Abstract
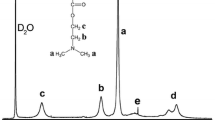
This paper is focused on the synthesis and characterization of hydrophobically modified polyelectrolytes and their use as reducing as well as stabilizing agents for the formation of gold nanoparticles. Commercially available poly(acrylic acid) has been hydrophobically modified with various degrees of grafting of butylamine introduced randomly along the chain. Different analytical methods are performed, i.e., IR and 1H-NMR spectroscopy in combination with elemental analysis to determine the degree of grafting. The modified polymers can successfully be used for the controlled single-step synthesis and stabilization of gold nanoparticles. The process of nanoparticle formation is investigated by means of UV-vis spectroscopy. The size and shape of the particles obtained in the presence of unmodified or modified polyelectrolytes are characterized by dynamic light scattering, zeta potential measurements and transmission electron microscopy. The polyelectrolytes were involved in the crystallization process of the nanoparticles, and in the presence of hydrophobic microdomains at the particle surface, a better stabilization at higher temperature can be observed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demaille C, Brust M, Tsionsky M, Bard AJ (1997) Anal Chem 69(13):2323
Hayward RC, Saville DA, Aksay IA (2000) Nature 404:56
Braun E, Eichen Y, Sivan U, Ben-Yoseph G (1998) Nature 391:775
Chen M, Yamaruro S, Farrell D, Majetich SA (2003) J Appl Phys 93:7551
Ciebien JF, Cohen RE, Duran A (1998) Supramol Sci 5:31
Wilcoxon JP, Martin JE, Parsapour F, Wiedenman B, Kelley DF (1998) J Chem Phys 108(21):9137
Hayat MA (ed) (1989) Colloidal gold: principles, methods and applications. Academic, San Diego
Hyatt AD, Eaton BT (1993) Immuno-gold electron microscopy in virus diagnosis and research. CRC, Boca Raton
Quinn M, Mills GJ (1994) Phys Chem 98:9840
Wei Y, Cao C, Jin R, Mirkin CA (2002) Science 297:1536
Roucoux A, Schulz J, Patin H (2002) Chem Rev 102:3757
Faraday M (1857) Philos Trans R Soc Lond 147:145
Esumi K, Suzuki A, Aihara N, Usui K, Torigoe K (1998) Langmuir 14:3157
Mayer ABR, Mark JE (1998) Eur Polym J 34(1):103
Sidorov SN, Bronstein LM, Valetsky PM, Hartmann J, Cölfen H, Schnablegger H, Antonietti M (1998) J Colloid Interface Sci 212:197
Caruso RA, Giersig M, Willig F, Antonietti M (1998) Langmuir 14:6333
Caruso RA, Antonietti M, Giersig M, Hentze HP, Jia J (2001) Chem Mater 13:1114
Faul CFJ, Antonietti M, Hentze HP, Smarsly B (2003) Colloids Surf 212(2–3):115
Grohn F, Kim G, Bauer AJ, Amis EJ (2001) Macromolecules 34(7):2179
Saito H, Okamura S, Ishizu K (1992) Polymer 33:1099
Chan YNC, Schrock RR, Cohen RE (1992) Chem Mater 4:24
Capek I (2004) Adv Coll Int Sci 110:49
Mayer ABR, Mark JE (2000) Polymer 41:1627
Mayer ABR, Mark JE (1997) Colloid Polym Sci 275:333
Corbierre MK, Cameron NS, Lennox RB (2004) Langmuir 20:2867
Kim F, Connor S, Song H, Kuykendall T, Yang P (2004) Angew Chem Int Ed 43:3673
Pugh TL, Heller WJ (1960) Polym Sci 47(149):219
Mayer ABR, Mark JE (1997) J Macromol Sci A 34(11):2151
Sun X, Dong S, Wang E (2004) Polymer 45:2181
Hussain I, Brust M, Papworth AJ, Cooper AI (2003) Langmuir 19:4831
Sakai T, Alexandridis P (2004) Langmuir 208:426
Wang TK, Iliopoulos I, Audebert R (1988) Polym Bull 20:577
Anghel DF, Alderson V, Winnik FM, Mizusaki M, Morishima Y (1998) Polymer 39(14):3035
Garces FO, Sivadasan K, Somasundaran P, Turro NJ (1994) Macromolecules 27:272
Moharram MA, Rabie SM, El-Gendy HM (2002) J Appl Polym Sci 85:1619
Limin Q, Cölfen H, Antonietti M (2000) Angew Chem Int Ed 39(3):604
Shu-Hong Y, Cölfen H, Antonietti M (2003) Adv Mater 15(2):133
Dubin PL (1985) Microdomains in polymer solutions. Plenum, New York
Laschewski A (1995) Adv Polym Sci 124:1
Koetz J, Kosmella S, Beitz T (2001) Prog Polym Sci 26:1199
Acknowledgements
The authors thank A. Laschewsky, University of Potsdam & Fraunhofer Institut für Angewandte Polymerforschung Golm, for useful discussions on polymer analysis, for the use of elemental analysis facilities and for providing access to the Infrared and the UV-vis spectroscopy instruments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Note, C., Koetz, J., Kosmella, S. et al. Hydrophobically modified polyelectrolytes used as reducing and stabilizing agent for the formation of gold nanoparticles. Colloid Polym Sci 283, 1334–1342 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-005-1349-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-005-1349-7