Abstract
Background
Both infarct size and microvascular obstruction (MO) assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) are known to be predictors for adverse clinical outcome after ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). We hypothesized that a ratio of MO and infarct size (MO/infarct size) might be an even stronger predictor for outcome after STEMI, which has not been investigated yet.
Methods
STEMI patients reperfused by primary angioplasty (n = 438) within 12 h after symptom onset underwent contrast-enhanced CMR at a median of 3 days (interquartile range [IQR] 2;4) after the index event. MO and infarct size were measured 15 min after intravenous gadolinium injection. Follow-up was conducted after 19 months (IQR 10;27). The primary end point was defined as a composite of death, non-fatal myocardial reinfarction and congestive heart failure (major adverse cardiac events [MACE]).
Results
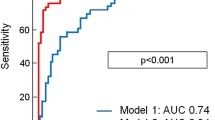
The extent of MO was only weakly correlated with infarct size (r = 0.21, p < 0.001). In a first multivariate analysis including extent of MO, infarct size, ejection fraction, end-systolic and end-diastolic volume, the extent of MO was independently associated with MACE (hazard ratio [HR] 1.03, 95%CI 1.02–1.05, p < 0.001). In a second multivariate analysis including MO/infarct size on top of the extent of MO, infarct size, ejection fraction, end-systolic and end-diastolic volume, MO/infarct size was identified as the strongest independent predictor for MACE (HR 2.22 [95%CI 1.60–3.08, p < 0.001]).
Conclusions
In contrast to infarct size, MO is associated with adverse clinical outcome after STEMI even after adjustment for other CMR parameters. However, MO/infarct size is a more powerful predictor for long-term outcome after STEMI than either parameter alone.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ndrepepa G, Mehilli J, Schulz S, Iijima R, Keta D, Byrne RA, Pache J, Seyfarth M, Schömig A, Kastrati A (2008) Prognostic significance of epicardial blood flow before and after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol 52(7):512–517
TIMI Study Group (1985) The thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) trial: phase 1 findings. N Engl J Med 312:932–936. doi:10.1056/NEJM198504043121435
Schroder R (2004) Prognostic impact of early ST-segment resolution in acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Circulation 110:e506–e510. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000147778.05979.E6
Morrow DA, Antman EM, Charlesworth A, Cairns R, Murphy SA, de Lemos JA, Giugliano RP, McCabe CH, Braunwald E (2000) TIMI risk score for ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a convenient, bedside, clinical score for risk assessment at presentation. Circulation 102:2031–2037. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.102.17.2031
Klug G, Mayr A, Mair J, Schocke M, Nocker M, Trieb T, Jaschke W, Pachinger O, Metzler B (2011) Role of biomarkers in assessment of early infarct size after successful p-PCI for STEMI. Clin Res Cardiol 100(6):501–510. doi:10.1007/s00392-010-0273-0
Neizel M, Futterer S, Steen H, Giannitsis E, Reinhardt L, Lossnitzer D, Lehrke S, Jaffe AS, Katus HA (2009) Predicting microvascular obstruction with cardiac troponin T after acute myocardial infarction: a correlative study with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Res Cardiol 98(9):555–562. doi:10.1007/s00392-009-0041-1
Neizel M, Steen H, Korosoglou G, Lossnitzer D, Lehrke S, Ivandic BT, Katus HA, Giannitsis E (2009) Minor troponin T elevation in patients 6 months after acute myocardial infarction: an observational study. Clin Res Cardiol 98(5):297–304. doi:10.1007/s00392-009-0002-8
Kim RJ, Fieno DS, Parrish TB, Harris K, Chen E-L, Simonetti O, Bundy J, Finn JP, Klocke FJ, Judd RM (1999) Relationship of MRI delayed contrast enhancement to irreversible injury, infarct age, and contractile function. Circulation 100:1992–2002
Rochitte CE, Lima JAC, Bluemke DA, Reeder SB, McVeigh ER, Furuta T, Becker LC, Melin JA (1998) Magnitude and time course of microvascular obstruction and tissue injury after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 98:1006–1014
Schujif JD, Kaandorp TA, Lamb HJ, van der Geest RJ, Viergever EP, van der Wall EE, de Roos A, Bax JJ (2004) Quantification of myocardial infarct size and transmurality by contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Cardiol 94:284–288
Wu KC, Zerhouni EA, Judd RM, Lugo-Olivieri CH, Barouch LA, Schulman SP, Blumenthal RS, Lima JAC (1998) Prognostic significance of microvascular obstruction by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 97:765–772. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.97.8.765
Hombach V, Grebe O, Merkle N, Waldenmaier S, Höher M, Kochs M, Wöhrle J, Kestler HA (2005) Sequelae of acute myocardial infarction regarding cardiac structure and function and their prognostic significance as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Heart J 26:549–557
Cochet AA, Lorgis L, Lalande A, Zeller M, Beer JC, Walker PM, Touzery C, Wolf JE, Brunotte F, Cottin Y (2009) Major prognostic impact of persistent microvascular obstruction as assessed by contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance in reperfused acute myocardial infarction. Eur Radiol 19(9):2117–2126. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1395-5
Larose E, Rodes-Cabau J, Pibarot P, Rinfret S, Proulx G, Nguyen CM, Dery JP, Gleeton O, Roy L, Noel B, Barbeau G, Rouleau J, Boudreault JR, Amyot M, De Larochelliere R, Bertrand OF (2010) Predicting late myocardial recovery and outcomes in the early hours of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction traditional measures compared with microvascular obstruction, salvaged myocardium, and necrosis characteristics by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(22):2459–2469. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.02.033
de Waha S, Desch S, Eitel I, Fuernau G, Zachrau J, Leuschner A, Zachrau J, Schuler G, Thiele H (2010) Impact of early versus late microvascular obstruction assessed by magnetic resonance imaging on long-term outcome after ST-elevation myocardial infarction—a comparison to traditional prognostic markers. Eur Heart J 31(21):2660–2668. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehq247
Niccoli G, Burzotta F, Galiuto L, Crea F (2009) Myocardial no-reflow in humans. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:281–292
Bekkers SC, Yazdani SK, Virmani R, Waltenberger J (2010) Microvascular obstruction: underlying pathophysiology and clinical diagnosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(16):1649–1660. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.12.037
Hombach V, Grebe O, Merkle N, Waldenmaier S, Hoher M, Kochs M, Wohrle J, Kestler HA (2005) Sequelae of acute myocardial infarction regarding cardiac structure and function and their prognostic significance as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Heart J 26(6):549–557. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi147
Antman EM, Anbe DT, Armstrong PW, Bates ER, Green LA, Hand M, Hochman JS, Krumholz HM, Kushner FG, Lamas GA, Mullany CJ, Ornato JP, Pearle DL, Sloan MA, Smith SC (2004) ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction—executive summary. Circulation 110:588–636. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000134791.68010.FA
Van de Werf F, Bax J, Betriu A, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Crea F, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fox K, Huber K, Kastrati A, Rosengren A, Steg PG, Tubaro M, Verheugt F, Weidinger F, Weis M (2008) Management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with persistent ST-segment elevation: The Task Force on the management of ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J 29(23):2909–2945. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehn416
Abdel-Aty H, Zagrosek A, Schulz-Menger J, Taylor AJ, Messroghli D, Kumar A, Gross M, Dietz R, Friedrich MG (2004) Delayed enhancement and T2-weighted cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging differentiate acute from chronic myocardial infarction. Circulation 109:2411–2416. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000127428.10985.C6
Thiele H, Kappl MJ, Conradi S, Niebauer J, Hambrecht R, Schuler G (2006) Reproducibility of chronic and acute infarct size measurement by delayed enhancement magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 47(8):1641–1645. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.11.065
Desch S, Engelhardt H, Meissner J, Eitel I, Sareban M, Fuernau G, de Waha S, Grothoff M, Gutberlet M, Schuler G, Thiele H (2011) Reliability of myocardial salvage assessment by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in acute reperfused myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. doi:10.1007/s10554-011-9802-9 (Epub ahead of print)
Nijveldt R, Beek AM, Hirsch A, Stoel MG, Hofman MBM, Umans VAWM, Algra PR, Twisk JWR, van Rossum AC (2008) Functional recovery after acute myocardial infarction: comparison between angiography, electrocardiography, and cardiovascular magnetic resonance measures of microvascular injury. J Am Coll Cardiol 52(3):181–189
Nijveldt R, Beek AM, Hofman MB, Umans VA, Algra PR, Spreeuwenberg MD, Visser CA, van Rossum AC (2007) Late gadolinium-enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance evaluation of infarct size and microvascular obstruction in optimally treated patients after acute myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 9:765–770
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD, Jaffe AS, Apple FS, Galvani M, Katus HA, Newby LK, Ravkilde J, Chaitman B, Clemmensen PM, Dellborg M, Hod H, Porela P, Underwood R, Bax JJ, Beller GA, Bonow R, Van der Wall EE, Bassand JP, Wijns W, Ferguson TB, Steg PG, Uretsky BF, Williams DO, Armstrong PW, Antman EM, Fox KA, Hamm CW, Ohman EM, Simoons ML, Poole-Wilson PA, Gurfinkel EP, Lopez-Sendon JL, Pais P, Mendis S, Zhu JR, Wallentin LC, Fernandez-Aviles F, Fox KM, Parkhomenko AN, Priori SG, Tendera M, Voipio-Pulkki LM, Vahanian A, Camm AJ, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL, Morais J, Brener S, Harrington R, Morrow D, Lim M, Martinez-Rios MA, Steinhubl S, Levine GN, Gibler WB, Goff D, Tubaro M, Dudek D, Al-Attar N (2007) Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation 116(22):2634–2653. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.187397
Amado LC, Gerber BL, Gupta SN, Rettmann DW, Szarf G, Schock R, Nasir K, Kraitchman DL, Lima JAC (2004) Accurate and objective infarct sizing by contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in a canine myocardial infarction model. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:2383–2389
Orn S, Manhenke C, Greve OJ, Larsen AI, Bonarjee VV, Edvardsen T, Dickstein K (2009) Microvascular obstruction is a major determinant of infarct healing and subsequent left ventricular remodelling following primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Eur Heart J 30(16):1978–1985. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehp219
Reffelmann T, Kloner RA (2002) The “no-reflow” phenomenon: basic science and clinical correlates. Heart 87:162–168
Rogers WJ Jr, Kramer CM, Geskin G, Hu YL, Theobald TM, Vido DA, Petruolo S, Reichek N (1999) Early contrast-enhanced MRI predicts late functional recovery after reperfused myocardial infarction. Circulation 99(6):744–750
Kramer CM, Lima JA, Reichek N, Ferrari VA, Llaneras MR, Palmon LC, Yeh IT, Tallant B, Axel L (1993) Regional differences in function within noninfarcted myocardium during left ventricular remodeling. Circulation 88(3):1279–1288
Wu KC, Kim RJ, Bluemke DA, Rochitte CE, Zerhouni EA, Becker LC, Lima JAC (1998) Quantification and time course of microvascular obstruction by contrast-enhanced echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging following acute myocardial infarction and reperfusion. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:1756–1764. doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(98)00429-X
Dall’Armellina E, Karia N, Lindsay AC, Karamitsos TD, Ferreira V, Robson MD, Kellman P, Francis JM, Forfar C, Prendergast BD, Banning AP, Channon KM, Kharbanda RK, Neubauer S, Choudhury RP (2011) Dynamic changes of edema and late gadolinium enhancement after acute myocardial infarction and their relationship to functional recovery and salvage index. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 4(3):228–236. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.111.963421
Engblom H, Hedstrom E, Heiberg E, Wagner GS, Pahlm O, Arheden H (2009) Rapid initial reduction of hyperenhanced myocardium after reperfused first myocardial infarction suggests recovery of the peri-infarction zone: one-year follow-up by MRI. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2(1):47–55. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.108.802199
Ibrahim T, Hackl T, Nekolla SG, Breuer M, Feldmair M, Schomig A, Schwaiger M (2011) Acute myocardial infarction: serial cardiac MR imaging shows a decrease in delayed enhancement of the myocardium during the 1st week after reperfusion. Radiology 254(1):88–97. doi:10.1148/radiol.09090660
Mather AN, Fairbairn TA, Artis NJ, Greenwood JP, Plein S (2011) Timing of cardiovascular MR imaging after acute myocardial infarction: effect on estimates of infarct characteristics and prediction of late ventricular remodeling. Radiology. doi:10.1148/radiol.11110228
Beek AM, Bondarenko O, Afsharzada F, van Rossum AC (2009) Quantification of late gadolinium enhanced CMR in viability assessment in chronic ischemic heart disease: a comparison to functional outcome. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 11:6. doi:10.1186/1532-429X-11-6
Bondarenko O, Beek AM, Hofman MB, Kuhl HP, Twisk JW, van Dockum WG, Visser CA, van Rossum AC (2005) Standardizing the definition of hyperenhancement in the quantitative assessment of infarct size and myocardial viability using delayed contrast-enhanced CMR. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 7(2):481–485
Flett AS, Hasleton J, Cook C, Hausenloy D, Quarta G, Ariti C, Muthurangu V, Moon JC (2011) Evaluation of techniques for the quantification of myocardial scar of differing etiology using cardiac magnetic resonance. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 4(2):150–156. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2010.11.015
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Waha, S., Desch, S., Eitel, I. et al. Relationship and prognostic value of microvascular obstruction and infarct size in ST-elevation myocardial infarction as visualized by magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Res Cardiol 101, 487–495 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-012-0419-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-012-0419-3