Abstract
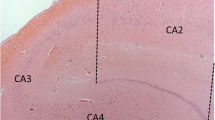
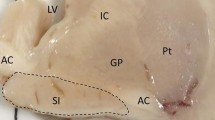
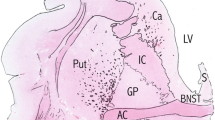
The cholinergic basal forebrain is divided into four subregions (Ch1–4), and cholinergic neuronal loss in the nucleus basalis of Meynert (Ch4) has been correlated with cognitive impairments in both Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). However, the Ch1–2 regions, which provide the major cholinergic innervation to the hippocampus, have not been investigated in DLB. The purpose of this study was to reveal the cholinergic neuronal changes in the medial septum (Ch1) and the nucleus of the vertical limb of the diagonal band (Ch2) of DLB brains. Using choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) immunohistochemistry, we showed that the number of ChAT-immunoreactive neurons in DLB brains was significantly lower than the numbers in AD and non-demented (control) brains. No significant difference in the number of ChAT-immunoreactive neurons was found between the AD and control brains. Moreover, the size of the ChAT-immunoreactive neurons was significantly smaller in the AD and DLB brains than in the control brains. These results show that cholinergic neurons of the Ch1-2 regions are more severely affected in DLB than in AD. Our DLB cases did not fulfill the neuropathologic criteria for definite AD. Furthermore, some Lewy bodies were observed in the Ch1-2 regions. Thus, cholinergic neuronal loss in the Ch1-2 regions might be specific to the pathology of DLB. Taking the distribution of cholinergic fibers in the hippocampus into consideration, this study suggests a possibility that hippocampal cholinergic projection is involved in Lewy-related neurites in the CA2–3 regions, the origin of which remains unclear.



Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Akatsu H, Takahashi M, Matsukawa N, Ishikawa Y, Kondo N, Sato T, Nakazawa H, Yamada T, Okada H, Yamamoto T, Kosaka K (2002) Subtype analysis of neuropathologically diagnosed patients in a Japanese geriatric hospital. J Neurol Sci 196:63–69
Bohnen NI, Kaufer DI, Ivanco LS, Koeppe RA, Davis JG, Mathis CA, Moore RY, DeKosky ST (2003) Cortical cholinergic function is more severely affected in parkinsonian dementia than in Alzheimer disease: an in vivo positron emission tomographic study. Arch Neurol 60:1745–1748
Brenneis C, Wenning GK, Egger KE, Schocke M, Trieb T, Seppi K, Marksteiner J, Ransmayr G, Benke T, Poewe W (2004) Basal forebrain atrophy is a distinctive pattern in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neuroreport 15:1711–1714
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Collerton D, Burn D, McKeith I, O’Brien J (2003) Systematic review and meta-analysis show that dementia with Lewy bodies is a visual-perceptual and attentional-executive dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 16:229–237
Dickson DW, Ruan D, Crystal H, Mark MH, Davies P, Kress Y, Yen S-H (1991) Hippocampal degeneration differentiates diffuse Lewy body disease (DLBD) from Alzheimer’s disease: light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of CA2-3 neurites specific to DLBD. Neurology 41:1402–1409
Dickson DW, Schmidt ML, Lee VM-Y, Zhao M-L, Yen S-H, Trojanowski JQ (1994) Immnoreactivity profile of hippocampal CA2/3 neurites in diffuse Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 87:269–276
Folstein M, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) Mini-mental state. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Galvin JE, Uryu K, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (1999) Axon pathology in Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia hippocampus contains α-, β-, and γ-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13450–13455
Iraizoz I, Guijarro JL, Gonzalo LM, De Lacalle S (1999) Neuropathological changes in the nucleus basalis correlate with clinical measures of dementia. Acta Neuropathol 98:186–196
Iseki E, Li F, Odawara T, Kosaka K (1997) Hippocampal pathology in diffuse Lewy body disease using ubiquitin immunohistochemistry. J Neurol Sci 149:165–169
Janisiezka AM, Jackson O III, Firoz EF, Baxter MG (2004) Environment-spatial conditional learning in rats with selective lesions of medial septal cholinergic neurons. Hippocampus 14:265–273
Kaufer DI (2004) Pharmacologic treatment expectations in the management of dementia with Lewy bodies. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17:32–39
Kitt CA, Mitchell SJ, Delong MR, Wainer BH, Price DL (1987) Fiber pathways of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in monkeys. Brain Res 406:192–206
Kordower JH, Gash DM, Bothwell M, Hersh L, Mufson EJ (1989) Nerve growth factor and choline acetyltransferase remain colocalized in the nucleus basalis (Ch4) of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neurobiol Aging 10:287–294
Lippa CF, Smith TW, Perry E (1999) Dementia with Lewy bodies: choline acetyltransferase parallels nucleus basalis pathology. J Neural Transm 106:525–535
Marui W, Iseki E, Kato M, Akatsu H, Kosaka K (2004) Pathological entity of dementia with Lewy bodies and its differentiation from Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 108:121–128
McKeith IG, Galasko D, Kosaka K, Perry EK, Dickson DW, Hansen LA, Salmon DP, Lowe J, Mirra SS, Byrne EJ, Lennox G, Quinn NP, Edwardson JA, Ince PG, Bergeron C, Burns A, Miller BL, Lovestone S, Collerton D, Jansen ENH, Ballard C, de Vos RAI, Wilcock GK, Jellinger KA, Perry RH (1996) Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). Neurology 47:1113–1124
Mesulam M-M, Mufson EJ, Levey AI, Wainer BH (1983) Cholinergic innervation of cortex by the basal forebrain: cytochemistry and cortical connections of the septal area, diagonal band nuclei, nucleus basalis (substantia innominata) and hypothalamus in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 214:170–197
Mori E, Shimomura T, Fujimori M, Hirono N, Imamura T, Hashimoto M, Tanimukai S, Kazui H, Hanihara T (2000) Visuoperceptual impairment in Dementia with Lewy bodies. Arch Neurol 57:489–493
Mufson EJ, Bothwell M, Kordower JH (1989) Loss of nerve growth factor receptor-containing neurons in Alzheimer’s disease: a quantitative analysis across subregions of the basal forebrain. Exp Neurol 105:221–232
Mufson EJ, Bothwell M, Hersh LB, Kordower JH (1989) Nerve growth factor receptor immunoreactive profiles in the normal, aged human basal forebrain: colocalization with cholinergic neurons. J Comp Neurol 285:196–217
Mufson EJ, Cochran E, Benzing W, Kordower JH (1993) Galaninergic innervation of the cholinergic vertical limb of the diagonal band (Ch2) and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in aging, Alzheimer’s disease and down’s syndrome. Dementia 4:237–250
Mufson EJ, Conner JM, Varon S, Kordower JH (1994) Nerve growth factor-like immunoreactive profiles in the primate basal forebrain and hippocampal formation. J Comp Neurol 341:507–519
Pearson RCA, Sofroniew MV, Cuello AC, Powell TPS, Eckenstein F, Esiri MM, Wilcock GK (1983) Persistence of cholinergic neurons in the basal nucleus in a brain with senile dementia of the Alzheimer’s type demonstrated by immunohistochemical staining for choline acetyltransferase. Brain Res 289:375–379
Perry EK, Irving D, Kerwin JM, McKeith IG, Thompson P, Collerton D, Fairbairn AF, Ince PG, Morris CM, Cheng AV, Perry RH (1993) Cholinergic transmitter and neurotrophic activities in Lewy body dementia: similarity to Parkinson’s and distinction from Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 7:69–79
Ransmayr G, Cervera P, Hirsch E, Ruberg M, Hersh LB, Duyckaerts C, Hauw J-J, Delumeau C, Agid Y (1989) Choline acetyltransferase-like immunoreactivity in the hippocampal formation of control subjects and patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 32:701–714
Ridley RM, Barefoot HC, Maclean CJ, Pugh P, Baker HF (1999) Different effects on learning ability after injection of the cholinergic immunotoxin ME20. 4IgG-saporin into the diagonal band of Broca, basal nucleus of Meynert, or both in monkeys. Behav Neurosci 113:303–315
Rinne JO, Paljarvi L, Rinne UK (1987) Neuronal size and density in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 79:67–76
Tirabosci P, Hansen LA, Alford M, Sabbagh MN, Schoos B, Masliah E, Thal LJ, Corey-Bloom J (2000) Cholinergic dysfunction in disease with Lewy bodies. Neurology 54:407–411
The national institute on aging, reagan institute working group on diagnostic criteria for the neuropathological assessment of Alzheimer’s disease (1997) Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 18:S1–S2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujishiro, H., Umegaki, H., Isojima, D. et al. Depletion of cholinergic neurons in the nucleus of the medial septum and the vertical limb of the diagonal band in dementia with Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol 111, 109–114 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-0004-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-0004-1