Abstract
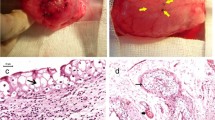
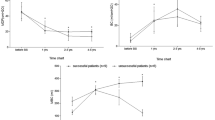
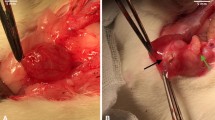
Significant side effects are correlated with bladder augmentation. Recently, small intestinal submucosa (SIS) has been proposed for clinical use. The efficacy of SIS bladder regeneration was studied in a porcine experimental model. Partial cystectomy (40–60% of bladder wall) was performed and replaced by SIS graft. Animals were planned to be killed at 2 weeks, 5 weeks and 3 months. Bladder capacity at 40 cmH2O pressure and macroscopic graft morphology were assessed before and after SIS implant. Histological examination was carried out with computer assisted morphometric analysis for collagen/smooth muscle ratio. Student’s t test was adopted for statistical analysis. Two piglets died on the 9th and 10th post-operative day due to urinary peritonitis. The remaining piglets were killed after uneventful post-operative period at 5 weeks (two animals) and 3 months (two animals). The bladder capacity was reduced (−18%) at the 5 week follow-up and quite similar to the pre-operative volume (+2.5%) at the 3 months control. No diverticular formation, bladder calculi, mucus and urinary infection were found. The SIS graft resulted not significantly contracted. Histology at 10 days showed SIS membrane lined by transitional epithelium islands with some capillaries. At 5 weeks, transitional epithelium was fully covering the graft; new blood vessels and fibroblasts with smooth muscle cells were observed. At 3 months, the SIS was not evident. Two layers were defined: inner transitional epithelium, outer collagen with fibroblasts and muscular bundles. Computer assisted morphometric analysis showed collagen/muscle ratio 70/30% (normal bladder=56/44%, P<0.05). The SIS was effective as a scaffold for bladder wall regeneration in four out of six animals. Long-term studies are required to confirm the efficacy of the newly developed wall and for eventual clinical use.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitchell ME, Gonzales R, Cabral BH, Bauer SB, Gearhart JP, Filmer RB (1987) Bladder augmentation problems in neurovesical dysfunction. Dial Pediatr Urol 10:1
Gleeson MJ, Griffith DP (1992) The use of alloplastic biomaterials in bladder substitution. J Urol 148:1377
Cartwright PC, Snow BW (1989) Bladder autoaugmentation: partial detrusor excision to augment the bladder without the use of bowel. J Urol 142:1050
Kropp BP, Pope JC IV (1997) Small intestinal submucosa: a novel substance for the study of cellular interaction and regeneration in the bladder. Dial Pediatr Urol 20 10:2
Kropp BP, Eppley BL, Prevel CD, Harruff RC, Badylak SF, Adams MC, Rink RC, Keating MA (1994) Experimental assessment of Small Intestine Submucosa as a bladder wall substitute. J Urol 151:501
Kropp BP, Eppley BL, Prevel CD, Harruff RC, Badylak SF, Adams MC, Rink RC, Keating MA (1995) Experimental assessment of Small Intestine Submucosa as a bladder wall substitute. Urology 46(3):396
Pope JC IV, Davis MM, Smith ER Jr, Walsh MJ, Ellison PK, Rink PC, Kropp BP (1997) The ontogeny of canine Small Intestinal Submucosa Regenerated Bladder. J Urol 158(3):1105–1110
Lantz GC, Badylak SF, Coffey AC, Gaddes LA, Sandusky GE (1990) Small Intestinal Submucosa as a small-diameter arterial graft in the dog. J Invest Surg 3:217
Lantz GC, Badylak SF, Coffey AC, Gaddes LA, Sandusky GE (1992) Small Intestinal Submucosa as a superior vena cava graft in the dog. J Surg Res 53:175
Gonzales R, Buson H, Ried C, Reinberg Y (1994) Seromuscolar colocystoplasty lined with urothelium: experimental study. Urology 44:743
Marte A, Di Meglio D, Cotrufo AM, Di Iorio G, De Pasquale M, Vessella A (2002) A long-term follow-up of autoaugmentation in myelodysplastic children. BJU Int 89(9):928
Tizzoni G, Poggi A (1898) Die Wiederherstellung der Harnblase: experimentelle Untersuchungen. Zcentrabl Chir 15:921
Atala A (2004) Tissue engineering for replacement of organ function in the genito-urinary system. Am J Transplant 6(Suppl 4):58–73
Zhang Y, Kropp BP, Lin HK, Cowan R, Cheng EY (2004) Bladder regeneration with cell-seeded small intestinal submucosa. Tissue Eng 10(1–2):181–187
Kropp PM, Lingeman JE, Siegel YL, Badylak SF, Demeter RJ (1994) Biocompatibility fo Small Intestinal Submucosa in urinary tract as augmentation cystoplasty graft and injectable suspension. J Endourol 8:125
Kropp BP, Rippy MK, Balylak SF, Adams MC, Keating MA, Rink RC, Thor KB (1996) Regenerative urinary bladder augmentation using Small Intestinal Submucosa: urodynamic and histopathologic assessment in long-term canine bladder augmentation. J Urol 155(6):2098
Kropp BP, Sawyer BD, Shannon HE, Rippy MK, Balylak SF, Adams MC, Keating MA, Rink RC, Thor KB (1996) Characterization of small intestinal submucosa regenerated canine detrusor: assessment of reinnervation in vitro compliance and contractility. J Urol 156(25):599–607
Vaught JD, Kropp BP, Sawyer BD, Rippy MK, Badylak SF, Shannon HE, Thor KB (1996) Detrusor regeneration in the rat using porcine Small Intestinal Submucosal graft: functional innervation and receptor expression. J Urol 155(1):374–378
O’Conner RC, Patel RV, Steinberg GD (2001) Successful repair of a uretero-neobladder stricture using porcine small intestine submucosa. J Urol 165(6):1995
Paterson RF, Lifshitz DA, Beck SD, Siqueira TM Jr, Cheng L, Lingeman JE, Shalhav AL (2002) Multilayered small intestinal submucosa is inferior to autologous bowel for laparoscopic bladder augmentation. J Urol 168(5):2253–2257
Chung SY, Krivorov NP, Rausei V, Thomas L, Frantzen M, Landsittel D, Kang YM, Chon CH, Christopher S, Fuchs G (2005) Bladder reconstitution with bone marrow derived stem cells seeded on small intestinal submucosa improves morphological and molecular composition. J Urol 174(1):353–359
Rink RC, Kropp BP (2003) Personal communication
Metwalli AR, Colvert Jr III, Kropp BP (2003) Tissue engineering in urology: where are we going? Curr Urol Rep 4(2):156–163
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caione, P., Capozza, N., Zavaglia, D. et al. In vivo bladder regeneration using small intestinal submucosa: experimental study. Ped Surgery Int 22, 593–599 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-006-1705-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-006-1705-9