Abstract
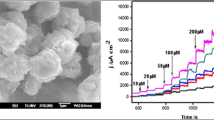
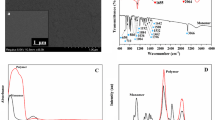
A nanocomposite of CuO/rGO was prepared by a simple liquid approach. After characterization by XRD, SEM, EDS and FTIR, a facile and inexpensive route has been developed to determine ascorbic acid by modifying the surface of conductive fabric with CuO/rGO through electrochemical deposition. The synergistic effect, arising from combining the unique properties of Gr with the intriguing properties of CuO, shows highly electrocatalytic activity towards the oxidation of ascorbic acid. The electrochemical sensor showed a wide linear response in the concentration range from 500 to 2000 µM with 189.053 µM detection limit. It also exhibited good stability, reproducibility and specificity. The sensor was compared to a range of other available ascorbate sensors and found to be comparable or superior in terms of analytical performance.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings will be available on the reasonable request.
References
M.R. Ganjali, F.G. Nejad, H. Beitollahi, S. Jahani, M. Rezapour, B. Larijani, Highly sensitive voltammetric sensor for determination of ascorbic acid using graphite screen printed electrode modified with ZnO/Al2O3 nanocomposite. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 12, 3231–3240 (2017)
H. Lee, C. Song, Y.S. Hong, M.S. Kim, H.R. Cho, T. Kang, K. Shin, S.H. Choi, T. Hyeon, D.H. Kim, Wearable/disposable sweat-based glucose monitoring device with multistage transdermal drug delivery module. Sci. Adv. 3(3), e1601314 (2017)
Y.M. Tang, D.G. Wang, J. Li, X.H. Li, Q. Wang, N. Liu, W.T. Liu, Y.X. Li, Relationships between micronutrient losses in sweat and blood pressure among heat-exposed steelworkers. Ind. Health. 54(3), 2014–0225 (2016)
L.A. Tortajada-Genaro, Determination of L-ascorbic acid in tomato by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chem. Educ. 89(9), 1194–1197 (2012)
L. Nováková, P. Solich, D. Solichová, HPLC methods for simultaneous determination of ascorbic and dehydroascorbic acids. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 27(10), 942–958 (2008)
Y.L. Chang, M. Rossetti, H. Vlamakis, D. Casero, G. Sunga, N. Harre, S. Miller, R. Humphries, T. Stappenbeck, K.W. Simpson, R.B. Sartor, A screen of crohn’s disease-associated microbial metabolites identifies ascorbate as a novel metabolic inhibitor of activated human T cells. Mucosal Immunol. 12(2), 457–467 (2019)
A. Kamišalić, I. Fister, M. Turkanović, S. Karakatič, Sensors and functionalities of non-invasive wrist-wearable devices: a review. Sensors 18(6), 1714 (2018)
B. Ibarlucea, X. Munoz-Berbel, P. Ortiz, S. Büttgenbach, C. Fernández-Sánchez, A. Llobera, Self-validating lab-on-a-chip for monitoring enzyme-catalyzed biological reactions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 237, 16–23 (2016)
J. Gupta, S. Arya, S. Verma, A. Singh, A. Sharma, B. Singh, R. Sharma, Performance of template-assisted electrodeposited copper/cobalt bilayered nanowires as an efficient glucose and uric acid senor. Mater. Chem. Phys. 238, 121969 (2019)
A. Singh, A. Sharma, A. Ahmed, A.K. Sundramoorthy, H. Furukawa, S. Arya, A. Khosla, Recent advances in electrochemical biosensors: applications, challenges, and future scope. Biosensors 11(9), 336 (2021)
A. Koh, D. Kang, Y. Xue, S. Lee, R.M. Pielak, J. Kim, T. Hwang, S. Min, A. Banks, P. Bastien, M.C. Manco, A soft, wearable microfluidic device for the capture, storage, and colorimetric sensing of sweat. Sci. Transl. Med. 8(366), 366ra165-366ra165 (2016)
W. Jia, A.J. Bandodkar, G. Valdés-Ramírez, J.R. Windmiller, Z. Yang, J. Ramírez, G. Chan, J. Wang, Electrochemical tattoo biosensors for real-time noninvasive lactate monitoring in human perspiration. Anal. Chem. 85(14), 6553–6560 (2013)
M.L. Zamora, J.M. Domínguez, R.M. Trujillo, C.B. Goy, M.A. Sanchez, R.E. Madrid, Potentiometric textile-based pH sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 260, 601–608 (2018)
A. Márquez, C. Jiménez-Jorquera, C. Domínguez, X. Muñoz-Berbel, Electrodepositable alginate membranes for enzymatic sensors: an amperometric glucose biosensor for whole blood analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 97, 136–142 (2017)
L.R. Stromberg, J.A. Hondred, D. Sanborn, D. Mendivelso-Perez, S. Ramesh, I.V. Rivero, J. Kogot, E. Smith, C. Gomes, J.C. Claussen, Stamped multilayer graphene laminates for disposable in-field electrodes: application to electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Microchim. Acta 186(8), 1–13 (2019)
S.Y. Oh, S.Y. Hong, Y.R. Jeong, J. Yun, H. Park, S.W. Jin, G. Lee, J.H. Oh, H. Lee, S.S. Lee, J.S. Ha, Skin-attachable, stretchable electrochemical sweat sensor for glucose and pH detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10(16), 13729–13740 (2018)
J.R. Sempionatto, A.A. Khorshed, A. Ahmed, A.N. De Loyola e Silva, A. Barfidokht, L. Yin, K.Y. Goud, M.A. Mohamed, E. Bailey, J. May, C. Aebischer, Epidermal enzymatic biosensors for sweat vitamin C: toward personalized nutrition. ACS Sens. 5(6), 1804–1813 (2020)
G. Amala, S.M. Gowtham, Recent advancements, key challenges and solutions in non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors based on graphene platforms. RSC Adv. 7(59), 36949–36976 (2017)
X. Zhang, Y. Cao, S. Yu, F. Yang, P. Xi, An electrochemical biosensor for ascorbic acid based on carbon-supported PdNinanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 44, 183–190 (2013)
Y. Zhao, J. Qin, H. Xu, S. Gao, T. Jiang, S. Zhang, J. Jin, Gold nanorods decorated with graphene oxide and multi-walled carbon nanotubes for trace level voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid. Microchim. Acta 186(1), 1–10 (2019)
A. Savk, B. Özdil, B. Demirkan, M.S. Nas, M.H. Calimli, M.H. Alma, A.M. Asiri, F. Şen, Multiwalled carbon nanotube-based nanosensor for ultrasensitive detection of uric acid, dopamine, and ascorbic acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 99, 248–254 (2019)
F.A. Harraz, M. Faisal, A.A. Ismail, S.A. Al-Sayari, A.E. Al-Salami, A. Al-Hajry, M.S. Al-Assiri, TiO2/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite as efficient ascorbic acid amperometric sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 832, 225–232 (2019)
S. Krishnan, L. Tong, S. Liu, R. Xing, A mesoporous silver-doped TiO2–SnO2 nanocomposite on gC3N4 nanosheets and decorated with a hierarchical core−shell metal-organic framework for simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Microchim. Acta 187(1), 1–9 (2020)
H. Huang, Y. Yue, Z. Chen, Y. Chen, S. Wu, J. Liao, S. Liu, H.R. Wen, Electrochemical sensor based on a nanocomposite prepared from TmPO4 and graphene oxide for simultaneous voltammetric detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Microchim. Acta 186(3), 1–9 (2019)
M. Asif, A. Aziz, H. Wang, Z. Wang, W. Wang, M. Ajmal, F. Xiao, X. Chen, H. Liu, Superlattice stacking by hybridizing layered double hydroxide nanosheets with layers of reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid. Microchim. Acta 186(2), 61 (2019)
Y. Zhao, J. Zhou, Z. Jia, D. Huo, Q. Liu, D. Zhong, Y. Hu, M. Yang, M. Bian, C. Hou, In-situ growth of gold nanoparticles on a 3D-network consisting of a MoS2/rGO nanocomposite for simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Microchim. Acta 186(2), 1–10 (2019)
W. Liang, Y. Rong, L. Fan, C. Zhang, W. Dong, J. Li, J. Niu, C. Yang, S. Shuang, C. Dong, W.Y. Wong, Simultaneous electrochemical sensing of serotonin, dopamine and ascorbic acid by using a nanocomposite prepared from reduced graphene oxide, Fe3O4 and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Microchim. Acta 186(12), 1–9 (2019)
J.M. George, A. Antony, B. Mathew, Metal oxide nanoparticles in electrochemical sensing and biosensing: a review. Microchim. Acta 185(7), 1–26 (2018)
X. Cheng, X. Zhang, H. Yin, A. Wang, Y. Xu, Modifier effects on chemical reduction synthesis of nanostructured copper. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(5), 2727–2732 (2006)
Q. You, T. Liu, J. Pang, D. Jiang, Z. Chu, W. Jin, In situ fabrication of CuO nanowire film for high-sensitive ascorbic acid recognition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 296, 126617 (2019)
O. Akhavan, E. Ghaderi, R. Rahighi, Toward single-DNA electrochemical biosensing by graphene nanowalls. ACS Nano 6(4), 2904–2916 (2012)
H. Bagheri, A. Afkhami, Y. Panahi, H. Khoshsafar, A. Shirzadmehr, Facile stripping voltammetric determination of haloperidol using a high performance magnetite/carbon nanotube paste electrode in pharmaceutical and biological samples. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 37, 264–270 (2014)
O. Akhavan, Bacteriorhodopsin as a superior substitute for hydrazine in chemical reduction of single-layer graphene oxide sheets. Carbon 81, 158–166 (2015)
S. Pruneanu, F. Pogacean, A.R. Biris, M. Coros, F. Watanabe, E. Dervishi, A.S. Biris, Electro-catalytic properties of graphene composites containing gold or silver nanoparticles. Electrochim. Acta 89, 246–252 (2013)
A. Pendashteh, M.F. Mousavi, M.S. Rahmanifar, Fabrication of anchored copper oxide nanoparticles on graphene oxide nanosheets via an electrostatic coprecipitation and its application as supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta 88, 347–357 (2013)
J. Hu, C. Zou, Y. Su, M. Li, Y. Han, E.S.W. Kong, Z. Yang, Y. Zhang, An ultrasensitive NO2 gas sensor based on a hierarchical Cu2 O/CuO mesocrystal nanoflower. J. Mater. Chem. A 6(35), 17120–17131 (2018)
O. Akhavan, E. Ghaderi, Cu and CuO nanoparticles immobilized by silica thin films as antibacterial materials and photocatalysts. Surf. Coat. Technol. 205(1), 219–223 (2010)
G.S. Jamila, S. Sajjad, S.A.K. Leghari, T. Mahmood, Role of nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots on CuO nano-leaves as solar induced photo catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 138, 109233 (2020)
R. Shabu, A.M.E. Raj, C. Sanjeeviraja, C. Ravidhas, Assessment of CuO thin films for its suitablity as window absorbing layer in solar cell fabrications. Mater. Res. Bull. 68, 1–8 (2015)
L. He, J. Liu, L. Yang, Y. Song, M. Wang, D. Peng, Z. Zhang, S. Fang, Copper metal–organic framework-derived CuOx-coated three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide and polyaniline composite: excellent candidate free-standing electrodes for high-performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 275, 133–144 (2018)
M. Jannesari, O. Akhavan, H.R. Madaah Hosseini, B. Bakhshi, Graphene/CuO2 nanoshuttles with controllable release of oxygen nanobubbles promoting interruption of bacterial respiration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(32), 35813–35825 (2020)
O. Akhavan, H. Tohidi, A.Z. Moshfegh, Synthesis and electrochromic study of sol–gel cuprous oxide nanoparticles accumulated on silica thin film. Thin Solid Films 517(24), 6700–6706 (2009)
M.M. Sivalingam, J.A. Olmos-Asar, E. Vinoth, T. Tharmar, M. Shkir, Z. Said, K. Balasubramanian, Copper oxide nanorod/reduced graphene oxide composites for NH3 sensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4(12), 12977–12985 (2021)
A. Gupta, R. Jamatia, R.A. Patil, Y.R. Ma, A.K. Pal, Copper oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite-catalyzed synthesis of flavanones and flavanones with triazole hybrid molecules in one pot: a green and sustainable approach. ACS Omega 3(7), 7288–7299 (2018)
L. Luo, L. Zhu, Z. Wang, Nonenzymatic amperometric determination of glucose by CuO nanocubes–graphene nanocomposite modified electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 88, 156–163 (2012)
W.S. Hummers Jr., R.E. Offeman, Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80(6), 1339–1339 (1958)
C. Sun, J. Sun, G. Xiao, H. Zhang, X. Qiu, H. Li, L. Chen, Mesoscale organization of nearly monodisperse flowerlike ceria microspheres. J. Phys. Chem. B 110(27), 13445–13452 (2006)
S.F. Zheng, J.S. Hu, L.S. Zhong, W.G. Song, L.J. Wan, Y.G. Guo, Introducing dual functional CNT networks into CuO nanomicrospheres toward superior electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 20(11), 3617–3622 (2008)
F.T. Thema, M.J. Moloto, E.D. Dikio, N.N. Nyangiwe, L. Kotsedi, M. Maaza, M. Khenfouch, Synthesis and characterization of graphene thin films by chemical reduction of exfoliated and intercalated graphite oxide. J. Chem. 2013, 150536 (2013)
A. Singh, S. Arya, M. Khanuja, A.K. Hafiz, R. Datt, V. Gupta, A. Khosla, Eu doped NaYF4@Er:TiO2 nanoparticles for tunable ultraviolet light based anti-counterfeiting applications. Microsyst. Technol. 28, 295–304 (2022)
B. Zhao, P. Liu, H. Zhuang, Z. Jiao, T. Fang, W. Xu, B. Lu, Y. Jiang, Hierarchical self-assembly of microscale leaf-like CuO on graphene sheets for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 1(2), 367–373 (2013)
M.S. Alhumaimess, I.H. Alsohaimi, H.M. Alshammari, O.F. Aldosari, H.M. Hassan, Synthesis of gold and palladium nanoparticles supported on CuO/rGO using imidazolium ionic liquid for CO oxidation. Res. Chem. Intermed. 46(12), 5499–5516 (2020)
S. Alehashem, F. Chambers, J.W. Strojek, G.M. Swain, R. Ramesham, Cyclic voltammetric studies of charge transfer reactions at highly boron-doped polycrystalline diamond thin-film electrodes. Anal. Chem. 67(17), 2812–2821 (1995)
S. Bilal, A. Akbar, A.U.H.A. Shah, Highly selective and reproducible electrochemical sensing of ascorbic acid through a conductive polymer coated electrode. Polymers 11(8), 1346 (2019)
S. Liu, X. Jiang, M. Yang, Electrochemical sensing of L-ascorbic acid by using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a molybdophosphate film. Microchim. Acta 186(7), 1–7 (2019)
J.M.M. Droog, C.A. Alderliesten, P.T. Alderliesten, G.A. Bootsma, Initial stages of anodic oxidation of polycrystalline copper electrodes in alkaline solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 111, 61–70 (1980)
O. Akhavan, E. Ghaderi, Copper oxide nanoflakes as highly sensitive and fast response self-sterilizing biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. 21(34), 12935–12940 (2011)
A. Sharma, S. Arya, D. Chauhan, P.R. Solanki, S. Khajuria, A. Khosla, Synthesis of Au–SnO2 nanoparticles for electrochemical determination of vitamin B12. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9(6), 14321–14337 (2020)
M. Zhu, C. Zeng, J. Ye, Graphene-modified carbon fiber microelectrode for the detection of dopamine in mice hippocampus tissue. Electroanalysis 23(4), 907–914 (2011)
S. Thiagarajan, S.M. Chen, Preparation and characterization of PtAu hybrid film modified electrodes and their use in simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid. Talanta 74(2), 212–222 (2007)
L. Tan, K.G. Zhou, Y.H. Zhang, H.X. Wang, X.D. Wang, Y.F. Guo, H.L. Zhang, Nanomolar detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid at β-cyclodextrin/graphene nanocomposite platform. Electrochem. Commun. 12(4), 557–560 (2010)
C.F. Tang, S.A. Kumar, S.M. Chen, Zinc oxide/redox mediator composite films-based sensor for electrochemical detection of important biomolecules. Anal. Biochem. 380(2), 174–183 (2008)
Y. Wang, Y. Li, L. Tang, J. Lu, J. Li, Application of graphene-modified electrode for selective detection of dopamine. Electrochem. Commun. 11(4), 889–892 (2009)
M. Li, W. Guo, H. Li, W. Dai, B. Yang, Electrochemical biosensor based on one-dimensional MgO nanostructures for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 204, 629–636 (2014)
Z. Zhuang, J. Li, R. Xu, D. Xiao, Electrochemical detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid using overoxidized polypyrrole/graphene modified electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 6(6), 2149–2161 (2011)
W. Ren, H.Q. Luo, N.B. Li, Simultaneous voltammetric measurement of ascorbic acid, epinephrine and uric acid at a glassy carbon electrode modified with caffeic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 21(7), 1086–1092 (2006)
H. Cheng, X. Wang, H. Wei, Ratiometric electrochemical sensor for effective and reliable detection of ascorbic acid in living brains. Anal. Chem. 87(17), 8889–8895 (2015)
F. Wantz, C.E. Banks, R.G. Compton, Direct oxidation of ascorbic acid at an edge plane pyrolytic graphite electrode: a comparison of the electroanalytical response with other carbon electrodes. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted Fundam. Pract Asp. Electroanal. 17(17), 1529–1533 (2005)
Acknowledgements
The principal author is grateful to the CSIR, New Delhi, India, for financial support (JRF (CSIR) Fellowship, 09/100(0246)/2020-EMR-I)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Sharma, A., Ahmed, A. et al. Highly selective and efficient electrochemical sensing of ascorbic acid via CuO/rGO nanocomposites deposited on conductive fabric. Appl. Phys. A 128, 262 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05436-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05436-w