Abstract
Purpose
Agreement between the correction objectives and the instrumentation strategies remains controversial in idiopathic scoliosis. Most studies have focus on the frontal and sagittal plane. The goal of this study was to evaluate the change on vertebral axial rotation after posterior instrumentation in fused and unfused segments.
Methods
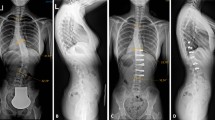
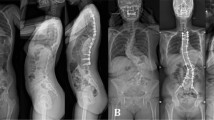
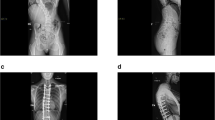
Fourteen patients operated on for idiopathic scoliosis were prospectively included. Fusion and instrumentation were done by posterior approach. All patients had a pre-operative and a 10-day post-operative radiological evaluation with the EOS system. Axial orientation of the vertebrae with special interest to the apical, junctional, and unfused areas was obtained thanks to the reconstruction software.
Results
Mean apical vertebra axial rotation statistically decreased from 21° pre-operatively to 13° post-operatively. But, there were no statistically significant differences between pre-operative and post-operative mean axial intervertebral rotations in the main curve and axial rotation of the non-instrumented lower counter curve.
Conclusions
3D analysis of the spine in standing position is a great advancement for post-operative analysis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) corrections. This study confirmed that actual instrumentations are able to achieve “en bloc” 3D correction of the spine but not intervertebral axial rotation correction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Majdouline Y, Aubin CE, Labelle H (2006) Objectives for correction and related instrumentation strategies in scoliosis surgery for Lenke curve types 2, 3 and 5. Stud Health Technol Inform 123:315–320
Aubin CE, Labelle H, Cheriet F, Villemure I, Mathieu PA, Dansereau J (2007) Tridimensional evaluation and optimization of the orthotic treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Med Sci (Paris) 23(11):904–909. doi:10.1051/medsci/20072311904
Majdouline Y, Aubin CE, Robitaille M, Sarwark JF, Labelle H (2007) Scoliosis correction objectives in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop 27(7):775–781. doi:10.1097/BPO.0b013e31815588d8
Lenke LG, Betz RR, Clements D, Merola A, Haher T, Lowe T, Newton P, Bridwell KH, Blanke K (2002) Curve prevalence of a new classification of operative adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: does classification correlate with treatment? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27(6):604–611
Yang X, Liu L, Song Y, Zhou C, Zhou Z, Wang L (2015) Pre- and postoperative spinopelvic sagittal balance in adolescent patients with Lenke type 5 idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 40(2):102–108. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000000685
Lenke LG (2014) Sagittal balance. J Neurosurg Spine 20(5):512. doi:10.3171/2013.10.SPINE13793, discussion 513-514
Borges PA, Ocampos GP, Mancuso Filho JA, Letaif OB, Marcon RM, Cristante AF (2014) The sagital balance in idiopatic and neuromuscular scoliosis. Acta Ortop Bras 22(4):179–182. doi:10.1590/1413-78522014220400949
Roussouly P, Labelle H, Rouissi J, Bodin A (2013) Pre- and post-operative sagittal balance in idiopathic scoliosis: a comparison over the ages of two cohorts of 132 adolescents and 52 adults. Eur Spine J 22(Suppl 2):S203–215. doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2571-x
Cotrel Y, Dubousset J (1984) A new technic for segmental spinal osteosynthesis using the posterior approach. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 70(6):489–494
Cotrel Y, Dubousset J, Guillaumat M (1988) New universal instrumentation in spinal surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res 227:10–23
Clements DH, Betz RR, Newton PO, Rohmiller M, Marks MC, Bastrom T (2009) Correlation of scoliosis curve correction with the number and type of fixation anchors. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34(20):2147–2150. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181adb35d
Lee SM, Suk SI, Chung ER (2004) Direct vertebral rotation: a new technique of three-dimensional deformity correction with segmental pedicle screw fixation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29(3):343–349
Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Chung YJ, Park YB (1995) Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20(12):1399–1405
Robitaille M, Aubin CE, Labelle H (2009) Effects of alternative instrumentation strategies in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a biomechanical analysis. J Orthop Res 27(1):104–113. doi:10.1002/jor.20654
Kadoury S, Cheriet F, Beausejour M, Stokes IA, Parent S, Labelle H (2009) A three-dimensional retrospective analysis of the evolution of spinal instrumentation for the correction of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 18(1):23–37. doi:10.1007/s00586-008-0817-4
Vrtovec T, Pernus F, Likar B (2009) A review of methods for quantitative evaluation of spinal curvature. Eur Spine J 18(5):593–607. doi:10.1007/s00586-009-0913-0
Courvoisier A, Drevelle X, Dubousset J, Skalli W (2013) Transverse plane 3D analysis of mild scoliosis. Eur Spine J. doi:10.1007/s00586-013-2862-x
Courvoisier A, Drevelle X, Vialle R, Dubousset J, Skalli W (2013) 3D analysis of brace treatment in idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. doi:10.1007/s00586-013-2881-7
Ilharreborde B, Dubousset J, Le Huec JC (2014) Use of EOS imaging for the assessment of scoliosis deformities: application to postoperative 3D quantitative analysis of the trunk. Eur Spine J 23(Suppl 4):S397–405. doi:10.1007/s00586-014-3334-7
Ilharreborde B, Even J, Lefevre Y, Fitoussi F, Presedo A, Pennecot GF, Mazda K (2010) Hybrid constructs for tridimensional correction of the thoracic spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a comparative analysis of universal clamps versus hooks. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35(3):306–314. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181b7c7c4
Humbert L, De Guise JA, Aubert B, Godbout B, Skalli W (2009) 3D reconstruction of the spine from biplanar X-rays using parametric models based on transversal and longitudinal inferences. Med Eng Phys 31(6):681–687. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2009.01.003
Pomero V, Mitton D, Laporte S, de Guise JA, Skalli W (2004) Fast accurate stereoradiographic 3D-reconstruction of the spine using a combined geometric and statistic model. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 19(3):240–247. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2003.11.014
Kalifa G, Charpak Y, Maccia C, Fery-Lemonnier E, Bloch J, Boussard JM, Attal M, Dubousset J, Adamsbaum C (1998) Evaluation of a new low-dose digital x-ray device: first dosimetric and clinical results in children. Pediatr Radiol 28(7):557–561. doi:10.1007/s002470050413
Dubousset J, Charpak G, Dorion I, Skalli W, Lavaste F, Deguise J, Kalifa G, Ferey S (2005) A new 2D and 3D imaging approach to musculoskeletal physiology and pathology with low-dose radiation and the standing position: the EOS system. Bull Acad Natl Med 189(2):287–297, discussion 297-300
Dubousset J, Charpak G, Skalli W, Kalifa G, Lazennec JY (2007) EOS stereo-radiography system: whole-body simultaneous anteroposterior and lateral radiographs with very low radiation dose. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 93(6 Suppl):141–143
Labelle H, Dansereau J, Bellefleur C, de Guise J, Rivard CH, Poitras B (1995) Peroperative three-dimensional correction of idiopathic scoliosis with the Cotrel-Dubousset procedure. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20(12):1406–1409
Conflict of interest
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, and patent/licensing arrangements) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Courvoisier, A., Garin, C., Vialle, R. et al. The change on vertebral axial rotation after posterior instrumentation of idiopathic scoliosis. Childs Nerv Syst 31, 2325–2331 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2891-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2891-3