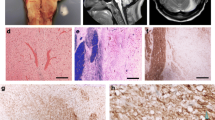
Abstract
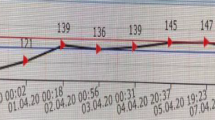
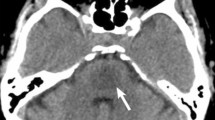
Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM, osmotic demyelination syndrome) and acquired chronic hepatocerebral degeneration (ACHD) both occur in patients with liver failure, but are not thought to be caused by similar etiopathogenic mechanisms despite the fact that occasional patients exhibit both disorders. In our autopsy practice we have recently encountered three patients with the pontine lesions of acute or subacute osmotic demyelination syndrome, coupled with superimposed non-Wilsonian ACHD. All three patients had well-documented rapid elevations in serum sodium proximate to their demise, as well as terminal liver failure. A close intermingling and juxtaposition of lesions with severe demyelination and macrophage breakdown [thought to represent extrapontine myelinolysis (EPM)] to those with vacuolization of myelin but no cellular reaction or myelin loss (ACHD) was noted within some of the same anatomic areas. Particular overlap was seen in lesions at the cerebral cortical gray–white junction and in pencil fibers of the striatum. In these areas it was difficult to be certain whether the lesions were due to EPM or ACHD. We concluded that there was a synergism between the two disorders and raise the possibility that there may be factors common to both disorders that lead to similar anatomic sites for involvement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JH (1961) Central pontine myelinolysis. In: Proceedings of the fourth international congress of neuropathology, Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 303–308
Adams R, Victor M, Mancall E (1959) Central pontine myelinolysis. a hitherto undescribed disease occurring in alcoholic and malnourished patients. Arch Neurol 81:154–172
Finlayson MH, Superville B (1981) Distribution of cerebral lesions in acquired hepatocerebral degeneration. Brain 104:79–95
Gocht A, Colmant HJ (1987) Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: a report of 58 cases. Clin Neuropathol 6:262–270
Goebel HH, Herman-Ben Zur P (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology. North Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam, vol 28, pp 285–316
Goebel HH, Herman-Ben Zur P (1972) Central pontine myelinolysis: a clinical and pathological study of 10 cases. Brain 95:495–504
Karp BI, Laureno RL (2000) Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis after correction of hyponatremia. Neurologist 6:255–266
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Norenberg MD (1981) Rapid correction of hyponatremia causes demyelination. Relation to central pontine myelinolysis. Science 211:1068–1070
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, Rojiani AM, Filley CM (2006) Central and extrapontine myelinolysis: Then...and now. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:1–11
Lampl C, Yazdi K (2002) Central pontine myelinolysis. Eur Neurol 47:3–10
Laureno R (1983) Central pontine myelinolysis following rapid correction of hyponatremia. Ann Neurol 13:232–242
Martin RJ (2004) Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: the osmotic demyelination syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75(Suppl 3):iii22–iii28
Norenberg MD, Leslie KO, Robertson AS (1982) Ann Neurol 11:128–135
Popoff H, Budzilovich G, Goodgold A, Feigin I (1965) Heptocerebral degeneration. Its occurrence in the presence and in the absence of abnormal copper metabolism. Neurology 15:919–930
Rojiani AM, Cho E-S, Sharer L, Prineas J (1994) Electrolyte-induced demyelination in rats. 2. Ultrastructural evolution. Acta Neuropathol 88:293–299
Rojiani AM, Prineas J, Cho E-S (1994) Electrolyte-induced demyelination in rats: 1. Role of the blood–brain barrier and edema. Acta Neuropathol 88:287–292
Rojiani AM, Prineas J, Cho E-S (1987) Protective effect of steroids on electrolyte induced demyelination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46:495-505
Shiraki H (1964) Comparative neuropathologic study of Wilson’s disease and other types of hepatocerebral disease. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser 4:64–73
Shiraki H, Oda M (1968) Neuropathology of hepatocerebral disease with emphasis on comparative studies. In: Minckler J (ed) Pathology of the nervous system. McGraw Hill, New York, vol 78, pp 1089–1103
Silver SM, Schroeder BM, Sterns RH, Rojiani AM (2006) Myoinositol administration improves survival and reduces myelinolysis after rapid correction of chronic hyponatremia in rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:37–44
Soffer D, Sherman Y, Tur-Kaspa R, Eid A (1995) Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration in a liver transplant recipient. Acta Neuropathol 90:107–111
Sterns RH, Riggs JE, Schochet SS Jr (1986) Osmotic demyelination syndrome following correction of hyponatremia. N Engl J Med 314:1535–1542
Victor M, Adams RD, Cole M (1965) The acquired (non-Wilsonian) type of chronic hepatocerebral degeneration. Medicine 44:345–396
Wright DG, Laureno R, Victor M (1979) Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Brain 102:361–385
Acknowledgments
This article is dedicated to Dr. Michael Norenberg, whose work on CPM inspired all of our careers and to Dr.Eun-Sook Cho whose mentorship guided one of us (AMR) into a career in academic neuropathology. The authors thank Ms. Susan Peth for expert manuscript preparation and Ms. Lisa Litzenberger for photographic expertise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K., Filley, C.M. & Rojiani, A.M. Overlapping features of extrapontine myelinolysis and acquired chronic (non-Wilsonian) hepatocerebral degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 112, 605–616 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0112-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0112-6