Abstract
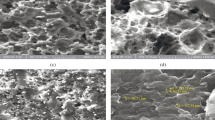
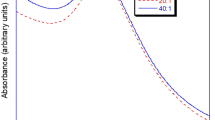
Several stable palladium, platinum, silver, and gold colloids were prepared by reducing the corresponding metal precursors in the presence of protective amphiphilic block copolymers. Some palladium and platinum precursors with different hydrophobicities, namely palladium chloride PdCl2, palladium acetate Pd(CH3COO)2, hexachloroplatinic acid H2PtCl6, and platinum acetylacetonate Pt(CH3COCH = C(O-)CH3)2, have been used in order to investigate differences in their catalytic activity. The polymers investigated for their ability to stabilize such transition metal colloids were polystyrene-b-poly(ethylene oxide) and polystyrene-b-poly (methacrylic acid). The metal particle sizes and morphologies were determined by transmission electron microscopy and found to be in the nanometer range. The catalytic activity of the palladium and platinum colloids was tested by the hydrogenation of cyclohexene as a model reaction. The protected palladium and platinum nanoparticles were found to be catalytically active, and final conversions up to 100% cyclohexane could be obtained. Depending on the choice of polymer block types and lengths, the precursor type, and the reduction method, different nanoparticle morphologies and catalytic activities could be obtained. These novel catalytically active metal-polymer systems are thus promising candidates for the development of tailored catalyst systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Puddephatt RJ (1978) The Chemistry of Gold. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam
Hirai H, Toshima N (1986) In: Iwasawa Y (ed) Catalysis by Metal Complexes, Tailored Metal Catalysts. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht
Bradley JS (1994) In: Schmid G (ed) Clusters and Colloids. From Theory to Applications. VCH, Weinheim
Moffitt M, Eisenberg A (1995) Chem Mater 7:1178
Napper DH (1983) Polymeric Stabilization of Colloidal Dispersions. Academic Press, London
Hirai H, Chawanya H, Toshima N (1981) Makromol Chem Rapid Commun 2:99
Toshima N, Yonezawa T, Kushihashi K (1993) J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 89:2537
Hirai H, Chawanya H, Toshima N (1985) Reactive Polymers 3:127
Warshawsky A, Upson DA (1989) J Pol Sci: Part A: Pol Chem 27:2963
Mayer ABR, Mark JE (1995) PMSE Preprints 73:220
Mayer ABR, Mark JE (1996) In: Chow G-M, Gonsalves KE (eds) Nanotechnology, Molecularly Designed Materials. ACS Symposium Series 622. ACS, Washington, p 137
Mayer ABR, Mark JE (1996) Polym Bull 37:683
Mayer ABR, Mark JE (1996) Macromol Rept 33:451
Moffitt M, McMahon L, Pessel V, Eisenberg A (1995) Chem Mater 7:1185
Antonietti M, Wenz E, Bronstein L, Seregina M (1995) PMSE Preprints 73:283
Antonietti M, Wenz E, Bronstein L, Seregina M (1995) Adv Mat 7:1000
Antonietti M, Förster S, Hartmann J, Oestreich S (1996) Macromolecules 29: 3800
Spatz JP, Roescher A, Möller M (1996) Polymer Preprints 37:409
Roescher A, Möller M (1995) PMSE Preprints 73:156
Spatz JP, Roescher A, Möller M (1996) Adv Mat 8:337
Cummins CC, Schrock RR, Cohen RE (1992) Chem Mater 4:27
Chan YNC, Craig GSW, Schrock RR, Cohen RE (1992) Chem Mater 4:885
Hirai H, Nakao Y, Toshima N (1979) J Macromol Sci-Chem A13:727
Bönnemann H, Brijoux W, Joussen T (1990) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 29:273
Bönnemann H, Brijoux W, Brinkmann R, Fretzen R, Joussen T, Köppler R, Korall B, Neiteler P, Richter J (1994) J Mol Cat 86:129
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayer, A.B.R., Mark, J.E. Transition metal nanoparticles protected by amphiphilic block copolymers as tailored catalyst systems. Colloid Polym Sci 275, 333–340 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960050090
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960050090