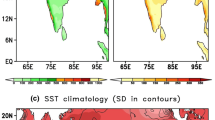
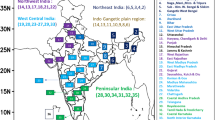
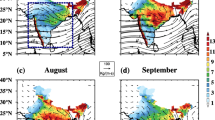
Abstract
The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is an important coupled ocean–atmosphere phenomenon in the tropical Pacific and an important modulator of the spatio-temporal variability of Indian summer monsoon rainfall (ISMR). Here, we explore the impact of ENSO during onset (June), peak (July–August) and withdrawal (September) phases of ISMR for the period 1951–2015, by studying the changes in the ENSO-monsoon relationship from early decades (1951–1980) to recent decades (1986–2015). We observe noticeable changes in the ENSO-monsoon relationship from the early to recent decades during all the three phases. During El Niño events, rainfall over most of the Indian regions is significantly increased in recent decades during onset phase, but a significant decrease in rainfall is observed during peak and withdrawal phases. On the other hand, the rainfall during La Niña events is significantly decreased over the monsoon core zone of India during all the three phases. A significant increase (decrease) in sea surface temperature (SST) is observed over the central equatorial Pacific and Indian Ocean during El Niño (La Niña) events in recent decades. These changes differ from one phase to another and related to the observed rainfall patterns over the Indian region. Apart from these, the changes in the anomalies of low level circulation and Walker circulation over the Indo-Pacific domain are also linked to the changes in rainfall during the ENSO events, with most significant relationship during the onset phase.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annamalai H, Liu P (2005) Response of the Asian summer monsoon to changes in El Niño properties. Q J R Meteorol Soc 131:805–831
Ashok K, Guan Z, Saji NH, Yamagata T (2001) Impact of the Indian Ocean Dipole on the relationship between Indian monsoon rainfall and ENSO. Geophys Res Lett 28:4499–4502
Ashok K, Guan Z, Saji NH, Yamagata T (2004) Individual and combined influences of ENSO and the Indian Ocean Dipole on the Indian summer monsoon. J Clim 17:3141–3155
Ashrit RG, Kumar R, Krishna Kumar K (2001) ENSO-monsoon relationship in a greenhouse warming scenario. Geophys Res Lett 28:1727–1730
Behera SK, Luo JJ, Masson S, Rao SA, Sakuma H (2006) A GCM study on the interaction between IOD and ENSO. J Clim 19:1688–1705
Bjerknes J (1969) Atmospheric teleconnections from the equatorial Pacific. Mon Weather Rev 97:163–172
Chang CP, Harr P, Ju J (2001) Possible roles of Atlantic circulation on the weakening Indian monsoon—ENSO relationship. J Clim 14:2376–2380
Cherchi A, Navarra A (2013) Influence of ENSO and of the Indian Ocean Dipole on the Indian summer monsoon variability. Clim Dyn 41:81–103
Collins M, An SI, Cai W, Ganachaud A, Guilyardi E, Jin FF, Jochum M, Lengaigne M, Power S, Timmermann A, Veccgi G, Wittenberg A (2010) The impact of global warming on the tropical Pacific and El Nino. Nat Geosci 3:391–397
Feba F, Ashok K, Ravichandran M (2018) Role of changed Indo-Pacific atmospheric circulation in the recent disconnect between Indian summer monsoon and ENSO. Clim Dyn 52:1461–1470
Francis PA, Gadgil S (2013) A note on new indices for the equatorial Indian Ocean oscillation. J Earth Syst Sci 122(4):1005–1011
Gadgil S, Francis PA (2016) El Niño and the Indian rainfall in June. Curr Sci 110:1010–1022
Goswami BN, Madhusoodanan MS, Neema CP, Sengupta D (2006) A physical mechanism for North Atlantic SST influence on the Indian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL024803
Guhathakurta P, Rajeevan M (2008) Trends in the rainfall pattern over India. Int J Climatol 28:1453–1469
Guilyardi E (2006) El Niño-mean state-seasonal cycle interactions in a multi model ensemble. Clim Dyn 26:329–348
Harris I, Jones PD, Osbornaand TJ, Listera DH (2014) Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations—the CRU TS3.10 Dataset. Int J Climatol 34:623–642
Hrudya PH, Varikoden H, Vishnu R (2020) A review on the Indian Summer Monsoon rainfall. Variability and their association with ENSO and IOD. Meteorol Atmos Phys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-020-00734-5
Ihara C, Kushnir Y, Cane MA, De La Pena VH (2007) Indian summer monsoon and its link with ENSO and Indian Ocean climate indices. Int J Climatol 27:179–187
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, Collins W, Deaven D, Gandin L, Iredell M, Saha S, Walt G, Woollen J, Zhu Y, Chelliah M, Ebisuzaki W, Higgins W, Janowiak J, Mo KC, Ropelewski C, Wang J, Leetmaa A, Reynolds R, Jenne R, Joseph D (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–471
Kishore P, Jyothi S, Bhasha G, Rao SVB, Rajeevan M, Velicogna I, Sutterley TC (2015) Precipitation climatology over India: validation with observational and reanalysis datasets and spatial trends. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-105-2597-y
Krishna Kumar K, Rajagopalan B, Cane MA (1999) On the weakening relationship between the Indian monsoon and ENSO. Science 284:2156–2159
Krishnaswami J, Vaidyanathan S, Rajagopalan B, Bonnel M, Sankaran M, Bhalla RS, Badiger S (2014) Non-stationary and non-linear influence of ENSO and Indian Ocean Dipole on Indian summer monsoon rainfall and extreme rain events. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2288-0
Kucharski F, Abid A (2018) Interannual variability of the Indian monsoon and its link to ENSO. Oxf Res Encycl Clim Sci. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190228620.013.615
Kumar KK, Rajagopalan B, Hoerling M, Bates G, Cane M (2006) Unraveling the mystery of Indian monsoon failure during El Nino. Science 314:115–119
Mishra V, SmoliakBV Lettenmaier DP, Wallace JM (2012) A prominent pattern of year-to-year variability in Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall. PNAS 109:7213–7217
Mooley DA, Parthasarathy B (1983) Variability of Indian summer monsoon and tropical circulation features. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 111:967–978
Mooley DA, Shukla J (1987) Characteristics of the westward-moving summer monsoon low pressure systems over the Indian region and their relationship with the monsoon rainfall. University of Maryland Center for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Interactions Rep., 47 pp
Nair PJ, Chakraborty A, Varikoden H, Francis PA, Kuttipurath J (2018) The local and global climate forcings induced inhomogeneity of Indian rainfall. Sci Rep 8:6026. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24021-x
Pant GB, Rupakumar K (1997) Climates of South Asia. Wiley, West Sussex, p 320
Parthasarathy B, Pant GB (1985) Seasonal relationships between Indian summer monsoon rainfall and the southern oscillation. J Climatol 5:369–378
Preethi B, Ramya R, Patwardhan SK, Mujumdar M, Kripalani RH (2019) Variability of Indian summer monsoon droughts in CMIP5 climate models. Clim Dyn 53:1937–1962
Rajeevan M, Bhate J, Kale JD, Lal B (2006) High resolution daily gridded rainfall data for the Indian region: analysis of break and active monsoon spells. Curr Sci 91:296–306
Rao YP (1976) Southwest Monsoon. Meteorological Monograph No. 1, India Meteorological Department, New Delhi
Rao SA, Behera SK, Masumoto Y, Yamagata T (2002) Interannual subsurface variability in the Tropical Indian Ocean with a special emphasis on the Indian Ocean Dipole. Deep Sea Res Part II 49:1549–1572
Rasmusson EM, Carpenter TH (1983) The relationship between eastern equatorial Pacific sea surface temperatures and rainfall over India and Sri Lanka. Mon Weather Rev 111:517–528
Rayner NA, Parker DE, Horton EB, Folland CK, Alexander LV, Rowell DP, Kent E, Kaplan A (2003) Global analyzes of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002670
Roy I, Tedeschi RG (2016) Influence of ENSO on regional Indian summer monsoon precipitation—local atmospheric influences or remote influence from Pacific. Atmosphere. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7020025
Roy I (2017) Indian summer monsoon and El Niño Southern Oscillations in CMIP5 models: a few areas of agreement and disagreement. Atmosphere. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8080154
Roy I, Gagnon AS, Siingh D (2019) Evaluating ENSO teleconnections using observations and CMIP5 models. Theor Appl Climatol 136:1085–1098
Saji NH, Goswami BN, Vinayachandran PN, Yamagata T (1999) A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 401:360–363
Sandeep S, Ajayamohan RS, Boos WR, Sabin TP, Praveen V (2018). Decline and poleward shift in Indian summer monsoon synoptic activity in a warming climate. PNAS 115(11):2681–2686
Seetha CJ, Varikoden H, Babu CA, Kuttipurath J (2020) Significant changes in the ENSO-monsoon relationship and associated circulation features on multidecadal timescale. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-05071-x
Sikka DR (1980) Some aspects of the large scale fluctuations of summer monsoon rainfall over India in relation to fluctuations in the planetary and regional scale circulation parameters. Proc Indian Acad Sci Earth Planet Sci 89:179–195
Suthinkumar PS, Babu CA, Varikoden H (2019) Spatial distribution of extreme rainfall events during 2017 Southwest Monsoon over Indian Subcontinent. Pure Appl Geophys 176:5431–5443
Ummenhofer CC, Sen Gupta A, Li Y, Taschetto AS, England MH (2011) Multi-decadal modulation of the El Niño-Indian monsoon relationship by Indian Ocean variability. Environ Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/6/3/034006
Varikoden H, Babu CA (2015) Indian summer monsoon rainfall and its relation with SST in the equatorial Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Int J Climatol 35:1192–1200
Varikoden H, Preethi B (2013) Wet and dry years of Indian summer monsoon and its relation with Indo-Pacific sea surface temperatures. Int J Climatol 33:1761–1771
Varikoden H, Revadekar JV (2019) On the extreme rainfall events during the southwest monsoon season in northeast regions of the Indian subcontinent. Meteorol Appl 27:1–13
Varikoden H, Revadekar JV, Kuttippurath J, Babu CA (2019) Contrasting trends in southwest monsoon rainfall over the Western Ghats region of India. Clim Dyn 52(7–8):4557–4566
Wang B, Wu R, Li T (2003) Atmosphere–warm Ocean interaction and Its Impacts on Asian-Australian monsoon variation. J Clim 16:1195–1211
Webster PJ, Moore AM, Loschnigg JP, Leben RR (1999) Coupled ocean-atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Nature 401:356–360
Xavier PK, Marzin C, Goswami BN (2007) An objective definition of the Indian summer monsoon season and a new perspective on the ENSO-monsoon relationship. Q J R Meteorol Soc 133:749–764
Yamagata T, Behera SK, Luo JJ, Masson S, Jury MR, Rao SA (2004) Coupled ocean-atmosphere variability in the tropical Indian Ocean. Geophys Monogr Ser. https://doi.org/10.1029/147GM12
Yun KS, Timmermann A (2014) Decadal monsoon-ENSO relationships reexamined. Geophys Res Lett 45:2014–2021
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) for providing the necessary facilities and to the Executive Director, Centre for Climate Change Research, IITM for encouragement. The first and third authors are grateful to Sree Krishna College, Guruvayoor for providing facility. The authors also acknowledge the CRU data for the rainfall analysis. We also thank NCEP-NCAR, HadISST data products. The JK is funded by the Department of Science Technology, Climate Change Programme (SPLICE). The CCCR, IITM is fully funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hrudya, P.H., Varikoden, H., Vishnu, R. et al. Changes in ENSO-monsoon relations from early to recent decades during onset, peak and withdrawal phases of Indian summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 55, 1457–1471 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05335-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05335-x