Abstract
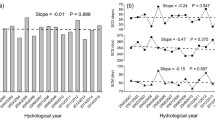
Based on the snow cover fraction (SCF) data acquired from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on the NASA Terra spacecraft from 2000–2006, statistical analyses are performed to explore the spatial and temporal distribution and variation of the snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau (TP). It is found that the snow persistence over the TP varies in different elevation ranges generally becomes longer with increases in the terrain elevation. In addition, the spatial distribution of the snow cover not only depends on the elevation but also varies with terrain features, such as aspect, slope, and curvature in the local areas. With 7-year observational data, seasonal and interannual variability of snow cover has been detected. There are slight decreasing trends in SFCs from 2000–2006. With MODIS satellite snow-cover fraction data and the National Centers for Environmental Predictions and U.S. Department of Energy NCEP/DOE reanalysis II dataset, the relationship between snow cover anomalies over the TP and the East Asian Summer Monsoon (EASM) is examined. Results indicate that the onset of the EASM is closely associated with snow cover anomalies in the spring. Specifically, a positive (negative) snow cover anomaly is followed by a later (earlier) onset of the EASM.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong RL, Brodzik MJ (2001) Validation of passive microwave snow algorithms. Remote Sensing Hydrology (pp 87–93), [Proceeding of a symposium held at Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA, April 2000], IAHS Publ. no. 267
Bamzai AS, Shukla J (1999) Relation between Eurasian snow cover, snow depth, and the Indian summer monsoon: an observational study. J Climate 12:3117–3132
Blanford HF (1884) On the connection of the Himalayan snowfall with dry winds and seasons of drought in India. Proc R Soc Lond 37:3–22
Chang A, Foster JL, Hall DK (1987) Nimbus-7 SMMR-derived global snow cover parameters. Ann Glaciol 9:39–44
Chang A, Foster JL, Hall DK, Powell HW, Chien YL (1990) Nimbus-7 SMMR-derived global snow cover and snow depth data set. The Pilot Land Data System. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD, p 40
Che T, Li X, Gao F (2004) Estimation of snow water equivalent in the Tibetan Plateau using passive microwave remote sensing data (SSM/ I) (In Chinese). J Glaciol Geocryol 26:363–368
Cohen J, Rind D (1991) The effect of snow cover on the climate. J Climate 4:689–706
Dey B, Kathuria SN, Kumar OB (1985) Himalayan summer snow cover and withdrawal of the Indian summer monsoon. J Appl Meteor 24:865–868
Dickson RR (1984) Eurasian snow cover versus Indian monsoon rainfall—an extension of the Hahn–Shukla results. J Appl Meteor 23:171–173
Ding Y (1993) Monsoons over China. Kluwer Academic Publishers, p 432
Frei A, Robinson DA (1999) Northern hemisphere snow extent: regional variability 1972–1994. Inter J Climatol 19:1535–1560
Guo Y, Zhai P, Li W (2004) Snow cover in China, derived from NOAA Satellite Remote Sensing and Conventional Observation (In Chinese). J Glaciol Geocryol 26:755–760
Hahn DG, Shukla J (1976) An apparent relationship between Eurasian snow cover and Indian monsoon rainfall. J Atmos Sci 33:2461–2462
Hall DK et al (2001) Development of technique to assess snow cover mapping errors from space. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 39:432–438
Hall DK et al (2002a) MODIS snow cover products. Remote Sens Environ 83:181–194
Hall DK, Kelly REJ, Riggs GA, Chang ATC, Foster JL (2002b) Assessment of the relative accuracy of hemispheric-scale snow-cover maps. Ann Glaciol 34:24–30
Huffman GJ (2007) README for accessing experimental real-time TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA-RT) data set. [Available online at ftp://trmmopen.gsfc.nasa.gov/pub/merged/3B4XRT_README.]
Jin M (2006) MODIS observed seasonal and interannual variations of atmospheric conditions associated with hydrological cycle over Tibetan Plateau. Geophys Res Lett 33:L19707. doi:10.1029/2006GL026713
Kanamitsu M, Ebisuzaki W, Woollen J, Yang S, Hnilo JJ, Fiorino M, Potter GL (2002) NCEP–DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis (R-2). Bull Am Meteorol 83:1631–1643
Kripalani RH, Kulkarni A (1999) Climatology and variability of historical Soviet snow depth data: some new perspectives in snow—Indian monsoon teleconnections. Climate Dyn 15:475–489
Li P-J (1993) Characteristics of snow cover in western China (In Chinese). Acta Geograph Sin 48:505–514
Li J, Zhang L (2008) Wind onset and withdrawal of Asian summer monsoon and their simulated performance in AMIP models. Climate Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0465-8
Moore GWK (2004) Mount Everest snow plume: a case study. Geophys Res Lett 31:L22102. doi:10.1029/2004GL021046
Parthasarathy B, Yang S (1995) Relationships between regional Indian summer monsoon rainfall and Eurasian snow cover. Adv Atmos Sci 12:143–150
Pu Z, Xu L, Salomonson V (2007) MODIS/Terra observed seasonal variations of snow cover over the Tibet Plateau. Geophys Res Lett 34:L06706. doi:10.1029/2007GL029262
Qin D, Liu S, Li P (2006) Snow cover distribution, variability and response to climate change in western china. J Climate 19:1820–1833
Qu J, Gao W, Kafatos M, Murphy R, Salomonson V (2006) Earth Science Satellite Remote Sensing: Vol. I: science and instruments. Tsinghua University Press and Springer, p 500
Riggs GA, Hall DK, Salomonson VV (2003) MODIS Snow Products User Guide. [Available online at http://www.modis-snow-ice.gsfc.nasa.gov]
Sankar-Rao M, Lau K-M, Yang S (1996) On the relationship between Eurasian snow cover and the Asian summer monsoon. Int J Climatol 16:605–616
Walker GT (1910) Correlation in seasonal variation of weather 11. Mem Ind Meteor Dept 21:22–45
Walland DJ, Simmonds I (1997) Modeled atmospheric response to changes in Northern hemisphere snow cover. Climate Dyn 13:25–34
Wang B (2006) The Asian monsoon. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 373–397
Wang B, Fan Z (1999) Choice of South Asian summer monsoon indices. Bull Am Meteorol Sci 80:629–638
Wang B, Wu R, Lau K-M (2001) Interannual variability of Asian summer monsoon: contrast between the Indian and western North Pacific-East Asian Monsoons. J Climate 14:4073–4090
Wu T-W, Qian Z (2003) The relationship between the Tibetan winter snow and the Asian summer monsoon and rainfall: an observational investigation. J Climate 16:2038–2051
Yanai M, Li C, Song Z (1992) Seasonal heating of the Tibetan Plateau and its effects on the evolution of the Asian summer monsoon. J Atmos Sci 57:2374–2396
Yang S (1996) ENSO-snow-monsoon associations and seasonal-interannual predictions. Int J Climatol 16:125–134
Yeh T-C, Gao YX, Tang MC, Luo SW, Shen CB, Gao DY, Song ZS, Qian YF, Yuan FM, Li GQ, Ding YH, Chen ZT, Zhou MY, Yang KJ, Wang QQ (1979) Meteorology of Qinhai- Xizhang (Tibetan) Plateau (in Chinese). Science Press, Beijing, p 300
Zhang L, Li J (2007) Seasonal rotation features of wind vectors and application to evaluate monsoon simulations in AMIP Models. Climate Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-007-0327-9
Zhang S, Tao S (2001) Influence of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau on Asian summer monsoon (in Chinese). Chin J Atmos Sci 25:372–390
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Jianping Li and two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and reviews. The authors also would like to thank Drs. Vincent Salomonson, James Steenburgh, and Jan Paegle for their valuable comments that greatly improved the first manuscript of this paper. The MODIS snow data used in this study are obtained from the National Snow and Ice Data Center (http://nsidc.org).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, Z., Xu, L. MODIS/Terra observed snow cover over the Tibet Plateau: distribution, variation and possible connection with the East Asian Summer Monsoon (EASM). Theor Appl Climatol 97, 265–278 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-008-0074-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-008-0074-9