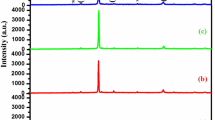
Abstract
Copper oxide thin films have been grown by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction technique, which is inexpensive, environmentally friendly and simple onto soda-lime glass substrates from an aqueous copper (II) chloride dehydrate solution with and without the addition of ascorbic acid (AA) at 70 °C. Surface morphology, crystalline structure, chemical compositions, optical and electrical properties of thin films were investigated with a focus on the influences of different concentrations of AA. The analysis exhibited that the main physical performances of the CuO films were found to change with AA content. Estimated crystallite sizes decreased from 24.64 to 12.78 nm with the addition of AA in the growth bath solutions. The optical bandgap energy of CuO is found to increase from 1.42 to 1.55 eV as a consequence of the increasing AA content. As the AA concentration in the solution bath increases the transmittance increases from ≈ 5 to ≈28%. FTIR transmittance spectra of CuO have a characteristic stretching vibration mode of the metal–oxide bonds and the addition of AA caused the appearance of many peaks of this molecule. Contact resistance values decreased with the AA content from 0.657 × 109 to 0.342 × 109 Ω. It is worth noting that the deposition technique is low cost and very simple; obtained CuO thin films could be appropriate for different technological applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.A.A. Ahmed, E.A.A. Alahsab, A. Abdulwahab, The influence of Zn and Mg doping on the structural and optical properties of NiO nano-structures for optoelectronic applications. Results Phys. 22, 103938 (2021)
B. Şahin, S. Soylu, M. Kara, M. Türkmen, R. Aydin, H. Çetin, Superior antibacterial activity against seed-borne plant bacterial disease agents and enhanced physical properties of novel green synthesized nanostructured ZnO using Thymbra spicata plant extract. Ceram. Int. 47, 341–350 (2021)
B. Şahin, T. Kaya, Facile preparation and characterization of nanostructured ZnO/CuO composite thin film for sweat concentration sensing applications. Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 121, 105428 (2021)
A. Maleki, F. Moradi, B. Shahmoradi, R. Rezaee, S.-M. Lee, The photocatalytic removal of diazinon from aqueous solutions using tungsten oxide doped zinc oxide nanoparticles immobilized on glass substrate. J. Mol. Liq. 297, 111918 (2020)
M. Khan, B. Mehmood, G.M. Mustafa, K. Humaiyoun, N. Alwadai, A.H. Almuqrin, H. Albalawi, M. Iqbal, Effect of silver (Ag) ions irradiation on the structural, optical and photovoltaic properties of Mn doped TiO2 thin films based dye sensitized solar cells. Ceram. Int. 47, 15801–15806 (2021)
B. Şahin, R. Aydın, H. Cetin, Variation of the key morphological, structural, optical and electrical properties of SILAR CdO with alkaline earth Ca2+ ions doping. Ceram. Int. 45, 16748–16758 (2019)
W. He, Z. Wang, T. Zheng, L. Wang, S. Zheng, Origin of the Band Gap Reduction of In-Doped β-Ga2O3. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 3856–3861 (2021)
M. Aghazadeh, H. Forati-Rad, K. Yavari, K. Mohammadzadeh, On-pot fabrication of binder-free composite of iron oxide grown onto porous N-doped graphene layers with outstanding charge storage performance for supercapacitors. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 13156–13176 (2021)
B.P. Singh, M. Chaudhary, A. Kumar, A.K. Singh, Y.K. Gautam, S. Rani, R. Walia, Effect of Co and Mn doping on the morphological, optical and magnetic properties of CuO nanostructures. Solid State Sci. 106, 106296 (2020)
S. Kamble, V. Mote, Optical and room-temperature ferromagnetic properties of Ni-doped CuO nanocrystals prepared via auto-combustion method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 5309–5315 (2021)
Y. Zhou, J. Li, W. Peng, Y. Liu, J. Zhang, G. Xiang, X. Zhu, R. Li, H. Wang, G. Deng, Near-white light-emitting diode from p-CuO/n-GaN heterojunction with an i-CuO electron blocking layer. J. Alloy Compd. 867, 159145 (2021)
M. Ajili, N.T. Kamoun, Structural and optoelectronic studies of CuO, In2-xAlxS3 and SnO2: F sprayed thin films for solar cell application: Au/CuO (p)/In2-xAlxS3 (n)/SnO2: F. Optik 229, 166222 (2021)
F.I. Ali, S.T. Mahmoud, F. Awwad, Y.E. Greish, A.F. Abu-Hani, Low power consumption and fast response H2S gas sensor based on a chitosan-CuO hybrid nanocomposite thin film. Carbohydr. Polym. 236, 116064 (2020)
N. Akram, J. Guo, Y. Guo, Y. Kou, H. Suleman, J. Wang, Enhanced synergistic catalysis of novel Ag2O/CuO nanosheets under visible light illumination for the photodecomposition of three dyes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 104824 (2021)
M. Ristova, V. Mirceski, R. Neskovska, Voltammetry of chemically deposited CuxO electrochromic films, coated with ZnO or TiO2 electrocatalyst layers. J. Solid State Electr. 19, 749–756 (2015)
K. Sahu, A. Bisht, S.A. Khan, A. Pandey, S. Mohapatra, Engineering of morphological, optical, structural, photocatalytic and catalytic properties of nanostructured CuO thin films fabricated by reactive DC magnetron sputtering. Ceram. Int. 46, 7499–7509 (2020)
J. Sultana, S. Paul, A. Karmakar, G.K. Dalapati, S. Chattopadhyay, Optimizing the thermal annealing temperature: technological route for tuning the photo-detecting property of p-CuO thin films grown by chemical bath deposition method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 12878–12887 (2018)
Y. Zhou, H. Zhang, Y. Yan, Catalytic oxidation of ethyl acetate over CuO/ZSM-5 zeolite membrane coated on stainless steel fibers by chemical vapor deposition. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 157, 13–24 (2020)
S.Y. Khew, C.F. Tan, H. Yan, S. Lin, E. San Thian, R. Zhou, M. Hong, Nanosecond laser ablation for enhanced adhesion of CuO nanowires on copper substrate and its application for oil-water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 465, 995–1002 (2019)
A. Inyang, G. Kibambo, M. Palmer, F. Cummings, M. Masikini, C. Sunday, M. Chowdhury, One step copper oxide (CuO) thin film deposition for non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose detection. Thin Solid Films 709, 138244 (2020)
S. Shehayeb, X. Deschanels, L. Ghannam, I. Karame, G. Toquer, Tandem selective photothermal absorbers based on EPD of CuO colloidal suspension coupled with dip-coated silica. Surf. Coat. Technol. 408, 126818 (2021)
K. Yang, P. Hu, S. Wu, L. Ren, M. Yang, W. Zhou, F. Yu, Y. Wang, M. Meng, G. Wang, Room-temperature ferromagnetic CuO thin film grown by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy. Mater. Lett. 166, 23–25 (2016)
O. Daoudi, A. Elmadani, M. Lharch, M. Fahoume, A new efficient synthesis of CuO thin films using modified SILAR method. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52, 1–17 (2020)
A. Ravichandran, K. Dhanabalan, S. Valanarasu, A. Vasuhi, A. Kathalingam, Role of immersion time on the properties of SILAR deposited CuO thin films. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 921–926 (2015)
S. Visalakshi, R. Kannan, S. Valanarasu, H.-S. Kim, A. Kathalingam, R. Chandramohan, Effect of bath concentration on the growth and photovoltaic response of SILAR-deposited CuO thin films. Appl. Phys. A 120, 1105–1111 (2015)
K. Raja, P. Ramesh, D. Geetha, T. Kokila, R. Sathiyapriya, Synthesis of structural and optical characterization of surfactant capped ZnO nanocrystalline. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 136, 155–161 (2015)
M. Amanullah, S. Rizwan, Surfactant-assisted carbon doping in ZnO nanowires using Poly Ethylene Glycol (PEG). Mater. Chem. Phys. 180, 128–134 (2016)
A.A. Kassem, H.N. Abdelhamid, D.M. Fouad, S.A. Ibrahim, Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and MOFs-derived CuO@ C for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44, 31230–31238 (2019)
A. Othmani, Z. Kouki, S. Kouass, F. Touati, H. Dhaouadi, A highly sensitive hydrazine and hydrogen peroxide non-enzymatic sensor based on CuO nanoplatelets. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 3566–3576 (2021)
S.-B. He, A.-L. Hu, Q.-Q. Zhuang, H.-P. Peng, H.-H. Deng, W. Chen, G.-L. Hong, Ascorbate oxidase mimetic activity of Copper(II) oxide nanoparticles. ChemBi Chem 21, 978–984 (2020)
E. Sharmin, S. Shreaz, F. Zafar, D. Akram, V. Raja, S. Ahmad, Linseed polyol-assisted, microwave-induced synthesis of nano CuO embedded in polyol-polyester matrix: antifungal behavior and coating properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 105, 200–211 (2017)
A. Umer, S. Naveed, N. Ramzan, M.S. Rafique, M. Imran, A green method for the synthesis of copper nanoparticles using L-ascorbic acid. Matéria. (Rio de janeiro) 19, 197–203 (2014)
O. Motyka, K. Štrbová, E. Olšovská, J. Seidlerová, Influence of nano-ZnO exposure to plants on l-ascorbic acid levels: Indication of nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 19, 3019–3023 (2019)
A. Pruna, D. Tamvakos, M. Sgroi, D. Pullini, E.A. Nieto, D. Busquets-Mataix, Electrocapacitance of hybrid film based on graphene oxide reduced by ascorbic acid. Int. J. Mater. Res. 106, 398–405 (2015)
M.R. Ganjali, F.G. Nejad, H. Beitollahi, S. Jahani, M. Rezapour, B. Larijani, Highly sensitive voltammetric sensor for determination of ascorbic acid using graphite screen printed electrode modified with ZnO/Al2O3 nanocomposite. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 12, 3231–3240 (2017)
A. Wang, L. Chen, F. Xu, Z. Yan, In situ synthesis of copper nanoparticles within ionic liquid-in-vegetable oil microemulsions and their direct use as high efficient nanolubricants. Rsc. Adv. 4, 45251–45257 (2014)
A. Akkaya, E. Ayyıldız, Automation software for semiconductor research laboratories: electrical parameter calculation program (SeCLaS-PC). J. Circuits, Syst. Comput. 29, 2050215 (2020)
A. Akkaya, E. Ayyıldız, Automation software for semiconductor research laboratories: measurement system and instrument control program (SeCLaS-IC). Mapan 35, 343–350 (2020)
Y. Zhao, J. Zhao, Z. Su, X. Hao, D. Ma, Y. Lu, J. Guo, Effect of surfactants on fabricating CuO nanoleaves and Cu nanocages at room temperature. Colloids Surf., A 436, 34–40 (2013)
V. Rajendran, J. Gajendiran, Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline CuO powders with the different surfactants and complexing agent mediated precipitation method. Mater. Res. Bull. 56, 134–137 (2014)
A. Abedini, A.R. Daud, M.A. Abdul Hamid, N. Kamil Othman, E. Saion, A review on radiation-induced nucleation and growth of colloidal metallic nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 474 (2013)
Y. Wang, X. Xu, Z. Tian, Y. Zong, H. Cheng, C. Lin, Selective heterogeneous nucleation and growth of size-controlled metal nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes in solution. Chem.—A Eur. J. 12, 2542–2549 (2006)
T. Atwee, A.S. Gadallah, M.A. Salim, A.M. Ghander, Effect of film thickness on structural, morphological, and optical properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films prepared by sol–gel spin coating. Appl. Phys. A 125, 270 (2019)
E. Beltrán-Partida, B. Valdez-Salas, E. Valdez-Salas, G. Pérez-Cortéz, N. Nedev, Synthesis, characterization, and in situ antifungal and cytotoxicity evaluation of ascorbic acid-capped copper nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2019, 1–10 (2019)
D.D. Thongam, J. Gupta, N.K. Sahu, D. Bahadur, Investigating the role of different reducing agents, molar ratios, and synthesis medium over the formation of ZnO nanostructures and their photo-catalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. 53, 1110–1122 (2018)
M.M. Rashad, A.E. Shalan, Surfactant-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of titania nanoparticles for solar cell applications. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 3189–3194 (2013)
H.M. Pathan, C.D. Lokhande, Deposition of metal chalcogenide thin films by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method. Bull Mater. Sci. 27, 85–111 (2004)
H. Siddiqui, M.S. Qureshi, F.Z. Haque, Surfactant assisted wet chemical synthesis of copper oxide (CuO) nanostructures and their spectroscopic analysis. Optik 127, 2740–2747 (2016)
S. Cho, H. Jeong, D.-H. Park, S.-H. Jung, H.-J. Kim, K.-H. Lee, The effects of vitamin C on ZnO crystal formation. CrystEngComm 12, 968–976 (2010)
L. Al-Salem, R. Seoudi, Influence of ascorbic acid as modifier on the particle size and the optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 22642–22651 (2020)
A. Moshalagae Motlatle, S. Kesavan Pillai, M. Rudolf Scriba, S. Sinha Ray, Chemical synthesis, characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial properties of Cu and its oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 18, 312 (2016)
Z. Tang, A. Shahzad, W.-S. Kim, T. Yu, Cost-effective aqueous-phase synthesis of long copper nanowires. Rsc. Adv. 5, 83880–83884 (2015)
R. Aydın, B. Şahin, The role of Triton X-100 as a surfactant on the CdO nanostructures grown by the SILAR method. J. Alloy Compd. 705, 9–13 (2017)
A. Akkaya, B. Şahin, R. Aydın, H. Çetin, E. Ayyıldız, Solution-processed nanostructured ZnO/CuO composite films and improvement its physical properties by lustrous transition metal silver doping. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 14400–14410 (2020)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray Diffraction (Addison-Wesley Publishing, 1956)
P. Scherrer, Bestimmung der Grösse und der Inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen Mittels Röntgenstrahlen, Nahrichten von der Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften, Göttingen, Mathematisch-Physikalische Klasse, Vol. 2, 1918, pp. 98–100
J. Xiong, Y. Wang, Q. Xue, X. Wu, Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using l-ascorbic acid. Green Chem. 13, 900–904 (2011)
M.Y. Alawadhi, S. Sabbaghianrad, Y. Huang, T.G. Langdon, Evaluating the paradox of strength and ductility in ultrafine-grained oxygen-free copper processed by ECAP at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 802, 140546 (2021)
A. Badawi, S.S. Alharthi, M.G. Althobaiti, A.N. Alharbi, H. Assaedi, H.I. Alkhammash, N. Al-Hosiny, Structure investigation and optical bandgap tuning of La-doped CuO nanostructured films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Appl. Phys. A 127, 235 (2021)
K.D. Arun Kumar, S. Valanarasu, V. Ganesh, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, H. Algarni, Effect of potential voltages on key functional properties of transparent AZO thin films prepared by electrochemical deposition method for optoelectronic applications. J. Mater. Res. 33, 1523–1533 (2018)
L.M. Bertus, C. Faure, A. Danine, C. Labrugere, G. Campet, A. Rougier, A. Duta, Synthesis and characterization of WO3 thin films by surfactant assisted spray pyrolysis for electrochromic applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 140, 49–59 (2013)
J.K. Sharma, M.S. Akhtar, S. Ameen, P. Srivastava, G. Singh, Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles with leaf extract of Calotropis gigantea and its dye-sensitized solar cells applications. J. Alloy Compd. 632, 321–325 (2015)
A. Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, S. Hushmandrad, Solar photodecolorization of methylene blue by CuO/X zeolite as a heterogeneous catalyst. Appl. Catal. A 388, 149–159 (2010)
N. Phutanon, P. Pisitsak, H. Manuspiya, S. Ummartyotin, Synthesis of three-dimensional hierarchical CuO flower-like architecture and its photocatalytic activity for rhodamine b degradation. J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Device. 3, 310–316 (2018)
C.Y. Panicker, H.T. Varghese, D. Philip, FT-IR, FT-Raman and SERS spectra of Vitamin C. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 65, 802–804 (2006)
K.R. Ahammed, M. Ashaduzzaman, S.C. Paul, M.R. Nath, S. Bhowmik, O. Saha, M.M. Rahaman, S. Bhowmik, T.D. Aka, Microwave assisted synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles in a noble approach: utilization for antibacterial and photocatalytic activity. SN Appl. Sci. 2, 1–14 (2020)
G. Richner, G. Puxty, Assessing the chemical speciation during CO2 absorption by aqueous amines using in situ FTIR. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51, 14317–14324 (2012)
A. Tasdemir, R. Aydin, A. Akkaya, N. Akman, Y. Altinay, H. Cetin, B. Sahin, A. Uzun, E. Ayyildiz, A green approach for the preparation of nanostructured zinc oxide: characterization and promising antibacterial behaviour. Ceram. Int. 47, 19362–19373 (2021)
J. Tauc, R. Grigorovici, A. Vancu, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 15, 627–637 (1966)
J. Tauc, Amorphous and Liquid Semiconductors (Plenum Press, New York, 1974)
S. Benramache, Y. Aoun, S. Lakel, B. Benhaoua, The effect of film thickness on the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by ultrasonic spray deposition. Mater. Res. Express 6, 126418 (2019)
H. Ben Saâd, M. Ajili, S. Dabbabi, N.T. Kamoun, Investigation on thickness and annealing effects on physical properties and electrical circuit model of CuO sprayed thin films. Superlattice Microst. 142, 106508 (2020)
F.S. Kodeh, T.M. Hammad, Influence of surfactants on the optical properties of WO3 nanoparticles synthesis by precipitation method. Biomed. J. of Sci. Tech. Res. 28, 21907–21912 (2020)
T.S. Tripathi, I. Terasaki, M. Karppinen, Anomalous thickness-dependent optical energy gap of ALD-grown ultra-thin CuO films. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 28, 475801 (2016)
G.G. Welegergs, H.G. Gebretnisae, M.G. Tsegay, Z.Y. Nuru, S. Dube, M. Maaza, Thickness dependent morphological, structural and optical properties of SS/CuO nanocoatings as selective solar absorber. Infrared Phys. Techn. 113, 103619 (2021)
G. Kaur, A. Mitra, K.L. Yadav, Pulsed laser deposited Al-doped ZnO thin films for optical applications. Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int. 25, 12–21 (2015)
H. Cavusoglu, R. Aydin, Complexing agent triethanolamine mediated synthesis of nanocrystalline CuO thin films at room temperature via SILAR technique. Superlattice Microst. 128, 37–47 (2019)
L. De Los Santos Valladares, D.H. Salinas, A.B. Dominguez, D.A. Najarro, S.I. Khondaker, T. Mitrelias, C.H.W. Barnes, J.A. Aguiar, Y. Majima, Crystallization and electrical resistivity of Cu2O and CuO obtained by thermal oxidation of Cu thin films on SiO2/Si substrates, Thin Solid Films, 520 6368-6374 (2012)
B. Şahin, T. Kaya, Highly improved hydration level sensing properties of copper oxide films with sodium and potassium doping. Appl. Surf. Sci. 362, 532–537 (2016)
S. Dinç, B. Şahin, T. Kaya, Improved sensing response of nanostructured CuO thin films towards sweat rate monitoring: Effect of Cr doping. Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 105, 104698 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akkaya, A., Kahveci, O., Aydın, R. et al. Amplifying main physical characteristics of CuO films using ascorbic acid as the reducer and stabilizer agent. Appl. Phys. A 127, 911 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05078-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05078-4