Abstract.
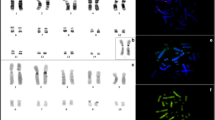
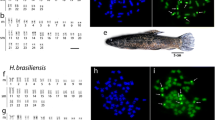
We report on the construction of the first comparative Zoo-FISH map of a marine mammal. Zoo-FISH with DNA probes from a human chromosome-specific library to metaphase spreads of the harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) disclosed 31 conserved syntenic segments covering the complete autosomal complement and the X chromosome. Comparison with Zoo-FISH maps of other species reveals that the harbor seal shares a high degree of karyotypic homeology with the human complement and an even higher degree with the conordinal cat complement. These findings suggest that pinniped, felid and human karyotypes have maintained conserved complements. Based on data of Zoo-FISH and comparative cytogenetics, a Zoo-FISH map of the ancestral carnivore karyotype (Z-CAR) is proposed. Flow cytometry revealed that the DNA value of the harbor seal genome is 79% that of the human genome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 October 1996; in revised form: 16 December 1996 / Accepted: 18 December 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frönicke, L., Müller-Navia, J., Romanakis, K. et al. Chromosomal homeologies between human, harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) and the putative ancestral carnivore karyotype revealed by Zoo-FISH. Chromosoma 106, 108–113 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004120050230
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004120050230