Abstract
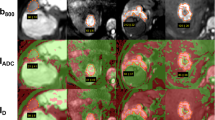
The purpose of this study was to measure apparent diffusion coefficient values of normal liver parenchyma and focal liver lesions utilizing a respiratory gated diffusion sequence with multiple b-values and to investigate whether apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) measurements may be utilized to characterize and differentiate between malignant and benign focal hepatic lesions. Thirty-eight consecutive patients underwent MRI of the liver including diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). A single-shot echo planar imaging sequence was applied in coronal orientation with multiple b-values (0, 50, 500, 1,000 s/mm2) and respiratory gating. ADC values were recorded on corresponding maps utilizing region of interest measurements in patients with benign (group A), malignant (group B) focal lesions and liver parenchyma (group C). Statistical analysis was applied to check whether differences in mean ADC values were significant (p<0.05). No focal lesions were detected in 11 patients, with a mean ADC value (CI 95%) of liver parenchyma 1.25×10−3 mm2/s (1.21×10−3 mm2/s−1.29×10−3 mm2/s). Differences in mean ADC of liver parenchyma between group A and B were not significant (p=0.054, 1.30×10−3 mm2/s and 1.31×10−3 mm2/s, respectively). Mean ADC value (95% CI) of 22 benign lesions found in 18 patients was 2.55×10−3 mm2/s (2.35×10−3 mm2/s−2.74×10−3 mm2/s), while the mean ADC value (95% CI) of 16 malignant lesions recorded in 9 patients was 1.04×10−3 mm2/s (0.9×10−3 mm2/s−1.17×10−3 mm2/s). The difference between mean ADC values of benign and malignant focal lesions was statistically significant (p<0.0001). Respiratory gated diffusion-weighted imaging in the liver is technically feasible. Apparent diffusion coefficient measurements can be useful in differentiating malignant from benign focal liver lesions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moseley ME, Kucharczyk J, Mintorovitch J et al (1990) Diffusion weighted MR imaging of acute stroke: correlation with T2-weighted and magnetic susceptibility-enhanced MR imaging in cats. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 11:423–429
Provenzale JM, Mukundan S, Barboriak DP (2006) Diffusion-weighted and perfusion MR imaging for brain tumor characterization and assessment of treatment response. Radiology 239(3):632–649
Dorenbeck U, Butz B, Schlaier J, Bretschneider T, Schuierer G, Feuerbach S (2003) Diffusion weighted echo-planar MRI of the brain with calculated ADCs: a useful tool in the differential diagnosis of tumor necrosis from abscess? J Neuroimaging 13(4):330–338
Tanimoto A, Nakashima J, Kohno H, Shinmoto H, Kuribayashi S (2007) Prostate cancer screening: the clinical value of diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic MR imaging in combination with T2-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 25(1):146–152
Matsuki M, Inada Y, Tatsugami F, Tanikake M, Narabayashi I, Katsuoka Y (2007) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging for urinary bladder carcinoma: initial results. Eur Radiol 17(1):201–204
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F (2007) Extracranial applications of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol 17(6):1385–1393
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Kuroki S, Murakami K, Nawano S, Moriyama N (2004) Diffusion-weighted single shot echo planar imaging of colorectal cancer using a sensitivity-encoding technique. Jpn J Clin Oncol 34(10):620–626
Squillaci E, Manenti G, Cova M, Di Roma M, Miano R, Palmieri G, Simonetti G (2004) Correlation of diffusion-weighted MR imaging with cellularity of renal tumours. Anticancer Res 24(6):4175–4179
Yoshikawa T, Kawamitsu H, Mitchell DG, Ohno Y, Ku Y, Seo Y, Fujii M, Sugimura K (2006) ADC measurement of abdominal organs and lesions using parallel imaging technique. Am J Roentgenol 187(6):1521–1530
Yamada I, Aung W, Himeno Y, Nakagawa T, Shibuya H (1999) Diffusion coefficients in abdominal organs and hepatic lesions: evaluation with intravoxel incoherent motion echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 210:617–623
Kim T, Murakami T, Takahashi S, Hori M, Tsuda K, Nakamura H (1999) Diffusion-weighted single-shot echoplanar MR imaging for liver disease. Am J Roentgenol 173:393–398
Semelka RC, Martin DR, Balci C, Lance T (2001) Focal liver lesions: comparison of dual-phase CT and multisequence multiplanar MR imaging including dynamic gadolinium enhancement. J Magn Reson Imaging 13(3):397–401
Pirovano G, Vanzulli A, Marti-Bonmati L, Grazioli L, Manfredi R, Greco A, Holzknecht N, Daldrup-Link HE, Rummeny E, Hamm B, Arneson V, Imperatori L, Kirchin MA, Spinazzi A (2000) Evaluation of the accuracy of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR imaging in the detection and characterization of focal liver lesions. Am J Roentgenol 175(4):1111–1120
Matsuo M, Kanematsu M, Inaba Y, Matsueda K, Yamagami T, Kondo H, Arai Y, Hoshi H (2001) Pre-operative detection of malignant hepatic tumours: value of combined helical CT during arterial portography and biphasic CT during hepatic arteriography. Clin Radiol 56(2):138–145
von Herbay A, Vogt C, Haussinger D (2004) Differentiation between benign and malignant hepatic lesions: utility of color stimulated acoustic emission with the microbubble contrast agent Levovist. J Ultrasound Med 23(2):207–215
Koh DM, Scurr E, Collins DJ, Pirgon A, Kanber B, Karanjia N, Brown G, Leach MO, Husband JE (2006) Colorectal hepatic metastases: quantitative measurements using single-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Eur Radiol 16(9):1898–1905
Taouli B, Vilgrain V, Dumont E, Daire JL, Fan B, Menu Y (2003) Evaluation of liver diffusion isotropy and characterization of focal hepatic lesions with two single-shot echo-planar MR imaging sequences: prospective study in 66 patients. Radiology 226(1):71–78
Theilmann RJ, Borders R, Trouard TP, Xia G, Outwater E, Ranger-Moore J, Gillies RJ, Stopeck A (2004) Changes in water mobility measured by diffusion MRI predict response of metastatic breast cancer to chemotherapy. Neoplasia 6(6):831–837
Szafer A, Zhong J, Anderson AW, Gore JC (1995) Diffusion-weighted imaging in tissues: theoretical models. NMR Biomed 8:289–296
Namimoto T, Yamashita Y, Sumi S, Tang Y, Takahashi M (1997) Focal liver masses: characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 204:739–744
Ichikawa T, Haradome H, Hachiya J, Nitatori T, Araki T (1998) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with a single-shot echoplanar sequence: detection and characterization of focal hepatic lesions. Am J Roentgenol 170:397–402
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gourtsoyianni, S., Papanikolaou, N., Yarmenitis, S. et al. Respiratory gated diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: value of apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in the differentiation between most commonly encountered benign and malignant focal liver lesions. Eur Radiol 18, 486–492 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0798-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0798-4