Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to determine the effects of fish oil-derived n-3 PUFA on glycemic control and lipid profiles in type 2 diabetic patients with abdominal obesity.
Methods
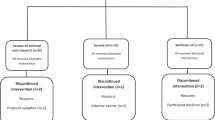
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 100 type 2 diabetic patients with abdominal obesity were randomized into two groups including 4 g/day of fish oil (2.4 g n-3 PUFA) or placebo (corn oil) for 6 months. Serum fatty acid, body composition, as well as markers of glucose regulation and lipid parameters were measured before and after intervention.
Results
Thirty-five men and 64 women aged 65.4 ± 5.3 years completed the intervention. Although body composition was unchanged, serum EPA and DHA were higher in the fish oil group than those in the placebo group (P < 0.001 and P < 0.001, respectively). Serum triglyceride (TG) decreased (P = 0.007), whereas high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) increased (P = 0.006) in the fish oil group compared with the placebo group after 6 months. Serum total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), the ratio of LDL-C to HDL-C, and glycemic control (measured by serum glucose, glycated hemoglobin, insulin, and homeostasis model assessment–insulin resistance) were not significantly different between the two groups after 6 months.
Conclusions
This study showed that 6 months of fish oil supplement had no statistically significant effects on glycemic control, but improved TG and HDL-C in type 2 diabetic patients with abdominal obesity.
Trial registration
Chictr.org ChiCTR-TRC-14005084.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
NCD-RisC (2016) Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet 387:1513–1530. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)00618-8
Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T, Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, Xu M, Li Y, Hu N, Li J, Mi S, Chen CS, Li G, Mu Y, Zhao J, Kong L, Chen J, Lai S, Wang W, Zhao W, Ning G (2013) Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA 310:948–959. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.168118
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 444:840–846. doi:10.1038/nature05482
Mouratoff GJ, Carroll NV, Scott EM (1967) Diabetes mellitus in Eskimos. JAMA 199:107–112
Bang HO, Dyerberg J, Sinclair HM (1980) The composition of the Eskimo food in north western Greenland. Am J Clin Nutr 33:2657–2661
Fumagalli M, Moltke I, Grarup N, Racimo F, Bjerregaard P, Jorgensen ME, Korneliussen TS, Gerbault P, Skotte L, Linneberg A, Christensen C, Brandslund I, Jorgensen T, Huerta-Sanchez E, Schmidt EB, Pedersen O, Hansen T, Albrechtsen A, Nielsen R (2015) Greenlandic Inuit show genetic signatures of diet and climate adaptation. Science 349:1343–1347. doi:10.1126/science.aab2319
Djousse L, Gaziano JM, Buring JE, Lee IM (2011) Dietary omega-3 fatty acids and fish consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 93:143–150. doi:10.3945/ajcn.110.005603
Kaushik M, Mozaffarian D, Spiegelman D, Manson JE, Willett WC, Hu FB (2009) Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, fish intake, and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Clin Nutr 90:613–620. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2008.27424
van Woudenbergh GJ, van Ballegooijen AJ, Kuijsten A, Sijbrands EJ, van Rooij FJ, Geleijnse JM, Hofman A, Witteman JC, Feskens EJ (2009) Eating fish and risk of type 2 diabetes: a population-based, prospective follow-up study. Diabetes Care 32:2021–2026. doi:10.2337/dc09-1042
Brostow DP, Odegaard AO, Koh WP, Duval S, Gross MD, Yuan JM, Pereira MA (2011) Omega-3 fatty acids and incident type 2 diabetes: the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr 94:520–526. doi:10.3945/ajcn.110.009357
Nanri A, Mizoue T, Noda M, Takahashi Y, Matsushita Y, Poudel-Tandukar K, Kato M, Oba S, Inoue M, Tsugane S, Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study G (2011) Fish intake and type 2 diabetes in Japanese men and women: the Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study. Am J Clin Nutr 94:884–891. doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.012252
Villegas R, Xiang YB, Elasy T, Li HL, Yang G, Cai H, Ye F, Gao YT, Shyr Y, Zheng W, Shu XO (2011) Fish, shellfish, and long-chain n-3 fatty acid consumption and risk of incident type 2 diabetes in middle-aged Chinese men and women. Am J Clin Nutr 94:543–551. doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.013193
Zheng JS, Huang T, Yang J, Fu YQ, Li D (2012) Marine N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are inversely associated with risk of type 2 diabetes in Asians: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 7:e44525. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044525
Chen C, Yu X, Shao S (2015) Effects of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on glucose control and lipid levels in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 10:e0139565. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0139565
Glauber H, Wallace P, Griver K, Brechtel G (1988) Adverse metabolic effect of omega-3 fatty acids in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med 108:663–668
Schectman G, Kaul S, Kissebah AH (1988) Effect of fish oil concentrate on lipoprotein composition in NIDDM. Diabetes 37:1567–1573
Borkman M, Chisholm DJ, Furler SM, Storlien LH, Kraegen EW, Simons LA, Chesterman CN (1989) Effects of fish oil supplementation on glucose and lipid metabolism in NIDDM. Diabetes 38:1314–1319
Mostad IL, Bjerve KS, Bjorgaas MR, Lydersen S, Grill V (2006) Effects of n-3 fatty acids in subjects with type 2 diabetes: reduction of insulin sensitivity and time-dependent alteration from carbohydrate to fat oxidation. Am J Clin Nutr 84:540–550
Annuzzi G, Rivellese A, Capaldo B, Di Marino L, Iovine C, Marotta G, Riccardi G (1991) A controlled study on the effects of n-3 fatty acids on lipid and glucose metabolism in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Atherosclerosis 87:65–73
Pelikanova T, Kohout M, Valek J, Kazdova L, Base J (1993) Metabolic effects of omega-3 fatty acids in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci 683:272–278
Morgan WA, Raskin P, Rosenstock J (1995) A comparison of fish oil or corn oil supplements in hyperlipidemic subjects with NIDDM. Diabetes Care 18:83–86
McManus RM, Jumpson J, Finegood DT, Clandinin MT, Ryan EA (1996) A comparison of the effects of n-3 fatty acids from linseed oil and fish oil in well-controlled type II diabetes. Diabetes Care 19:463–467
Luo J, Rizkalla SW, Vidal H, Oppert JM, Colas C, Boussairi A, Guerre-Millo M, Chapuis AS, Chevalier A, Durand G, Slama G (1998) Moderate intake of n-3 fatty acids for 2 months has no detrimental effect on glucose metabolism and could ameliorate the lipid profile in type 2 diabetic men. Results of a controlled study. Diabetes Care 21:717–724
Kabir M, Skurnik G, Naour N, Pechtner V, Meugnier E, Rome S, Quignard-Boulange A, Vidal H, Slama G, Clement K, Guerre-Millo M, Rizkalla SW (2007) Treatment for 2 mo with n 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids reduces adiposity and some atherogenic factors but does not improve insulin sensitivity in women with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled study. Am J Clin Nutr 86:1670–1679
WGOC (2004) Guidelines for the prevention and control of overweight and obesity among Chinese adults (Excerpt). Acta Nutrimenta Sinica 26:1–4. doi:10.3321/j.issn:0512-7955.2004.01.001
Popp-Snijders C, Bilo HJ, Heine RJ (1990) Fish oil and glycemic control: importance of dose. Diabetes Care 13:80–81
McVeigh GE, Brennan GM, Johnston GD, McDermott BJ, McGrath LT, Henry WR, Andrews JW, Hayes JR (1993) Dietary fish oil augments nitric oxide production or release in patients with type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 36:33–38
Neil HA, Ceglarek U, Thiery J, Paul S, Farmer A, Holman RR (2010) Impact of atorvastatin and omega-3 ethyl esters 90 on plasma plant sterol concentrations and cholesterol synthesis in type 2 diabetes: a randomised placebo controlled factorial trial. Atherosclerosis 213:512–517. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.09.013
Sirtori CR, Paoletti R, Mancini M, Crepaldi G, Manzato E, Rivellese A, Pamparana F, Stragliotto E (1997) N-3 fatty acids do not lead to an increased diabetic risk in patients with hyperlipidemia and abnormal glucose tolerance. Italian Fish Oil Multicenter Study. Am J Clin Nutr 65:1874–1881
Vessby B, Boberg M (1990) Dietary supplementation with n-3 fatty acids may impair glucose homeostasis in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Intern Med 228:165–171
Puhakainen I, Ahola I, Yki-Jarvinen H (1995) Dietary supplementation with n-3 fatty acids increases gluconeogenesis from glycerol but not hepatic glucose production in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Clin Nutr 61:121–126
Shidfar F, Keshavarz A, Hosseyni S, Ameri A, Yarahmadi S (2008) Effects of omega-3 fatty acid supplements on serum lipids, apolipoproteins and malondialdehyde in type 2 diabetes patients. East Mediterr Health J 14:305–313
Pooya S, Jalali MD, Jazayery AD, Saedisomeolia A, Eshraghian MR, Toorang F (2010) The efficacy of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on plasma homocysteine and malondialdehyde levels of type 2 diabetic patients. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 20:326–331. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2009.04.002
Wong CY, Yiu KH, Li SW, Lee S, Tam S, Lau CP, Tse HF (2010) Fish-oil supplement has neutral effects on vascular and metabolic function but improves renal function in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 27:54–60. doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2009.02869.x
Clark LF, Thivierge MC, Kidd CA, McGeoch SC, Abraham P, Pearson DW, Horgan GW, Holtrop G, Thies F, Lobley GE (2016) Fish oil supplemented for 9 months does not improve glycaemic control or insulin sensitivity in subjects with impaired glucose regulation: a parallel randomised controlled trial. Br J Nutr 115:75–86. doi:10.1017/s0007114515004274
Marsh JB (2003) Lipoprotein metabolism in obesity and diabetes: insights from stable isotope kinetic studies in humans. Nutr Rev 61:363–375
Nestel PJ (1990) Effects of N-3 fatty acids on lipid metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 10:149–167. doi:10.1146/annurev.nu.10.070190.001053
Woodman RJ, Mori TA, Burke V, Puddey IB, Watts GF, Beilin LJ (2002) Effects of purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on glycemic control, blood pressure, and serum lipids in type 2 diabetic patients with treated hypertension. Am J Clin Nutr 76:1007–1015
Yang ZH, Miyahara H, Takemura S, Hatanaka A (2011) Dietary saury oil reduces hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in diabetic KKAy mice and in diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice by altering gene expression. Lipids 46:425–434. doi:10.1007/s11745-011-3553-1
Song Z, Yang L, Shu G, Lu H, Sun G (2013) Effects of the n-6/n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ratio on postprandial metabolism in hypertriacylglycerolemia patients. Lipids Health Dis 12:181. doi:10.1186/1476-511X-12-181
Yang LG, Song ZX, Yin H, Wang YY, Shu GF, Lu HX, Wang SK, Sun GJ (2016) Low n-6/n-3 PUFA ratio improves lipid metabolism, inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial function in rats using plant oils as n-3 fatty acid source. Lipids 51:49–59. doi:10.1007/s11745-015-4091-z
Jain S, Gaiha M, Bhattacharjee J, Anuradha S (2002) Effects of low-dose omega-3 fatty acid substitution in type-2 diabetes mellitus with special reference to oxidative stress—a prospective preliminary study. J Assoc Physicians India 50:1028–1033
Kesavulu MM, Kameswararao B, Apparao C, Kumar EG, Harinarayan CV (2002) Effect of omega-3 fatty acids on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme status in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab 28:20–26
Pedersen H, Petersen M, Major-Pedersen A, Jensen T, Nielsen NS, Lauridsen ST, Marckmann P (2003) Influence of fish oil supplementation on in vivo and in vitro oxidation resistance of low-density lipoprotein in type 2 diabetes. Eur J Clin Nutr 57:713–720. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601602
Pascot A, Lemieux I, Prud’homme D, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, Couillard C, Bergeron J, Lamarche B, Despres JP (2001) Reduced HDL particle size as an additional feature of the atherogenic dyslipidemia of abdominal obesity. J Lipid Res 42:2007–2014
Petersen M, Pedersen H, Major-Pedersen A, Jensen T, Marckmann P (2002) Effect of fish oil versus corn oil supplementation on LDL and HDL subclasses in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 25:1704–1708
Mocking RJ, Assies J, Bot M, Jansen EH, Schene AH, Pouwer F (2012) Biological effects of add-on eicosapentaenoic acid supplementation in diabetes mellitus and co-morbid depression: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 7:e49431. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049431
Haffner SM (2006) Abdominal obesity, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular risk in pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 8:B20–B25
Acknowledgements
Both fish oil and corn oil capsules were manufactured by By-Health Co. (Guangdong, China) according to our requirements. We are indebted to all the people who kindly participated in this study. This study was supported by the Grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81573144), the nutrition research foundation from the Chinese Nutrition Society (No. 201326), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the Graduate Research and Innovation Projects of Colleges in Jiangsu Province (No. KYLX15_0175).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Wang, Y., Zhu, Y. et al. Treatment for 6 months with fish oil-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids has neutral effects on glycemic control but improves dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetic patients with abdominal obesity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Nutr 56, 2415–2422 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1352-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1352-4