Abstract
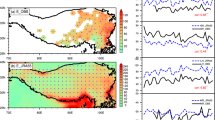
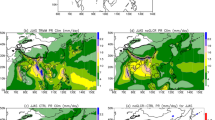
Data analysis based on station observations reveals that many meteorological variables averaged over the Tibetan Plateau (TP) are closely correlated, and their trends during the past decades are well correlated with the rainfall trend of the Asian summer monsoon. However, such correlation does not necessarily imply causality. Further diagnosis confirms the existence of a weakening trend in TP thermal forcing, characterized by weakened surface sensible heat flux in spring and summer during the past decades. This weakening trend is associated with decreasing summer precipitation over northern South Asia and North China and increasing precipitation over northwestern China, South China, and Korea. An atmospheric general circulation model, the HadAM3, is employed to elucidate the causality between the weakening TP forcing and the change in the Asian summer monsoon rainfall. Results demonstrate that a weakening in surface sensible heating over the TP results in reduced summer precipitation in the plateau region and a reduction in the associated latent heat release in summer. These changes in turn result in the weakening of the near-surface cyclonic circulation surrounding the plateau and the subtropical anticyclone over the subtropical western North Pacific, similar to the results obtained from the idealized TP experiment in Part I of this study. The southerly that normally dominates East Asia, ranging from the South China Sea to North China, weakens, resulting in a weaker equilibrated Sverdrup balance between positive vorticity generation and latent heat release. Consequently, the convergence of water vapor transport is confined to South China, forming a unique anomaly pattern in monsoon rainfall, the so-called “south wet and north dry.” Because the weakening trend in TP thermal forcing is associated with global warming, the present results provide an effective means for assessing projections of regional climate over Asia in the context of global warming.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe M, Kitoh A, Yasunari T (2003) An evolution of the Asian summer monsoon associated with mountain uplift—simulation with the MRI atmosphere-ocean coupled GCM. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 81(5):909–933. doi:10.2151/jmsj.81.909
Anderson DM, Overpeck JT, Gupta AK (2002) Increase in the Asian southwest monsoon during the past four centuries. Science 297(5581):596–599. doi:10.1126/science.1072881
Cox PM, Betts RA, Bunton CB, Essery RLH, Rowntree PR, Smith J (1999) The impact of new land surface physics on the GCM simulation of climate and climate sensitivity. Clim Dyn 15(3):183–203. doi:10.1007/s003820050276
Cusack S, Edward JM, Crowther JM (1999) Investigating k-distribution methods for parameterizing gaseous absorption in the Hadley Centre climate model. J Geophys Res 104(D2):2051–2057. doi:10.1029/1998JD200063
Dong BW, Sutton RT, Jewson SP, Neill AO, Slingo JM (2000) Predictable winter climate in the North Atlantic sector during the 1997–1999 ENSO cycle. Geophys Res Lett 27(7):985–988. doi:10.1029/1999GL010994
Duan A, Wu G (2008) Weakening trend in the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Part I: observations. J Clim 21(13):3149–3164. doi:10.1175/2007JCLI1912.1
Duan A, Wu G (2009) Weakening trend in the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Part II: connection with climate warming. J Clim 22(15):4197–4212. doi:10.1175/2009JCLI2699.1
Duan A, Wu G, Zhang Q, Liu Y (2006a) New proofs of the recent climate warming over the Tibetan Plateau as a result of the increasing greenhouse gases emissions. Chin Sci Bull 51(11):1396–1400. doi:10.1007/s11434-006-1396-6
Duan K, Yao T, Thompson LG (2006b) Response of monsoon precipitation in the Himalayas to global warming. J Geophys Res 111:D19110. doi:10.1029/2006JD007084
Edwards JM, Slingo A (1996) Studies with a flexible new radiation code. I: choosing a configuration for a large-scale model. Q J R Meteor Soc 122(531):689–719. doi:10.1002/qj.49712253107
Flohn H (1957) Large-scale aspects of the “summer monsoon” in South and East Asia. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 75:180–186
Fu C, Fletcher JO (1985) The relationship between Tibet-tropical ocean thermal contrast and interannual variability of Indian monsoon rainfall. J Appl Meteorol 24(8):841–847. doi:10.1175/1520-0450(1985)024<0841:TRBTTO>2.0.CO;2
Gregory D (1995) A consistent treatment of the evaporation of rain and snow for use in large-scale models. Mon Weather Rev 123(9):2716–2732. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1995)123<2716:ACTOTE>2.0.CO;2
Gregory D, Allen S (1991) The effect of convective scale downdrafts upon NWP and climate simulations. In: Ninth conf on numerical weather prediction, Denver, CO. Am Meteor Soc, pp 122–123
Gregory D, Morris D (1996) The sensitivity of climate simulations to the specification of mixed phase clouds. Clim Dyn 12(9):641–651. doi:10.1007/BF00216271
Gregory D, Rowntree PR (1990) A mass flux convection scheme with representation of cloud ensemble characteristics and stability-dependent closure. Mon Weather Rev 118(7):1483–1506. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1990)118<1483:AMFCSW>2.0.CO;2
Hoskins BJ (1991) Towards a PV-θ view of the general circulation. Tellus 43(4):27–35. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0870.1991.t01-3-00005.x
Hoskins BJ, McIntyre ME, Robertson AW (1985) On the use and significance of isentropic potential vorticity maps. Q J R Meteorol Soc 111:877–946
Hsu HH, Liu X (2003) Relationship between the Tibetan Plateau heating and East Asian summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 30(20):2066. doi:2010.1029/2003GL017909
Hulme M, Osborn TJ, Johns TC (1998) Precipitation sensitivity to global warming: comparison of observations with HadCM2 simulations. Geophys Res Lett 25(17):3379–3382. doi:10.1029/98GL02562
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2001) Climate change 2001: the scientific basis—contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge Univ Press, Cambridge and New York, p 881
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis—contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge Univ Press, Cambridge and New York, p 996
Kitoh A (2002) Effect of large-scale mountains on surface climate—a coupled ocean-atmosphere general circulation model study. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 80(5):1165–1181. doi:10.2151/jmsj.80.1165
Kitoh A (2004) Effects of mountain uplift on East Asian summer climate investigated by a coupled atmosphere-ocean GCM. J Clim 17(4):783–802. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0783:EOMUOE>2.0.CO;2
Lau WKM, Kim MK, Kim KM, Lee WS (2010) Enhanced surface warming and accelerated snow melt in the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau induced by absorbing aerosols. Environ Res Lett 5:025204
Li C, Yanai M (1996) The onset and interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon in relation to land-sea thermal contrast. J Clim 9:358–375
Li H, Dai A, Zhou T, Lu J (2010) Responses of East Asian summer monsoon to historical SST and atmospheric forcing during 1950–2000. Clim Dyn 34(4):501–514. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0482-7
Liang XY, Liu YM, Wu GX (2006) Roles of tropical and subtropical land-sea distribution and the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in the formation of the Asian summer monsoon. Chin J Geophys-Ch 49(4):983–992 (in Chinese)
Liu X, Chen B (2000) Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Int J Climatol 20(14):1729–1742. doi:10.1002/1097-0088(20001130)20:14<1729:AID-JOC556>3.0.CO;2-Y
Liu X, Yin ZY (2002) Sensitivity of East Asian monsoon climate to the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl 183(3–4):223–245. doi:10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00488-6
Liu Y, Wu G, Ren R (2004) Relationship between the subtropical anticyclone and diabatic heating. J Clim 17(4):682–698. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0682:RBTSAA>2.0.CO;2
Martin GM (1999) The simulation of the Asian summer monsoon, and its sensitivity to horizontal resolution, in the UK meteorological office unified model. Q J R Meteor Soc 125(557):1499–1525. doi:10.1002/qj.49712555703
Martin GM, Arpe K, Chauvin F, Ferranti L, Maynard K, Polcher J, Stephenson DB, Tschuck P (2000) Simulation of the Asian summer monsoon in five European general circulation models. Atmos Sci Lett 1(1):37–55. doi:10.1006/asle.2000.0004
Meehl GA (1994) Influence of the land surface in the Asian summer monsoon: external conditions versus internal feedbacks. J Clim 7(7):1033–1049. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1994)007<1033:IOTLSI>2.0.CO;2
Meehl GA, Washington WM (1993) South Asia summer monsoon variability in a model with doubled atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration. Science 260(5111):1101–1104. doi:10.1126/science.260.5111.1101
Meehl GA, Washington WM, Erickson DJ III, Briegleb BP, Jaumann PJ (1996) Climate change from increased CO2 and direct and indirect effects of sulfate aerosols. Geophys Res Lett 23(25):3755–3758. doi:10.1029/96GL03478
Pope VD, Gallani ML, Rowntree PR, Stratton RA (2000) The impact of new physical parameterizations in the Hadley Centre climate model: HadAM3. Clim Dyn 16(2–3):123–146. doi:10.1007/s003820050009
Qiu J (2008) China: the third pole. Nature 454(24):393–396. doi:10.1038/454393a
Ramanathan V, Carmichael G (2008) Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat Geosci 1:221. doi:10.1038/ngeo156
Ramanathan V et al (2005) Atmospheric brown clouds: impacts on South Asian climate and hydrologic cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5326
Rayner NA, Parker DE, Horton EB, Folland CK, Alexander LV, Rowell DP, Kent EC, Kaplan A (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res 108(D14):4407. doi:10.1029/2002JD002670
Sellers P, Randall D, Collatz G, Berry J, Field C, Dazlich D, Zhang C, Collelo G, Bounoua L (1996) A revised land surface parameterization (SiB2) for atmospheric GCMs. Part I: model formulation. J Clim 9(4):676–705
Senior CA, Mitchell JFB (1993) Carbon dioxide and climate: the impact of cloud parameterization. J Clim 6(3):393–418. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1993)006<0393:CDACTI>2.0.CO;2
Simmonds I, Bi D, Hope P (1999) Atmospheric water vapor flux and its association with rainfall over China in summer. J Clim 12(5):1353–1367. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012<1353:AWVFAI>2.0.CO;2
Smith RNB (1990) A scheme for predicting layer clouds and their water content in a general circulation model. Q J R Meteor Soc 116(492):435–460. doi:10.1002/qj.49711649210
Tao SY, Chen LX (1987) A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon in China. In: Chang CP, Krishnamurti TN (eds) Review of monsoon meteorology. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 60–92
Thorpe AJ (1985) Diagnosis of balanced vortex structure using potential vorticity. J Atmos Sci 42:97–406
Wang B, Bao Q, Hoskins B, Wu G, Liu Y (2008) Tibetan Plateau warming and precipitation changes in East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 35:L14702. doi:10.1029/2008GL034330
Wu G, Liu Y (2000) Thermal adaptation, overshooting, dispersion, and subtropical anticyclone Part I: thermal adaptation and overshooting. Chin J Atmos Sci 24(4):433–446 (in Chinese)
Wu TW, Qian ZA (2003) The Relation between the Tibetan winter snow and the Asian summer monsoon and rainfall: an observational investigation. J Clim 16(12):2038–2051
Wu G, Zhang Y (1998) Tibetan Plateau forcing and the timing of the monsoon onset over South Asia and the South China Sea. Mon Weather Rev 126(4):913–927. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1998)126<0913:TPFATT>2.0.CO;2
Wu GX, Li W, Guo H, Liu H, Xue J, Wang Z (1997) Sensible heat driven air-pump over the Tibetan Plateau and its impacts on the Asian summer monsoon. In: Ye DZ (ed) Collections on the memory of Zhao Jiuzhang. Chinese Science Press, Beijing, pp 116–126
Wu G, Liu Y, Wang T, Wan R, Liu X, Li W, Wang Z, Zhang Q, Duan A, Liang X (2007) The influence of the mechanical and thermal forcing of the Tibetan Plateau on the Asian climate. J Hydrometeorol 8(4):770–789. doi:10.1175/JHM609.1
Wu GX, Liu Y, Zhu X, Li W, Ren R, Duan A, Liang X (2009) Multi-scale forcing and the formation of subtropical desert and monsoon. Ann Geophys 27(9):3631–3644. doi:10.5194/angeo-27-3631-2009
Wu G, Liu Y, Liang X, Duan A, Bao Q, Yu J (2012) Revisiting Asian monsoon formation and change associated with Tibetan Plateau forcing—I. Formation. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1334-z
Xu M, Chang CP, Fu C, Qi Y, Robock A, Robinson D, Zhang H (2006) Steady decline of East Asian monsoon winds, 1969–2000: evidence from direct ground measurements of wind speed. J Geophys Res 111:D24111. doi:10.1029/2006JD007337
Yanai M, Wu GX (2006) Effects of the Tibetan Plateau. In: Wang B (ed) The Asian monsoon. Springer, Berlin, pp 513–549. doi:10.1007/3-540-37722-0-13
Yang K, Qin J, Guo X, Zhou D, Ma Y (2009) Method development for estimating sensible heat flux over the Tibetan Plateau from CMA data. J Appl Meteor Climatol 48(12):2474–2486
Yang K, Guo X, He J, Qin J, Koike T (2010) On the climatology and trend of the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau: an experiments-supported revisit. J Clim 24:1525–1541
Yang K, Guo XF, Wu BY (2011) Recent trends in surface sensible heat flux on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci China Ser D 54(1):19–28. doi:10.1007/s11430-010-4036-6
Ye DZ, Wu GX (1998) The role of the heat source of the Tibetan Plateau in the general circulation. Meteorol Atmos Phys 67(1–4):181–198. doi:10.1007/BF01277509
Yeh TC, Ye DZ, Lo SW, Chu PC (1957) The wind structure and heat balance in the lower troposphere over the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings. Acta Meteor Sinica 28:108–121. (in Chinese)
Zhao P, Chen L (2001) Climate features of atmospheric heat source/sink over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in 35 years and its relation to rainfall in China. Sci China Ser D 44(9):858–864. doi:10.1007/BF02907098
Zhao P, Zhou Z, Liu J (2007) Variability of Tibetan spring snow and its associations with the hemispheric extratropical circulation and East Asian summer monsoon rainfall: an observational investigation. J Clim 20(15):3942–3955. doi:10.1175/JCLI4205.1
Zhou TJ, Yu RC (2005) Atmospheric water vapor transport associated with typical anomalous summer rainfall patterns in China. J Geophys Res 110(D8):D08104. doi:10.1029/2004JD005413
Zhou T, Gong D, Li J, Li B (2009) Detecting and understanding the multi-decadal variability of the East Asian summer monsoon—recent progress and state of affairs. Meteorol Z 18(4):455–467. doi:10.1127/0941-2948/2009/0396
Zhu XY (2011) Relationship between summertime subtropical multi-scale forcing and the East Asian summer monsoon in interannual and interdecadal variability, Ph. D. thesis, Postgraduate School, Chinese Academy of Science, p 103
Acknowledgments
This study was jointly supported by the MOST Programme 2010CB950403 and 2012CB417203, CAS program (KZCX2-YW-Q11-01), and NSF of China Projects 40925015, 40875034. BD was supported by the UK National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate (NCAS-Climate). Thanks are due to the anonymous reviewers whose suggestions have helped the improvement of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is a contribution to the special issue on Global Monsoon Climate, a product of the Global Monsoon Working Group of the Past Global Changes (PAGES) project, coordinated by Pinxian Wang, Bin Wang, and Thorsten Kiefer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wu, G., Hong, J. et al. Revisiting Asian monsoon formation and change associated with Tibetan Plateau forcing: II. Change. Clim Dyn 39, 1183–1195 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1335-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1335-y