Abstract
Objective
To evaluate intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model-based liver lesion characterisation from three b-value diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI).
Methods
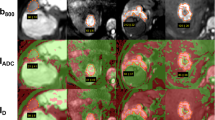
The 1.5-T DWI data from a respiratory gated spin-echo echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging sequence (b = 0, 50, 800 s/mm2) were retrospectively analysed in 38 patients with different liver lesions. Conventional apparent diffusion coefficient ADC = ADC(0,800) as well as IVIM-based parameters D′ = ADC(50,800), ADC_low = ADC(0,50), and f′ were calculated voxel-wise. Sixty-one regions of interest in hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs, n = 24), haemangiomas (HEMs, n = 11), focal nodular hyperplasias (FNHs, n = 11), and healthy liver tissue (REFs, n = 15) were analysed. Group differences were investigated using Student’s t-test and receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis.
Results
Mean values ± standard deviations of ADC, D′, ADC_low (in 10-5 mm2/s), and f′ (in %) for REFs/FNHs/HEMs/HCCs were 130 ± 11/143 ± 27/168 ± 16/113 ± 25, 104 ± 12/123 ± 25/162 ± 18/102 ± 23, 518 ± 66/437 ± 97/268 ± 69/283 ± 120, and 18 ± 3/14 ± 4/6 ± 3/9 ± 5, respectively. Differences between lesions and REFs were more significant for IVIM-based parameters than for conventional ADC. ROC analysis showed the best discriminability between HCCs and FNHs for ADC_low and f′ and between HEMs and FNHs or HCCs for D′.
Conclusion
Three instead of two b-value DWI enables a numerically stable and voxel-wise IVIM-based analysis for improved liver lesion characterisation with tolerable acquisition time.
Key Points
• Quantitative analysis of diffusion-weighted MRI helps liver lesion characterisation.
• Analysis of intravoxel incoherent motion is superior to apparent diffusion coefficient determination.
• Only three b-values enable separation of diffusion and microcirculation effects.
• The method presented is numerically stable, with voxel-wise results and short acquisition times.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padhani AR, Liu G, Koh DM et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: Consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 11:102–125
Taouli B, Koh DM (2010) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver. Radiology 254:47–66
Taouli B (2012) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging for liver lesion characterization: A critical look. Radiology 262:378–380
Sinkus R, Van Beers BE, Vilgrain V, DeSouza N, Waterton JC (2012) Apparent diffusion coefficient from magnetic resonance imaging as a biomarker in oncology drug development. Eur J Cancer 48:425–431
Takahara T, Kwee TC (2012) Low b-value diffusion-weighted imaging: Emerging applications in the body. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:1266–1273
Kwee TC, Takahara T (2011) Diffusion-weighted MRI for detecting liver metastases: Importance of the b-value. Eur Radiol 21:150
Goshima S, Kanematsu M, Kondo H et al (2008) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: Optimizing b value for the detection and characterization of benign and malignant hepatic lesions. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:691–697
Parikh T, Drew SJ, Lee VS et al (2008) Focal liver lesion detection and characterization with diffusion-weighted MR imaging: Comparison with standard breath-hold T2-weighted imaging. Radiology 246:812–822
Gourtsoyianni S, Papanikolaou N, Yarmenitis S, Maris T, Karantanas A, Gourtsoyiannis N (2008) Respiratory gated diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: value of apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in the differentiation between most commonly encountered benign and malignant focal liver lesions. Eur Radiol 18:486–492
Coenegrachts K, Delanote J, Ter BL et al (2007) Improved focal liver lesion detection: comparison of single-shot diffusion-weighted echoplanar and single-shot T2 weighted turbo spin echo techniques. Br J Radiol 80:524–531
Koh DM, Collins DJ, Orton MR (2011) Intravoxel incoherent motion in body diffusion-weighted MRI: reality and challenges. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:1351–1361
Guiu B, Cercueil JP (2011) Liver diffusion-weighted MR imaging: The tower of Babel? Eur Radiol 21:463–467
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: Application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161:401–407
Yamada I, Aung W, Himeno Y, Nakagawa T, Shibuya H (1999) Diffusion coefficients in abdominal organs and hepatic lesions: Evaluation with intravoxel incoherent motion echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 210:617–623
Le Bihan D (2008) Intravoxel incoherent motion perfusion MR imaging: A wake-up call. Radiology 249:748–752
Dyvorne HA, Galea N, Nevers T et al (2013) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver with multiple b values: Effect of diffusion gradient polarity and breathing acquisition on image quality and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters—a pilot study. Radiology 266:920–929
Andreou A, Koh DM, Collins DJ et al (2013) Measurement reproducibility of perfusion fraction and pseudodiffusion coefficient derived by intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging in normal liver and metastases. Eur Radiol 23:428–434
Leitao HS, Doblas S, D’Assignies G et al (2013) Fat deposition decreases diffusion parameters at MRI: a study in phantoms and patients with liver steatosis. Eur Radiol 23:461–467
Guiu B, Petit JM, Capitan V et al (2012) Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A 3.0-T MR study. Radiology 265:96–103
Lee JT, Liau J, Murphy P, Schroeder ME, Sirlin CB, Bydder M (2012) Cross-sectional investigation of correlation between hepatic steatosis and IVIM perfusion on MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 30:572–578
Dijkstra H, Baron P, Kappert P, Oudkerk M, Sijens PE (2012) Effects of microperfusion in hepatic diffusion weighted imaging. Eur Radiol 22:891–899
Lewin M, Arrive L, Lacombe C et al (2010) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of liver pathology: Principles and clinical applications. J Radiol 91:11–26
Luciani A, Vignaud A, Cavet M et al (2008) Liver cirrhosis: intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging–pilot study. Radiology 249:891–899
Patel J, Sigmund EE, Rusinek H, Oei M, Babb JS, Taouli B (2010) Diagnosis of cirrhosis with intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion MRI and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI alone and in combination: preliminary experience. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:589–600
Bruix J, Sherman M (2011) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology 53:1020–1022
Steudel A, Träber F, Reiser M (1993) Hepatic tumors: relaxometry and quantitative tissue characterization with magnetic resonance imaging. Frontiers Eur Radiol 9:45–61
Stanisz GJ, Odrobina EE, Pun J et al (2005) T1, T2 relaxation and magnetization transfer in tissue at 3T. Magn Reson Med 54:507–512
Lewin M, Fartoux L, Vignaud A, Arrive L, Menu Y, Rosmorduc O (2011) The diffusion-weighted imaging perfusion fraction f is a potential marker of sorafenib treatment in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A pilot study. Eur Radiol 21:281–290
Lemke A, Stieltjes B, Schad LR, Laun FB (2011) Toward an optimal distribution of b values for intravoxel incoherent motion imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 29:766–776
Cho GY, Kim S, Jensen JH, Storey P, Sodickson DK, Sigmund EE (2012) A versatile flow phantom for intravoxel incoherent motion MRI. Magn Reson Med 67:1710–1720
Koh DM, Blackledge M, Collins DJ et al (2009) Reproducibility and changes in the apparent diffusion coefficients of solid tumours treated with combretastatin A4 phosphate and bevacizumab in a two-centre phase I clinical trial. Eur Radiol 19:2728–2738
Coenegrachts K, Delanote J, Ter BL et al (2009) Evaluation of true diffusion, perfusion factor, and apparent diffusion coefficient in non-necrotic liver metastases and uncomplicated liver hemangiomas using black-blood echo planar imaging. Eur J Radiol 69:131–138
Schraml C, Schwenzer NF, Martirosian P et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted MRI of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma during sorafenib treatment: initial results. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:W301–W307
Bruegel M, Holzapfel K, Gaa J et al (2008) Characterization of focal liver lesions by ADC measurements using a respiratory triggered diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar MR imaging technique. Eur Radiol 18:477–485
Moteki T, Horikoshi H (2006) Evaluation of hepatic lesions and hepatic parenchyma using diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR with three values of gradient b-factor. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:637–645
Aoyagi T, Shuto K, Okazumi S et al (2012) Apparent diffusion coefficient correlation with oesophageal tumour stroma and angiogenesis. Eur Radiol 22:1172–1177
Le Bihan D, Turner R (1992) The capillary network: A link between IVIM and classical perfusion. Magn Reson Med 27:171–178
Duong TQ, Kim SG (2000) In vivo MR measurements of regional arterial and venous blood volume fractions in intact rat brain. Magn Reson Med 43:393–402
Coenegrachts K (2009) Magnetic resonance imaging of the liver: New imaging strategies for evaluating focal liver lesions. World J Radiol 1:72–85
Ichikawa T, Haradome H, Hachiya J, Nitatori T, Araki T (1998) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with a single-shot echoplanar sequence: Detection and characterization of focal hepatic lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170:397–402
Xing D, Papadakis NG, Huang CL, Lee VM, Carpenter TA, Hall LD (1997) Optimised diffusion-weighting for measurement of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in human brain. Magn Reson Imaging 15:771–784
Lemke A, Laun FB, Simon D, Stieltjes B, Schad LR (2010) An in vivo verification of the intravoxel incoherent motion effect in diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen. Magn Reson Med 64:1580–1585
Kartalis N, Loizou L, Edsborg N, Segersvard R, Albiin N (2012) Optimising diffusion-weighted MR imaging for demonstrating pancreatic cancer: A comparison of respiratory-triggered, free-breathing and breath-hold techniques. Eur Radiol 22:2186–2192
Taouli B, Sandberg A, Stemmer A et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: Comparison of navigator triggered and breathhold acquisitions. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:561–568
Kwee TC, Takahara T, Niwa T et al (2009) Influence of cardiac motion on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the liver. MAGMA 22:319–325
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Sekiguchi R, Kazama T, Nakajima H (2006) Measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient in the liver: Is it a reliable index for hepatic disease diagnosis? Radiat Med 24:438–444
Mürtz P, Flacke S, Träber F, van den Brink JS, Gieseke J, Schild HH (2002) Abdomen: diffusion-weighted MR imaging with pulse-triggered single-shot sequences. Radiology 224:258–264
Hollingsworth KG, Lomas DJ (2006) Influence of perfusion on hepatic MR diffusion measurement. NMR Biomed 19:231–235
Bilgili MY (2012) Reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficients measurements in diffusion-weighted MRI of the abdomen with different b values. Eur J Radiol 81:2066–2068
Rosenkrantz AB, Oei M, Babb JS, Niver BE, Taouli B (2011) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen at 3.0 Tesla: Image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient reproducibility compared with 1.5 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 33:128–135
Braithwaite AC, Dale BM, Boll DT, Merkle EM (2009) Short- and midterm reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficient measurements at 3.0-T diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen. Radiology 250:459–465
Kwee TC, Takahara T, Koh DM, Nievelstein RA, Luijten PR (2008) Comparison and reproducibility of ADC measurements in breathhold, respiratory triggered, and free-breathing diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:1141–1148
Kim SY, Soo LS, Bumwoo P et al (2012) Reproducibility of measurement of apparent diffusion coefficients of malignant hepatic tumors: Effect of DWI techniques and calculation methods. J Magn Reson Imaging 36:1131–1138
Kim SY, Lee SS, Byun JH et al (2010) Malignant hepatic tumors: short-term reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficients with breath-hold and respiratory-triggered diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 255:815–823
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penner, AH., Sprinkart, A.M., Kukuk, G.M. et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion model-based liver lesion characterisation from three b-value diffusion-weighted MRI. Eur Radiol 23, 2773–2783 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2869-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2869-z