Abstract
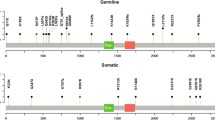
The gene for RE1-silencing transcription factor (REST) alias neuron-restrictive silencer factor NRSF, acts as a transcriptional repressor in the neuronal differentiation pathways in non-neuronal cells, and plays an important role in neuronal development. Inactivating mutations or overexpression of REST have previously been reported in various types of cancer, but no data is available for the role of REST alterations in gliomas. REST gene was screened for mutations in 161 nervous system tumors consisting of astrocytomas, glioblastomas, oligodendrogliomas, oligoastrocytomas, medulloblastomas, meningiomas and schwannomas. REST exons 1–3 were analyzed using denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) and direct sequencing. The gene copy numbers of REST were investigated by chromogenic (CISH) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) techniques. Non-synonymous SNPs (P797L, P815S) were found in eight different brain tumor samples. No truncating or activating novel mutations of REST were discovered. Since REST is located at 4q12, a chromosome region implicated in brain tumorigenesis, we conducted gene copy number analyses in medulloblastomas and gliomas. The majority of gliomas (67%) demonstrated low-level amplifications of REST, and only one oligodendroglioma showed high-level amplification of the gene. In medulloblastomas, 38% of samples were determined as aneuploidic, no high-level amplifications were found. Our data suggests that REST is neither activated nor inactivated via mutations in gliomas, while high-level amplification may rarely occur.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballas N, Battaglioli E, Atouf F, Andres ME, Chenoweth J, Anderson ME, Burger C, Moniwa M, Davie JR, Bowers WJ, Federoff HJ, Rose DW, Rosenfeld MG, Brehm P, Mandel G (2001) Regulation of neuronal traits by a novel transcriptional complex. Neuron 31:353–365
Ballas N, Grunseich C, Lu DD, Speh JC, Mandel G (2005) REST and its corepressors mediate plasticity of neuronal gene chromatin throughout neurogenesis. Cell 121:645–657
Chilton-Macneill S, Ho M, Hawkins C, Gassas A, Zielenska M, Baruchel S (2004) C-kit expression and mutational analysis in medulloblastoma. Pediatr Dev Pathol 7:493–498
Chong JA, Tapia-Ramírez J, Kim S, Toledo-Aral JJ, Zheng Y, Boutros MC, Altshuller YM, Frohman MA, Kraner SD, Mandel G (1995) REST: a mammalian silencer protein that restricts sodium channel gene expression to neurons. Cell 80:949–957
Cools J, Stover EH, Wlodarska I, Marynen P, Gilliland DG (2004) The FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha kinase in hypereosinophilic syndrome and chronic eosinophilic leukemia. Curr Opin Hematol 1:51–57
Coulson JM (2005) Transcriptional regulation: cancer, neurons and the REST. Curr Biol 15:665–667
Fuller GN, Su X, Price RE, Cohen ZR, Lang FF, Sawaya R, Majumder S (2005) Many human medulloblastoma tumors overexpress repressor element-1 silencing transcription (REST)/neuron-restrictive silencer factor, which can be functionally countered by REST-VP16. Mol Can Ther 4:343–349
Hartmann C, Bartels G, Gehlhaar C, Holtkamp N, von Deimling A (2005) PIK3CA mutations in glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neuropathol 109:639–642
Horiuchi M, Itoh T, Pleasure DE, Tomooka Y (2005) Multipotency of FBD-103a, a neural progenitor cell line from the p53-deficient mouse. Brain Res 1066:24–36
Joensuu H, Puputti M, Sihto H, Tynninen O, Nupponen NN (2005) Amplification of genes encoding KIT, PDGFRalpha and VEGFR2 receptor tyrosine kinases is frequent in glioblastoma multiforme. J Pathol 207:224–231
Jones FS, Meech R (1999) Knockout of REST/NRSF shows that the protein is a potent repressor of neuronally expressed genes in non-neural tissues. Bioessays 21:372–376
Kato H, Kato S, Kumabe T, Sonoda Y, Yoshimoto T, Kato S, Han SY, Suzuki T, Shibata H, Kanamaru R, Ishioka C (2000) Functional evaluation of p53 and PTEN gene mutations in gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 6:3937–3943
Kleihues P, Cavenee W (eds) (2000) Pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. IARC Press, Lyon
Lawinger P, Venugopal R, Guo ZS, Immaneni A, Sengupta D, Lu W, Rastelli L, Marin Dias Carneiro A, Levin V, Fuller GN, Echelard Y, Majumder S (2000) The neuronal repressor REST/NRSF is an essential regulator in medulloblastoma cells. Nat Med 7:826–831
McIntyre A, Summersgill B, Grygalewicz B, Gillis AJ, Stoop J, van Gurp RJ, Dennis N, Fisher C, Huddart R, Cooper C, Clark J, Oosterhuis JW, Looijenga LH, Shipley J (2005) Amplification and overexpression of the KIT gene is associated with progression in the seminoma subtype of testicular germ cell tumors of adolescents and adults. Cancer Res 65:8085–8089
Meletis K, Wirta V, Hede SM, Nister M, Lundeberg J, Frisen J (2006) p53 suppresses the self-renewal of adult neural stem cells. Development 133:363–369
Palm K, Belluardo N, Metsis M, Timmusk T (1998) Neuronal expression of zinc finger transcription factor REST/NRSF/XBR gene. J Neurosci 18:1280–1296
Rasheed BK, Wiltshire RN, Bigner SH, Bigner DD (1999) Molecular pathogenesis of malignant gliomas. Curr Opin Oncol 11:162–167
Schoenherr CJ, Paquette AJ, Anderson DJ (1996) Identification of potential target genes for the neuron-restrictive silencer factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93(18):9881–9886
Sihto H, Sarlomo-Rikala M, Tynninen O, Tanner M, Andersson LC, Franssila K, Nupponen NN, Joensuu H (2005) KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha tyrosine kinase gene mutations and KIT amplifications in human solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 23:49–57
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA, Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD, Dirks PB (2004a) Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 432:396–401
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Hide T, Dirks PB (2004b) Cancer stem cells in nervous system tumors. Oncogene 23:7267–7273
Su X, Kameoka S, Lentz S, Majumder S (2004) Activation of REST/NRSF target genes in neural stem cells is sufficient to cause neuronal differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 24:8018–8025
Su X, Gopalakrishnan V, Stearns D, Aldape K, Lang FF, Fuller G, Snyder E, Eberhart CG, Majumder S (2006) Abnormal expression of REST/NRSF and Myc in neural stem/progenitor cells causes cerebellar tumors by blocking neuronal differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 26:1666–1678
Sun Y-M, Greenway DJ, Johnson R, Street M, Belyaev ND, Deuchars J, Bee T, Wilde S, Buckley NJ (2005) Distinct profiles of REST interactions with its target genes at different stages of neuronal development. Mol Biol Cell 16:5630–5638
Walter WJ, North PE, Waner M, Mizeracki A, Blei F, Walker JWT, Reinisch JF, Marchuk DA (2002) Somatic mutation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in juvenile hemangioma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 33:295–303
Westbrook TF, Martin ES, Schlabac MR, Leng Y, Liang AC, Feng B, Zhao JJ, Roberts TM, Mandel G, Hannon GJ, DePinho RA, Chin L, Elledge SJ (2005) A Genetic Screen for Candidate Tumor Suppressors Identifies REST. Cell 121:837–848
Wood IC, Belyaev ND, Bruce AW, Jones C, Mistry M, Roopra A, Buckley NJ (2003) Interaction of the repressor element 1-silencing transcription factor (REST) with target genes. J Mol Biol 334:863–874
Zhu Y, Parada LF (2002) The molecular and genetic basis of neurological tumors. Nature 2:616–626
Acknowledgment
Authors thank Ms. Sari Toivola for skillful technical assistance and Dr. Alexandre Angers-Loustau for reading the manuscript. Grant funding was received from the Cancer Institute of Finland and the Academy of Finland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blom, T., Tynninen, O., Puputti, M. et al. Molecular genetic analysis of the REST/NRSF gene in nervous system tumors. Acta Neuropathol 112, 483–490 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0102-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0102-8