Abstract
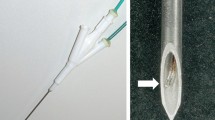
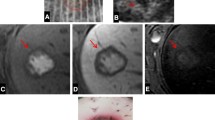
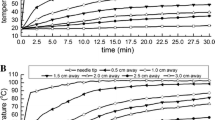
The aim of this study was to test the efficacy of four different radio-frequency ablation (RFA) systems in normal hepatic parenchyma in large animals. The RFA was applied to pig livers in vivo and to calf livers ex vivo using the Radionics cluster needle, RITA starburst XL needle, Radiotherapeutics Le Veen 4.0 needle, and the Berchtold 14-G saline-perfused 15-mm active-tip needle based on constructor specifications. The volume of tissue coagulation from RF was calculated from measurements of the vertical diameter (Dv) and transverse diameter (Dt). Lesion shape was characterized using the ratio between Dt/Dv. Radiotherapeutics and RITA produced in vivo lesion volume of 42±10, 39±4 cm3 with a reproducible spherical shape (Dt/Dv of 1.01±0.16 and 0.97±0.1, respectively). Radionics produced in vivo RF lesions volume of 29±11 cm3 with an ovoid shape (Dt/Dv 0.88±0.09). The RF lesions with the Berchtold device could not be assessed in vivo as 5 of 8 animals died during treatment. Ex vivo RF lesions had similar volumes with each system; however, the Radiotherapeutics device produced more reproducible shaped lesions than the other systems. In our experimental study, we found no difference between expandable needle systems in vivo. Cooled needles produced slightly smaller and ovoid shape in vivo lesions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldberg SN, Dupuy DE (2001) Image-guided radiofrequency tumor ablation: challenges and opportunities, part I. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12:1021–1032
McGahan JP, Griffey SM, Budenz RW, Brock JM (1995) Percutaneous ultrasound-guided radiofrequency electrocautery ablation of prostate tissue in dogs. Acad Radiol 2:61–65
de Baere T, Denys A, Johns-Wood B et al. (2001) Radiofrequency liver ablation: experimental comparative study of water—cooled vs expandable systems. Am J Roentgenol 176:187–192
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Solbiati L, Rittman WJ, Mueller PR (1996) Radiofrequency tissue ablation: increased lesion diameter with a perfusion electrode. Acad Radiol 3:636–644
Goldberg SN, Hahn PF, Tanabe KK et al. (1998) Percutaneous radiofrequency tissue ablation: Does perfusion-mediated tissue cooling limit coagulation necrosis? J Vasc Interv Radiol 9:101–111
Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Hahn PF et al. (1998) Large-volume tissue ablation with radiofrequency by using a clustered, internally-cooled electrode technique: laboratory and clinical experience in liver metastases. Radiology 209:371–379
Curley SA, Izzo F, Delrio P et al. (1999) Radiofrequency ablation of unresectable primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies: results in 123 patients (see comments). Ann Surg 230:1–8
Curley SA, Izzo F, Ellis LM, Nicolas-Vauthey J, Vallone P (2000) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg 232:381–391
Goldberg SN, Stein MC, Gazelle GS, Sheiman RG, Kruskal JB, Clouse ME (1999) Percutaneous radiofrequency tissue ablation: optimization of pulsed radiofrequency technique to increase coagulation necrosis. J Vasc Interv Radiol 10:907–916
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S et al. (2000) Hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology 214:761–768
Gangi A, Dupas B, Guth S et al. (2001) Application des électrodes humides de radiofréquence dans le traitement des tumeurs hépatiques. J Radiol 82:1430
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Monti F et al. (1997) Saline-enhanced radio-frequency tissue ablation in the treatment of liver metastases. Radiology 202:205–210
Miao Y, Ni Y, Mulier S et al. (1997) Ex-vivo experiment on radiofrequency liver ablation with saline infusion through a screw-tip cannulated electrode. J Surg Res 71:19–24
Goldberg SN, Ahmed M, Gazelle GS et al. (2001) Radio-frequency thermal ablation with NaCl solution injection: effect of electrical conductivity on tissue heating and coagulation-phantom and porcine liver study. Radiology 219:157–165
Denys AL, de Baere T, Mahe C et al. (2001) Radiofrequency tissue ablation of the liver: effects of vascular occlusion on lesion diameter and biliary and portal damages in a pig model. Eur Radiol 11:2102–2108
Goldberg S, Hahn P, Halpern E, Fogle R, Gazelle G (1998) Radiofrequency tissue ablation: effect of pharmacologic modulation of blood flow on coagulation diameter. Radiology 209:761–767
Acknowledgement We thank P. Frascarolo for his precious help in the statistical evaluation of our results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Denys, A.L., Baere, T.D., Kuoch, V. et al. Radio-frequency tissue ablation of the liver: in vivo and ex vivo experiments with four different systems. Eur Radiol 13, 2346–2352 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-1970-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-1970-0