-transporting tissues. J Biol Chem 269:5497–5500
Jordan-Sciutto KL, Wang G, Murphey-Corb M, Wiley CA (2002) Cell cycle proteins exhibit altered expression patterns in lentiviral-associated encephalitis. J Neurosci 22:2185–2195
Jung JS, Bhat RV, Preston GM, Guggino WB, Baraban JM, Agre P (1994) Molecular characterization of an aquaporin cDNA from brain: candidate osmoreceptor and regulator of water balance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:13052–13056
Kobayashi H, Minami S, Itoh S, Shiraishi S, Yokoo H, Yanagita U, Mohri M, Wada A (2001) Aquaporin subtypes in rat cerebral microvessels. Neurosci Lett 297:163–166
Landis DMD, Reese TS (1974) Arrays of particles in freeze-fractured astrocytic membranes. J Cell Biol 60:316–320
Liu JW, Wakayama Y, Inoue M, Shibuya S, Kojima H, Jimi T, Oniki H (1999) Immunocytochemical studies of aquaporin 4 in the skeletal muscle of mdx mouse. J Neurol Sci 164:24–28
Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS (2000) Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med 6:159–163
Murahashi M, Liu JW, Shibuya S, Jimi T, Wakayama Y (2000) Immunohistochemical findings of aquaporin 4 in the brain tissue of mdx mouse (in Japanese). Rinsho Shinkeigaku 40:1477
Neely JD, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP, Froehner C, Agre P, Adams ME (2001) Syntrophin-dependent expression and localization of aquaporin-4 water channel protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14108–14113
Nielsen S, Nagelhus EA, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Bourque C, Agre P, Ottersen P (1997) Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells: high-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J Neurosci 17:171–180
Papadopoulos MC, Manley GT, Krishna S, Verkman AS (2004) Aquaporin-4 facilitates reabsorption of excess fluid in vasogenic brain edema. FASEB J 18:1291–1293
Radhakrishnan S, Otte J, Enam S, Valle LD, Khalili K, Gordon J (2003) JC virus-induced changes in cellular gene expression in primary human astrocytes. J Virol 77:10638–10644
Rama Rao KV, Chen M, Simard JM, Norenberg MD (2003) Suppression of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling by cyclosporin A. J Neurosci Res 74:891–897
Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Davies DC, Krishna S, Bell BA (2002) Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in oedematous human brain tumours. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72:262–265
Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Krishna S (2003) Water transport becomes uncoupled from K+ siphoning in brain contusion, bacterial meningitis, and brain tumors: immunohistochemical case review. J Clin Pathol 12:972–975
Sobue K, Yamamoto N, Yoneda K, Fujita K, Miura Y, Asai K, Tsuda T, Katsuya H, Kato T (1999) Molecular cloning of two bovine aquaporin-4 cDNA isoforms and their expression in brain endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1489:393–398
Taniguchi M, Yamashita T, Kumura E, Tamatani M, Kobayashi A, Yokawa T, Maruno M, Kato A, Ohnishi T, Kohmura E, Tohyama M, Yoshimine T (2000) Induction of aquaporin-4 water channel mRNA after focal ischemia in rat. Mol Brain Rees 78:131–137
Vajda Z, Promeneur D, Doczi T, Sulyok E, Frøkiaer J, Ottersen OP, Nielsen S (2000) Increased aquqporin-4 immunoreactivity in rat brain in response to systemic hyponatremia. Biochem Biophysics Res Commun 270:495–4503
Venero JL, Vizuete ML, Ilundain AA, Machado A, Echevarria M, Cano J (1999) Detailed localization of aquaporin-4 messenger RNA in the CNS: preferential expression in periventricular organs. Neuroscience 94:239–250
Venero JL, Vizuete ML, Machado A, Cano J (2001) Aquaporins in the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 63:321–336
Vizuete ML, Venero JL, Vargas C, Ilundain AA, Echevarria M, Machado A, Cano J (1999) Differential upregulation of aquaporin-4 mRNA expression in reactive astrocytes after brain injury: potential role in brain edema. Neurobiol Dis 6:245–258
Yamamoto N, Sobue K, Miyachi T, Inagaki M, Miura Y, Katsuya H, Asai K (2001) Differential regulation of aquaporin expression in astrocytes by protein kinase C. Mol Brain Res 95:110–116
Yokota T, Miyagoe Y, Hosaka Y, Tsukita K, Kameya S, Shibuya S, Matsuda R, Wakayama Y, Takeda S (2000) Aquaporin-4 is absent at the sarcolemma and at perivascular astrocyte endfeet in α1-syntrophin knockout mice. Proc Jpn Acad 76:22–27
Yoneda K, Yamamoto N, Asai K, Sobue K, Fjita M, Mase M, Yamada K, Nakanishi M, Toda T, Miura Y, Kato T (2001) Regulation of aquaporin-4 expression in astrocytes. Mol Brain Res 89:94–102
Warth A, Kröger S, Wolburg H (2004) Redistribution of Aquaporin-4 in human glioblastoma correlates with loss of agrin immunoreactivity from brain capillary basal laminae. Acta Neuropathol 107:311–318
Zhou BY, He JJ (2004) Proliferation inhibition of astrocytes, neurons, and non-glial cells by intracellularly expressed human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Tat protein. Neurosci Lett 359:155-158
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoki-Yoshino, K., Uchihara, T., Duyckaerts, C. et al. Enhanced expression of aquaporin 4 in human brain with inflammatory diseases. Acta Neuropathol 110, 281–288 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-1052-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-1052-2