Abstract
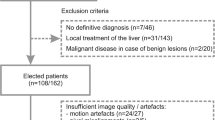
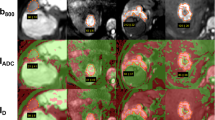
The aim of this study was to determine apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) of focal liver lesions on the basis of a respiratory triggered diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar MR imaging sequence (DW-SS-EPI) and to evaluate whether ADC measurements can be used to characterize lesions. One hundred and two patients with focal liver lesions [11 hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC), 82 metastases, 4 focal nodular hyperplasias (FNH), 56 hemangiomas and 51 cysts; mean size, 16.6 mm; range 5–92 mm] were examined on a 1.5-T system using respiratory triggered DW-SS-EPI (b-values: 50, 300, 600 s/mm2). Results were correlated with histopathologic data and follow-up imaging. The ADCs of different lesion types were compared, and lesion discrimination using optimal thresholds for ADCs was evaluated. Mean ADCs (×10−3mm2/s) were 1.24 and 1.04 for normal and cirrhotic liver parenchyma and 1.05, 1.22, 1.40, 1.92 and 3.02 for HCCs, metastases, FNHs, hemangiomas and cysts, respectively. Mean ADCs differed significantly for all lesion types except for comparison of metastases with HCCs and FNHs. Overall, 88% of lesions were correctly classified as benign or malignant using a threshold value of 1.63 × 10−3mm2/s. Measurements of the ADCs of focal liver lesions on the basis of a respiratory triggered DW-SS-EPI sequence may constitute a useful supplementary method for lesion characterization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ichikawa T, Haradome H, Hachiya J, Nitatori T, Araki T (1998) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with a single-shot echoplanar sequence: detection and characterization of focal hepatic lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170:397–402
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Nawano S et al (2006) Hepatic metastases: diffusion-weighted sensitivity-encoding versus SPIO-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 239:122–130
Okada Y, Ohtomo K, Kiryu S, Sasaki Y (1998) Breath-hold T2-weighted MRI of hepatic tumors: value of echo planar imaging with diffusion-sensitizing gradient. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22:364–371
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D et al (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Marks MP, de Crespigny A, Lentz D et al (1996) Acute and chronic stroke: navigated spin-echo diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 199:403–408
Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M et al (1999) Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:53–60
Bammer R (2003) Basic principles of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol 45:169–184
Turner R, Le Bihan D, Maier J et al (1990) Echo-planar imaging of intravoxel incoherent motion. Radiology 177:407–414
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F (2007) Extracranial applications of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol 17:1385–1393
Kim T, Murakami T, Takahashi S et al (1999) Diffusion-weighted single-shot echoplanar MR imaging for liver disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:393–398
Namimoto T, Yamashita Y, Sumi S, Tang Y, Takahashi M (1997) Focal liver masses: characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 204:739–744
Sun XJ, Quan XY, Huang FH, Xu YK (2005) Quantitative evaluation of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of focal hepatic lesions. World J Gastroenterol 11:6535–6537
Taouli B, Vilgrain V, Dumont E et al (2003) Evaluation of liver diffusion isotropy and characterization of focal hepatic lesions with two single-shot echo-planar MR imaging sequences: prospective study in 66 patients. Radiology 226:71–78
Yamada I, Aung W, Himeno Y, Nakagawa T, Shibuya H (1999) Diffusion coefficients in abdominal organs and hepatic lesions: evaluation with intravoxel incoherent motion echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 210:617–623
Amano Y, Kumazaki T, Ishihara M (1998) Single-shot diffusion-weighted echo-planar imaging of normal and cirrhotic livers using a phased-array multicoil. Acta Radiol 39:440–442
Ichikawa T, Haradome H, Hachiya J, Nitatori T, Araki T (1999) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with single-shot echo-planar imaging in the upper abdomen: preliminary clinical experience in 61 patients. Abdom Imaging 24:456–461
Deng J, Miller FH, Rhee TK et al (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging for determination of hepatocellular carcinoma response to yttrium-90 radioembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:1195–1200
Deng J, Rhee TK, Sato KT et al (2006) In vivo diffusion-weighted imaging of liver tumor necrosis in the VX2 rabbit model at 1.5 Tesla. Invest Radiol 41:410–414
Yoshikawa T, Kawamitsu H, Mitchell DG et al (2006) ADC measurement of abdominal organs and lesions using parallel imaging technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:1521–1530
Koh DM, Scurr E, Collins DJ et al (2006) Colorectal hepatic metastases: quantitative measurements using single-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Eur Radiol 16:1898–1905
Taouli B, Martin AJ, Qayyum A et al (2004) Parallel imaging and diffusion tensor imaging for diffusion-weighted MRI of the liver: preliminary experience in healthy volunteers. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:677–680
Bartolozzi C, Cioni D, Donati F, Lencioni R (2001) Focal liver lesions: MR imaging-pathologic correlation. Eur Radiol 11:1374–1388
Horton KM, Bluemke DA, Hruban RH, Soyer P, Fishman EK (1999) CT and MR imaging of benign hepatic and biliary tumors. Radiographics 19:431–451
Heid O (2000) Eddy Current-Nulled Diffusion Weighting. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 8: abstract number 799
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys 42:288–292
Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM et al (2002) Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med 47:1202–1210
Sandberg A, Parikh T, Johnson G, Stemmer A, Taouli B (2006) Feasibility of a respiratory-triggered SSEPI diffusion-weighted sequence for liver imaging using navigator echo technique: comparison with breath-hold diffusion-weighted sequence. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 14: abstract number 400
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Sekiguchi R, Nawano S (2006) The effect of simultaneous use of respiratory triggering in diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver. Magn Reson Med Sci 5:129–136
Mürtz P, Flacke S, Traber F et al (2002) Abdomen: diffusion-weighted MR imaging with pulse-triggered single-shot sequences. Radiology 224:258–264
Jones DK, Basser PJ (2004) “Squashing peanuts and smashing pumpkins”: how noise distorts diffusion-weighted MR data. Magn Reson Med 52:979–993
Chow LC, Bammer R, Moseley ME, Sommer FG (2003) Single breath-hold diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen. J Magn Reson Imaging 18:377–382
Müller MF, Prasad P, Siewert B et al (1994) Abdominal diffusion mapping with use of a whole-body echo-planar system. Radiology 190:475–478
Vilgrain V, Boulos L, Vullierme MP et al (2000) Imaging of atypical hemangiomas of the liver with pathologic correlation. Radiographics 20:379–397
Cieszanowski A, Szeszkowski W, Golebiowski M et al (2002) Discrimination of benign from malignant hepatic lesions based on their T2-relaxation times calculated from moderately T2-weighted turbo SE sequence. Eur Radiol 12:2273–2279
Farraher SW, Jara H, Chang KJ, Ozonoff A, Soto JA (2006) Differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic metastasis from cysts and hemangiomas with calculated T2 relaxation times and the T1/T2 relaxation times ratio. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:1333–1341
Fenlon HM, Tello R, DeCarvalho VL, Yucel EK (2000) Signal characteristics of focal liver lesions on double echo T2-weighted conventional spin echo MRI: observer performance versus quantitative measurements of T2 relaxation times. J Comput Assist Tomogr 24:204–211
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruegel, M., Holzapfel, K., Gaa, J. et al. Characterization of focal liver lesions by ADC measurements using a respiratory triggered diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar MR imaging technique. Eur Radiol 18, 477–485 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0785-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0785-9