Abstract
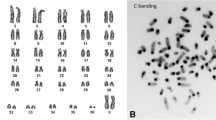
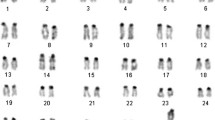
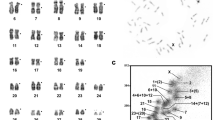
Microdissected arm specific paints (ASPs) for human (HSA) chromosomes (Chrs) 2, 5, 6, 16, and 19 were used as probes on pig (SSC) and horse (ECA) metaphase chromosomes. Regions homologous to individual human arms were delineated in the two species studied. Of the ten ASPs used, HSA6 and 16 ASPs showed complete synteny conservation of individual arms as single blocks/arms both in pig and horse. A similar trend was, in general, also observed for HSA19 ASPs. However, contrary to these observations, synteny conservation of individual arms of HSA2 and HSA5 was not observed in pig and horse. The arm specific painting data, coupled with the available gene mapping data, showed that, although HSA2 corresponded to two arms/chromosomes each in pig and horse, the breakpoint of this synteny in humans was not located at the centromere, but at HSA2q13 band. Similarly, arm specific paints for HSA5 showed that of the two blocks/chromosomes painted in pig and horse, one corresponded to HSA5q13-pter, the other to HSA5q13-qter. The findings suggest that 5q13 band may also be an evolutionary break point, similar to the one detected on HSA2q13. The microdissected human arm specific painting probes used in the present work provide more accurate and refined comparative information on pig and horse chromosomes than that available through the use of human whole chromosome specific paints.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold N, Stanyon R, Jauch A, O’Brien P, Wienberg J (1996) Identification of complex chromosome rearrangements in the gibbon by fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) of a human chromosome 2q specific microlibrary, yeast artificial chromosomes, and reciprocal chromosome painting. Cytogenet Cell Genet 74, 80–85
Avarello R, Pedicini A, Caiulo A, Zuffardi O, Fraccaro M (1992) Evidence for an ancestral alphoid domain on the long arm of human chromosome 2. Hum Genet 89, 247–249
BovMap: http://locus.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/bovmap/intro.pl
Bruch J, Rettenberger G, Leeb T, Meier-Ewert S, Klett C, Brenig B, Hameister H (1996) Mapping of type I loci from human chromosome 7 reveals segments of conserved synteny on pig chromosomes 3, 9, and 18. Cytogenet Cell Genet 73, 164–167
Chowdhary BP (1997) Cytogenetics and physical gene mapping. In Genetics of Pig M Rothschild, A Ruvinsky, eds.—: CAB International, pp xx–xx
Chowdhary BP, Ellegren H, Johansson M, Andersson L, Gustavasson I (1994) In situ hybridization mapping of the growth hormone receptor (GHR) gene assigns a linkage group (C9, FSA, GHR, and S0105) to Chromosome 16 in pigs. Mamm Genome 5, 160–162
Chowdhary BP, Frönicke L, Gustavsson I, Scherthan H (1996) Comparative analysis of the cattle and human genomes: detection of ZOO-FISH and gene mapping-based chromosomal homologies. Mamm Genome 7, 297–302
Frönicke L, Scherthan H (1997) Zoo-FISH analysis of human and Indian muntjac karyotypes (Muntiaws muntjak vaginalis) reveals satellite-DNA clusters at the margins of conserved syntenic segments. Chromosome Res. 5, 254–261
Frönicke L, Chowdhary BP, Scherthan H, Gustavsson I (1996) A comparative map of the porcine and human genomes demonstrates ZOO-FISH and gene mapping-based chromosomal homologies. Mamm Genome 7, 285–290
Frönicke L, Müller-Navia J, Romanakis K, Scherthan H (1997) Zoo-FISH maps of the harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) and the putative ancestral carnivore karyotype. Chromosoma 106, 108–113
GDB: http://www.hgmp.mrc.ac.uk/gdb7gdbtop.html
Goureau A, Yerle M, Schmitz A, Riquet J, Milan D, Pinton P, Frelat G, Gellin J (1996) Human and porcine correspondence of chromosome segments using bidirectional chromosome painting. Genomics 36, 252–262
Guan XY, Meltzer PS, Cao J, Trent JM (1992) Rapid generation of region-specific genomic clones by chromosome microdissection: isolation of DNA from a region frequently deleted in malignant melanoma. Genomics 14, 680–684
Guan XY, Trent JM, Meltzer PS (1993) Generation of band-specific painting probes from a single microdissected chromosome. Hum Mol Genet 2, 1117–1121
Guan XY, Meltzer PS, Trent JM (1994) Rapid generation of whole chromosome painting probes (WCPs) by chromosome microdissection. Genomics 22, 101–107
Hameister H, Klett Ch, Bruch J, Dixkens Ch, Vogel W, Christensen K (1997) Zoo-FISH analysis: the American mink (Mustela vison) closely resembles the cat karyotype. Chromosome Res 5, 5–11
Hayes H (1995) Chromosome painting with human chromosome-specific DNA libraries reveals the extent and distribution of conserved segments in bovine chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 71, 168–174
Ijdo JW, Baldini A, Wells RA, Ward DC, Reeders ST (1992) FRA2B is distinct from inverted telomere repeat arrays at 2q13. Genomics 12, 833–835
Lyons LA, Raymond MM, O’Brien SJ (1994) Comparative genomics: the next generation. Anim Biotechnol 5, 103–111
Mellink C, Lahbib-Mansais Y, Yerle M, Gellin J (1994) Mapping of the regulatory type I alpha and catalytic beta subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and interleukin 1 alpha and 1 beta in the pig. Mamm Genome 5, 298–302
Meltzer PS, Guan XY, Burgess A, Trent J (1992) Rapid generation of region specific probes by chromosome microdissection and their application. Nature Genet 1, 24–28
Millon LV, Bowling AT, Bickel LA (1993) Fluorescence in situ hybridization of C3 and 18SrDNA to horse chromosomes. Proc. 8th North American Colloq. on Domestic Animal Cytogenetics and Gene Mapping, Guelph, p. 163
Müller S, Koehler U, Wienberg J, Marzella R, Finelli P, Antonacci R, Rocchi M, Archidiacono N (1996) Comparative fluorescence in situ hybridization mapping of primate chromosomes with Alu polymerase chain reaction generated probes from human/rodent cell hybrids. Chromosome Res 4, 38–42
Raudsepp T, Frönicke L, Scherthan H, Gustavsson I, Chowdhary BP (1996). Zoo-FISH delineates conserved chromosomal segments between horse and man. Chromosome Res 4, 218–225
Rettenberger G, Klett Ch, Zechner U, Bruch J, Just W, Vogel W, Hameister H (1995a) Zoo-FISH analysis: cat and human karyotypes closely resemble the putative ancestral mammalian karyotype. Chromosome Res 3, 479–486
Rettenberger G, Klett C, Zechner U, Kunz J, Vogl W, Hameister H. (1995b) Visualization of the conservation of synteny between humans and pigs by heterologous chromosomal painting. Genomics 26, 372–378
Rettenberger G, Abdo G, Stranzinger G (1996) ZOO-FISH analysis in the horse, Equus caballus, detects regions homologous to human chromosomes 3 and 14. J Anim Breed Genet 113, 145–148
Scherthan H, Cremer T, Arnason U, Weier H-U, Lima-de-Faria A, Frönicke L (1994) Comparative chromosome painting discloses homologous segments in distantly related mammals. Nature Genet 6, 342–347
Solinas-Toldo S, Lengauer C, Fries R (1995) Comparative genome map of human and cattle. Genomics 27, 489–496
Telenius H, Pelmear A, Tunnacliffe A, Carter NP, Behmel A, Ferguson-Smith MA, Nordenskjold M, Pfragner R, Ponder B (1992) Cytogenetic analysis by chromosome painting using DOP-PCR amplified flow-sorted chromosomes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 4, 257–263
Viersbach R, Schwanitz G, Nöthen MM (1994) Delineation of marker chromosomes by reverse chromosome painting using only a small number of DOP-PCR amplified microdissected chromosomes. Hum Genet 93, 663–667
Wienberg J, Stanyon R (1995) Chromosome painting in mammals as an approach to comparative genomics. Curr Opin Genet Dev 5, 304–308
Wienberg J, Jauch A, Lüdecke H-J, Senger G, Horsthemke B, Claussen U, Cremer T, Arnold N, Lengauer C (1994) The origin of human chromosome 2 analyzed by comparative chromosome mapping with a DNA microlibrary. Chromosome Res 2, 405–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, R., Raudsepp, T., Guan, XY. et al. Zoo-FISH with microdissected arm specific paints for HSA2, 5, 6, 16, and 19 refines known homology with pig and horse chromosomes. Mammalian Genome 9, 44–49 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900677
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900677