Abstract
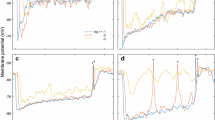
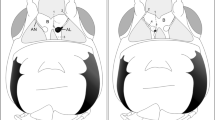
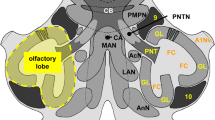
The morphology of visual interneurons in the tiger beetle larva was identified after recording their responses. Stained neurons were designated as either medulla or protocerebral neurons according to the location of their cell bodies. Medulla neurons were further subdivided into three groups. Afferent medulla neurons extended processes distally in the medulla neuropil and a single axon to the brain through the optic nerve. They received their main input from stemmata on the ipsilateral side. Two distance-sensitive neurons, near-by sensitive and far-sensitive neurons, were also identified. Atypical medulla neurons extended their neurites distally in the medulla and proximally to the brain, as afferent medulla neurons, but their input patterns and the shapes of their spikes differed from afferent neurons. Protocerebral neurons sent a single axon to the medulla neuropil. They spread collateral branches in the posterior region of the protocerebrum on its way to the medulla neuropil. They received main input from stemmata on the contralateral side. Medulla intrinsic neurons did not extend an axon to the brain, and received either bilateral or contralateral stemmata input only. The input patterns and discharge patterns of medulla neurons are discussed with reference to their morphology.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bullock TH, Horridge GA (1965) Structure and function in the nervous systems of invertebrates, vol II. Freeman, San Francisco
Franceschini N, Riehle A, Nestour AL (1989) Directionally selective motion detection by insect neurons. In: Stavenga DG, Hardie RC (eds) Facet of vision. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 360–390
Friederichs HF (1931) Beiträge zur Morphologie und Physiologie der Sehorgane der Cicindelinen. Z Morphol Oekol Tiere 21:1-172
Gilbert C (1989) Visual determinants of escape in tiger beetle larvae (Cicindelidae). J Insect Behav 2:557–574
Mizutani A, Toh Y (1995) Optical and physiological properties of the larval visual system of the tiger beetle, Cicindela chinensis. J Comp Physiol 178:591–599
Mizutani A, Toh Y (1998) Behavioral analysis of two distinct visual responses in the larva of the tiger beetle (Cicindela chinensis). J Comp Physiol 182:277–286
Nicholls JG, Martin AR, Wallace BG, Fuchs PA (2001) From neuron to brain, 4th edn. Sinauer, Sunderland
Okamura J-Y, Toh Y (2001) Responses of medulla neurons to illumination and movement stimuli in the tiger beetle larvae. J Comp Physiol 187:713–725
Toh Y, Iwasaki M (1982) Ocellar system of the swallowtail butterfly larva. II. Projection of retinular axons in the brain. J Ultrastruct Res 78:120–135
Toh Y, Kuwabara M (1978) Synaptic organization of the fleshfly ocellus. J Neurocytol 4:271–287
Toh Y, Mizutani A (1994a) Structure of the visual system of the larva of the tiger beetle (Cicindela chinensis). Cell Tissue Res 278:125–134
Toh Y, Mizutani A (1994b) Neural organization of the lamina neuropil of the larva of the tiger beetle (Cicindela chinensis). Cell Tissue Res 278:135–144
Toh Y, Okamura J-Y (2001) Behavioural responses of the tiger beetle larva to moving objects: role of binocular and monocular vision. J Exp Biol 204:1–12
Yamamoto K, Toh Y (1975) The fine structure of the lateral ocellus of the dobsonfly larva. J Morphol 146:415–430
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their thanks to Prof. S.R. Shaw and Prof. I.A. Meinertzhagen (Dalhousie University, Halifax) for their invaluable discussion and correction of the English. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan (11694091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okamura, JY., Toh, Y. Morphological and physiological identification of medulla interneurons in the visual system of the tiger beetle larva. J Comp Physiol A 190, 449–468 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-004-0509-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-004-0509-4