Abstract
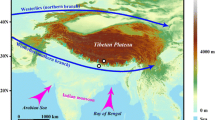
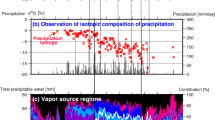
To further our understanding of the Asian monsoon system, particularly the onset dates of monsoon sub-systems over their respective East Asian domains, we present an 8-year (2007–2014) dataset of oxygen isotopes of precipitation (δ18Op) from three stations, Lulang and Nuxia in southeastern Tibetan Plateau (SETP) and Guangzhou in southeastern coastal China (SECN). The general agreement between isotopically identified monsoon onset dates with those identified by the meridional temperature gradient suggests that the initially sustained isotopic depletion is sensitive to the evolving thermal contrast between the Eurasian continent and the Indian Ocean. The 850 hPa meridional wind over nearby oceans is an efficient bridge linking isotopic variations in both regions with their respective monsoon sub-systems. The intensity of the South Asian High and tropical cyclone frequencies show stronger effects on isotopic depletion in the SECN than in the SETP and on monsoon onset timing over the South China Sea. Tibetan Plateau snow cover anomalies are significantly correlated with δ18Op in both regions on monthly timescales.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler RF, Huffman GJ, Chang A, Ferraro R, Xie P, Janowiak J, Rudolf B, Schneider U, Curtis S, Bolvin D, Gruber A, Susskind J, Arkin P, Nelkin E (2003) The version 2 Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979-present). J Hydrometeorol 4:1147–1167
Ananthakrishnan R, Pathan JM, Aralikatti SS (1983) The onset phase of the Southwest monsoon. Curr Sci India 52(16):755–764
Araguas-Araguas L, Froehlich K, Rozanski K (1998) Stable isotope composition of precipitation over southeast Asia. J Geophys Res Atmos 103(D22):28721–28742
Araguas-Araguas L, Froehlich K, Rozanski K (2000) Deuterium and oxygen-18 isotope composition of precipitation and atmospheric moisture. Hydrol Process 14(8):1341–1355
Banacos PC, Schultz DM (2005) The use of moisture flux convergence in forecasting convective initiation: historical and operational perspectives. Weather Forecast 20(3):351–366
Benetti M et al (2014) Deuterium excess in marine water vapor: dependency on relative humidity and surface wind speed during evaporation. J Geophys Res Atmos 119(2):584–593
Boos WR, Storelvmo T (2016) Near-linear response of mean monsoon strength to a broad range of radiative forcings. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(6):1510–1515
Cai ZY, Tian LD (2016) Atmospheric controls on seasonal and interannual variations in the precipitation isotope in the East Asian monsoon region. J Climate 29(4):1339–1352
Clark I, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. Lewis Publishers, Ann Arbor
Conroy JL, Overpeck JT (2012) Regionalization of present-day precipitation in the greater monsoon region of Asia (vol 24, pg 4073, 2011). J Climate 25(2):815–817
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16(4):436–468
Froehlich K et al (2008) Deuterium excess in precipitation of Alpine regions—moisture recycling. Isot Environ Health Stud 44(1):61–70
Gao J et al (2011) Precipitation water stable isotopes in the South Tibetan Plateau: observations and modeling. J Climate 24(13):3161–3178
Gat JR et al (1996) The stable isotope composition of waters of the eastern Mediterranean Sea. J Geophys Res Oceans 101(C3):6441–6451
Gat JR (2005) Some classical concepts of isotope hydrology:”Rayleigh fractionation, Meteoric Water Lines, the Dansgaard effects (altitude, latitude, distance from coast and amount effects) and the dexcess parameter”. In: Aggarwal PK, Gat JR, Froehlich K.F.O. (eds) Isotopes in the Water Cycle:, Present and Future of a Developing Science. IEA, Amsterdam, pp 127–137
Godfred-Spenning CR, Reason CJC (2002) Interannual variability of lower-tropospheric moisture transport during the Australian monsoon. Int J Climatol 22(5):509–532
Goswami BN, Jayavelu V (2001) On possible impact of the Indian summer monsoon on the ENSO. Geophys Res Lett 28(4):571–574
Goswami BN, Krishnamurthy V, Annamalai H (1999) A broad-scale circulation index for the interannual variability of the Indian summer monsoon. Q J Roy Meteor Soc 125(554):611–633
Guo QY (1983) The summer monsoon intensity index in East Asia and its variation. Acta Geogr Sin 38(3):11
Hartmann DL et al (2013) Observations: Atmosphere and Surface. In: Stocker TF et al (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Constribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Integovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
IPCC (2013) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. In: Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York, NY, pp 1535
Johnson KR, Ingram BL (2004) Spatial and temporal variability in the stable isotope systematics of modern precipitation in China: implications for paleoclimate reconstructions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 220(3–4):365–377
Kalnay E et al (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. B Am Meteorol Soc 77(3):437–471
Kim MJ, Yeh SW, Park RJ (2016) Effects of sulfate aerosol forcing on East Asian summer monsoon for 1985–2010. Geophys Res Lett 43(3):1364–1372
Konwar M, Parekh A, Goswami BN, 2012. Dynamics of east-west asymmetry of Indian summer monsoon rainfall trends in recent decades. Geophys Res Lett, 39
Kurita N (2013) Water isotopic variability in response to mesoscale convective system over the tropical ocean. J Geophys Res Atmos 118(18):10376–10390
Lau KM, Yang S (1996) Seasonal variation, abrupt transition, and intraseasonal variability associated with the Asian summer monsoon in the GLA GCM. J Climate 9(5):965–985
Liu YM et al (2012) Revisiting Asian monsoon formation and change associated with Tibetan Plateau forcing: II. Change. Clim Dyn 39(5):1183–1195
Liu ZF, Tian L, Yao TD, Yu WS (2008) Seasonal deuterium excess in Nagqu precipitation: influence of moisture transport and recycling in the middle of Tibetan Plateau. Environ Geol 55(7):1501–1506
Liu YM, Wu GX (2004) Progress in the study on the formation of the summertime subtropical anticyclone. Adv Atmos Sci 21(3):322–342
Liu BQ, Wu GX, Mao JY, He JH (2013) Genesis of the South Asian High and its impact on the Asian Summer monsoon onset. J Climate 26(9):2976–2991
Liu BQ, Zhu CW (2016) A possible precursor of the South China Sea summer monsoon onset: Effect of the South Asian High. Geophys Res Lett 43(20):11072–11079
Liu JR, Song XF, Yuan GF, Sun XM, Yang LH, 2014. Stable isotopic compositions of precipitation in China. Tellus Ser B Chem Phys Meteorol 66:22567
Mao JY, Chan JCL, Wu GX (2011) Interannual variations of early summer monsoon rainfall over South China under different PDO backgrounds. Int J Climatol 31(6):847–862
Moore M, Kuang Z, Blossey PN (2014) A moisture budget perspective of the amount effect. Geophys Res Lett 41(4):1329–1335
Parthasarathy B, Kumar KR, Kothawale DR (1992) Indian-Summer Monsoon Rainfall Indexes—1871–1990. Meteorol Mag 121(1441):174–186
Pu ZX, Xu L (2009) MODIS/Terra observed snow cover over the Tibet Plateau: distribution, variation and possible connection with the East Asian Summer Monsoon (EASM). Theor Appl Climatol 97(3–4):265–278
Qian W, Yang S (2000) Onset of the regional monsoon over Southeast Asia. Meteorol Atmos Phys 75(1–2):29–38
Rajeevan M (2002) Winter surface pressure anomalies over Eurasia and Indian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 29(10):1454. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2001GL014363
Risi C, Bony S, Vimeux F (2008) Influence of convective processes on the isotopic composition (delta O-18 and delta D) of precipitation and water vapor in the tropics: 2. Physical interpretation of the amount effect. J Geophys Res Atmos 113:D19
Robinson DA, Estilow TW, Program NC, 2012. NOAA climate data record (CDR) of Northern Hemisphere (NH) snow cover extenet (SCE), version 1: Eurasia monthly. NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville
Sengupta S, Sarkar A (2006) Stable isotope evidence of dual (Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal) vapour sources in monsoonal precipitation over north India. Earth Planet Sci Lett 250(3–4):511–521
Shen SSP et al (2015) Characteristics of the Tibetan Plateau snow cover variations based on daily data during 1997–2011. Theor Appl Climatol 120(3–4):445–453
Singh D (2016) Tug of war on rainfall changes. Nat Clim Change 6:20–22
Tian L, Masson-Delmotte V, Stievenard M, Yao T, Jouzel J (2001) Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon northward extent revealed by measurements of water stable isotopes. J Geophys Res Atmos 106(D22):28081–28088
Trenberth KE (2011) Changes in precipitation with climate change. Climate Res 47(1–2):123–138
Wallace JM, Hobbs PV (1977) Atmospheric sciences: an introductory survey. Academic Press, New York
Wang B, Fan Z (1999) Choice of south Asian summer monsoon indices. B Am Meteorol Soc 80(4):629–638
Wang B, Kang IS, Lee JY (2004b) Ensemble simulations of Asian-Australian monsoon variability by 11 AGCMs. J Climate 17(4):803–818
Wang B, LinHo LH (2002) Rainy season of the Asian-Pacific summer monsoon. J Climate 15(4):386–398
Wang B, LinHo LH, Zhang YS, Lu MM (2004a) Definition of South China Sea monsoon onset and commencement of the East Asia summer monsoon. J Climate 17(4):699–710
Webster PJ, Yang S (1992) Monsoon and Enso - Selectively Interactive Systems. Q J Roy Meteor Soc 118(507):877–926
Wu GX et al (2011) Vortex genesis over the Bay of Bengal in spring and its role in the onset of the Asian Summer Monsoon. Sci China Earth Sci 54(1):1–9
Wu GX, He B, Liu YM, Bao Q, Ren RC (2015) Location and variation of the summertime upper-troposphere temperature maximum over South Asia. Clim Dyn 45(9–10):2757–2774
Wu RG, Kirtman BP (2007) Observed relationship of spring and summer East Asian rainfall with winter and spring Eurasian snow. J Climate 20(7):1285–1304
Wu ZW, Li JP, Jiang ZH, Ma TT (2012) Modulation of the Tibetan plateau snow cover on the ENSO teleconnections: from the East Asian summer monsoon perspective. J Climate 25(7):2481–2489
Wu GX, Liu BQ (2014) Roles of forced and inertially unstable convection development in the onset process of Indian summer monsoon. Sci China Earth Sci 57(7):1438–1451
Wu GX, Zhang YS (1998) Tibetan Plateau forcing and the timing of the monsoon onset over South Asia and the South China Sea. Mon Weather Rev 126(4):913–927
Wushiki H, et al (1993) Isotope hydrological features of the Tarim Basin, China. In: Proceedings of the Japan-China international symposion on the study of the mechanism of desertification. Tsukuba, p. 380ff
Xavier PK, Marzin C, Goswami BN (2007) An objective definition of the Indian summer monsoon season and a new perspective on the ENSO-monsoon relationship. Q J Roy Meteor Soc 133(624):749–764
Xie L, Yan TZ, Pietrafesa LJ, Karl T, Xu XD (2005) Relationship between western North Pacific typhoon activity and Tibetan Plateau winter and spring snow cover. Geophys Res Lett 32(16)
Xu BQ et al. (2009) Black soot and the survival of Tibetan glaciers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(52): 22114–22118
Yang S (1996) ENSO-snow-monsoon associations and seasonal-interannual predictions. Int J Climatol 16(2):125–134
Yang XX et al (2012b) Isotopic signal of earlier summer monsoon onset in the Bay of Bengal. J Climate 25(7):2509–2516
Yang XX, Xu BQ, Yang W, Qu DM (2012a) The Indian monsoonal influence on altitude effect of delta O-18 in surface water on southeast Tibetan Plateau. Sci China Earth Sci 55(3):438–445
Yang XX, Yao TD, Yang WL, Yu WS, Qu DM (2011) Co-existence of temperature and amount effects on precipitation delta O-18 in the Asian monsoon region. Geophys Res Lett 38:L21809. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2011GL049353
Yao TD et al (2013) A review of climatic controls on delta O-18 in precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: observations and simulations. Rev Geophys 51(4):525–548
Yim SY, Jhun JG, Lu RY, Wang B (2010) Two distinct patterns of spring Eurasian snow cover anomaly and their impacts on the East Asian summer monsoon. J Geophys Res Atmos 115:D22113. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2010JD013996
Yoshimura K, Kanamitsu M, Dettinger M (2010) Regional downscaling for stable water isotopes: a case study of an atmospheric river event. J Geophys Res Atmos:115
Yu WS et al (2016) Short-term variability in the dates of the Indian monsoon onset and retreat on the southern and northern slopes of the central Himalayas as determined by precipitation stable isotopes. Clim Dyn 47(1–2):159–172
Yurtsever E, Moreshead J, Shillady D (1975) Semiempirical natural orbital analysis of bonding and rotational energy barrier in cyclopropylmethyl cation. Chem Phys Lett 36(3):365–368
Zhou TJ et al (2009) The CLIVAR C20C project: which components of the Asian-Australian monsoon circulation variations are forced and reproducible? Clim Dyn 33(7–8):1051–1068
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 41571074), the “International S&T Cooperation Program of China” (Grant No. 2015DFG22720) and the “Key Research Programs in Frontier Sciences” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. QYZDY-SSW-DQC003). The isotopic data in daily precipitation and corresponding amount used in this study are available at the Third Pole Environment Database (http://en.tpedatabase.cn/portal/index.jsp). X.Yang acknowledges the support of China Scholarship Council for the stay at Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center, the OSU, and appreciates the staffs at the field observation stations for their cooperation in precipitation sampling and record-keeping.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Davis, M.E., Acharya, S. et al. Asian monsoon variations revealed from stable isotopes in precipitation. Clim Dyn 51, 2267–2283 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-4011-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-4011-4