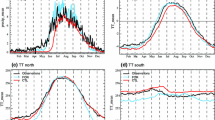
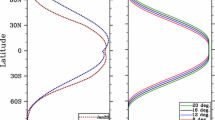
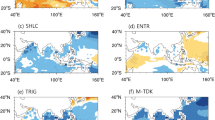
Abstract
The study compares the simulated poleward migration characteristics of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations (BSISO) in a suite of coupled ocean–atmospheric model sensitivity integrations. The sensitivity experiments are designed in such a manner to allow full coupling in specific ocean basins but forced by temporally varying monthly climatological sea surface temperature (SST) adopted from the fully coupled model control runs (ES10). While the local air–sea interaction is suppressed in the tropical Indian Ocean and allowed in the other oceans in the ESdI run, it is suppressed in the tropical Pacific and allowed in the other oceans in the ESdP run. Our diagnostics show that the basic mean state in precipitation and easterly vertical shear as well as the BSISO properties remain unchanged due to either inclusion or exclusion of local air–sea interaction. In the presence of realistic easterly vertical shear, the continuous emanation of Rossby waves from the equatorial convection is trapped over the monsoon region that enables the poleward propagation of BSISO anomalies in all the model sensitivity experiments. To explore the internal processes that maintain the tropospheric moisture anomalies ahead of BSISO precipitation anomalies, moisture and moist static energy budgets are performed. In all model experiments, advection of anomalous moisture by climatological winds anchors the moisture anomalies that in turn promote the northward migration of BSISO precipitation. While the results indicate the need for realistic simulation of all aspects of the basic state, our model results need to be taken with caution because in the ECHAM family of coupled models the internal variance at intraseasonal timescales is indeed very high, and therefore local air–sea interactions may not play a pivotal role.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajayamohan RS, Goswami BN (2007) Dependence of simulation of boreal summer tropical intraseasonal oscillations on the simulation of seasonal mean. J Atmos Sci 64:460–478. doi:10.1175/JAS3844.1
Ajayamohan RS, Rao SA, Luo JJ, Yamagata T (2009) Influence of Indian Ocean dipole on boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations in a coupled general circulation model. J Geophys Res 114:D06119. doi:10.1029/2008JD011096
Annamalai H (2009) Moist dynamical linkage between the equatorial Indian Ocean and the south Asian monsoon trough. J Atmos Sci. doi:10.1175/2009JAS2991.1
Annamalai H, Slingo JM (2001) Active/break cycles: diagnosis of the intraseasonal variability of the Asian summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 18:85–102
Annamalai H, Sperber KR (2005) Regional heat sources and the active and break phases of boreal summer intraseasonal (30–50 day) variability. J Atmos Sci 62:2726–2748
Bhat GS, Vecchi GA, Gadgil S (2004) Sea surface temperature of the Bay of Bengal derived from the TRMM microwave imager. J Atmos Ocean Technol 21:1283–1290
Cherchi A, Gualdi S, Behera S, Luo JJ, Masson S, Yamagata T, Navarra A (2007) The influence of tropical Indian Ocean SST on the Indian summer monsoon. J Clim 20:3083–3105
Ferranti L, Slingo JM, Palmer TN, Hoskins BJ (1999) The effect of land-surface feedbacks on monsoon circulation. Q J R Meteor Soc 125:1527–1550
Fu X, Wang B (2004) Differences of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations in an atmosphere–ocean coupled model and atmosphere-only model. J Clim 17:1263–1271
Fu X, Wang B, Li T, McCreary J (2003) Coupling between northward propagating intraseasonal oscillations and sea-surface temperature in the Indian Ocean. J Atmos Sci 60(15):1733–1753
Goswami BN (2005) South Asian monsoon. In: Lau WKM, Waliser DE (ed) Intraseasonal variability in the Atmosphere–Ocean climate system, chap 2. Praxis Springer, Berlin, pp 19–61
Goswami BN, Ajayamohan RS (2001) Intraseasonal oscillations and interannual variability of the Indian summer monsoon. J Clim 14:1180–1198
Goswami BN, Shukla J (1984) Quasi-periodic oscillations in a symmetric general circulation model. J Atmos Sci 41:20–37
Gualdi S, Navarra A, Tinarelli G (1999) The interannual variability of the MaddenJulian oscillation in an ensemble of GCM simulations. Clim Dyn 15:643–658
Gualdi S, Navarra A, Guilyardi E, Delecluse P (2003) Assessment of the tropical Indo-Pacific climate in the sintex CGCM. Ann Geophys 46:1–26
Guilyardi E, Delecluse P, Gualdi S, Navarra A (2003) Mechanisms for ENSO phase change in a coupled GCM. J Clim 16:1141–1158
Jiang X, Li T, Wang B (2004) Structures and mechanisms of the northward propagating boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J Clim 17:1022–1039
Jin EK, Kinter JL, Wang B, Park CK, Kang IS, Kirtman BP, Kug JS, Kumar A, Luo JJ, Schemm J, Shukla J, Yamagata T (2008) Current status of ENSO prediction skill in coupled ocean–atmosphere model. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0397-3
Kemball-Cook SR, Wang B (2001) Equatorial waves and air–sea interaction in the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J Clim 14:2923–2942
Kemball-Cook SR, Weare BC (2001) The onset of convection in the Madden-Julian oscillation. J Clim 14:780–793
Krishnan R, Zhang C, Sugi M (2000) Dynamics of breaks in the Indian summer monsoon. J Atmos Sci 57:1354–1372
Lau KM, Chen PH (1986) Aspects of 30–50 day oscillation during summer as inferred from outgoing longwave radiation. Mon Wea Rev 114:1354–1369
Lau KM, Peng L (1990) Orgin of low-frequency (intraseasonal) oscillations in the tropical atmosphere. Part III: monsoon dynamics. J Atmos Sci 47:1443–1462
Lawrence DM, Webster PJ (2001) Interannual variations of the intraseasonal oscillation in the south Asian summer monsoon region. J Clim 14:2910–2922
Lawrence DM, Webster PJ (2002) The boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation: relationship between northward and eastward movement of convection. J Atmos Sci 59:1593–1606
Luo JJ, Masson S, Roeckner E, Madec G, Yamagata T (2005) Reducing climatology bias in an ocean–atmosphere CGCM with improved coupling physics. J Clim 18:2344–2360
Luo JJ, Masson S, Behera S, Yamagata T (2007) Experimental forecasts of the Indian Ocean Dipole using a coupled OAGCM. J Clim 20:2178–2190
Luo JJ, Masson S, Behera S, Yamagata T (2008) Extended ENSO predictions using a fully coupled ocean–atmosphere model. J Clim 21:84–93
Luo JJ, Zhang R, Behera S, Masumoto Y, Jin FF, Lukas R, Yamagata T (2009) Interaction between El Niño and extreme Indian ocean dipole. J Clim. doi:10.1175/2009JCLI3104.1
Madden RA, Julian PR (1994) Observations of the 40–50 day tropical oscillation: a review. Mon Wea Rev 122:813–837
Madec G, Delecluse P, Imbard M, Lvy C (1998) Opa 8.1 Ocean general circulation model reference manual. Tech. Rep. Note 11, LODYC/IPSL, Paris, France
Maloney ED (2009) The moist static energy budget of a composite tropical intraseasonal oscillation in a climate model. J Clim 22:711–729
Neelin JD, Su H (2005) Moist teleconnection mechanisms for the tropical South America and Atlantic sector. J Clim 18:3928–3950
Roeckner E, Arpe K, Bengtsson L, Christoph M, Claussen M, Dmenil L, Esch M, Giorgetta M, Schlese U, Schulzweida U (1996) The atmospheric general circulation model ECHAM-4: model description and simulation of present-day climate. The Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany, report no:218, 90 pp
Sengupta D, Goswami BN, Senan R (2001) Coherent intraseasonal oscillations of ocean and atmosphere during the Asian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 28:4127–4130
Shinoda T, Hendon HH, Glick J (1998) Intraseasonal variability of surface fluxes and sea surface temperature in the tropical western Pacific and Indian Oceans. J Clim 11:2668–2685
Slingo JM, Inness PM, Sperber KR (2005) Modelling the MJO. In: Lau WKM, Waliser DE (eds) Intraseasonal variability in the atmosphere–ocean climate system, chap 11. Praxis Springer, Berlin, pp 361–388
Sperber KR, Annamalai H (2008) Coupled model simulations of boreal summer intraseasonal (3050 day) variability, part 1: Systematic errors and caution on use of metrics. Clim Dyn 31:345–372. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0367-9
Sperber KR, Gualdi S, Legutke S, Gayler V (2005) The Madden-Julian oscillation in ECHAM4 coupled and uncoupled general circulation models. Clim Dyn 25:117–140
Tian B, Waliser DE, Fetzer EJ, Lambrigtsen BH, Yung TL, Wang B (2006) Vertical moist thermodynamical structure and spatio-temporal evolution of the MJO in AIRS observations. J Atmos Sci 63:2462–2485
Valcke S, Terray L, Piacentini A (2000) Oasis 2.4 ocean atmosphere soil user’s guide. Tech. Rep. TR/CGMC/00-10, CERFACS, 42 Avenue Coriolis, 31057 Toulouse, 85 pp. http://citeseer.ist.psu.edu/valcke00oasis.html
Vecchi GA, Harrison DE (2002) Monsoon breaks and subseasonal sea surface temperature variability in the Bay of Bengal. J Clim 15:1485–1493
Waliser DE (2006) Intraseasonal variability. In: Wang B (ed) The Asian monsoon, chap 5. Praxis Springer, Chichester, pp 203–258
Waliser DE, Murtugudde R, Lucas L (2004) Indo-Pacific response to atmospheric intraseasonal variability. Part ii: boreal summer and the intraseasonal oscillation. J Geophys Res 109:C03030. doi:10.1029/2003JC002002
Wang B (2005) Theory. In: Lau WKM, Waliser DE (eds) Intraseasonal variability in the atmosphere–ocean climate system, chap 10. Praxis Springer, Berlin, pp 307–360
Wang B, Rui H (1990) Synoptic climatology of transient tropical intraseasonal convection anomalies: 1975–1985. Met Atmos Phys 44:43–61
Wang B, Xie X (1997) A model for the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations. J Atmos Sci 54:72–86
Webster PJ (1983) Mechanism of monsoon low-frequency variability: surface hydrological effects. J Atmos Sci 40:2110–2124
Webster PJ, Yang S (1992) Monsoon and ENSO: selectively interactive systems. Q J Meteor Soc 118:877–920
Woolnough SJ, Slingo JM, Hoskins BJ (2000) The relationship between convection and sea surface temperature anomalies on intraseasonal time scales. J Clim 13:2086–2104
Woolnough SJ, Slingo JM, Hoskins BJ (2001) The organization of tropical convection by intraseasonal sea surface temperature anomalies. Q J R Meteor Soc 127:888–907
Wu MLC, Schubert SD, Suarez MJ, Pegion PJ, Waliser DE (2006) Seasonality and meridional propagation of the MJO. J Clim 19:1901–1921
Yamagata T, and Y. Hayashi (1984) A simple diagnostic model for the 30–50 day oscillation in the tropics. J Meteor Soc Jpn 62(5):709–7117
Yamagata T, Behera SK, Luo JJ, Masson S, Jury MR, Rao SA (2004) Coupled ocean–atmosphere variability in the tropical Indian Ocean. In: Wang C, Xie SP, Carton JA (eds) In earth climate: the ocean–atmosphere interaction. Geophys. Monogr. Ser., vol 147. AGU, Washington, DC, pp 189–212
Acknowledgements
RSA is supported by the Global Atmosphere–Ocean Prediction and Predictability research network, funded by the Canadian Foundation for Climate and Atmospheric Sciences. H. Annamalai is supported by the IPRC through its institutional grants from NOAA, NASA and JAMSTEC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ajayamohan, R.S., Annamalai, H., Luo, JJ. et al. Poleward propagation of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations in a coupled model: role of internal processes. Clim Dyn 37, 851–867 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0839-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0839-6