Abstract
Key message
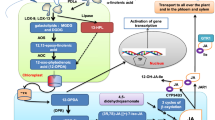
We review the recent progress on ABA signaling, especially ABA signaling for ABA-dependent gene expression, including the AREB/ABF regulon, SnRK2 protein kinase, 2C-type protein phosphatases and ABA receptors.
Abstract
Drought negatively impacts plant growth and the productivity of crops. Drought causes osmotic stress to organisms, and the osmotic stress causes dehydration in plant cells. Abscisic acid (ABA) is produced under osmotic stress conditions, and it plays an important role in the stress response and tolerance of plants. ABA regulates many genes under osmotic stress conditions. It also regulates gene expression during seed development and germination. The ABA-responsive element (ABRE) is the major cis-element for ABA-responsive gene expression. ABRE-binding protein (AREB)/ABRE-binding factor (ABF) transcription factors (TFs) regulate ABRE-dependent gene expression. Other TFs are also involved in ABA-responsive gene expression. SNF1-related protein kinases 2 are the key regulators of ABA signaling including the AREB/ABF regulon. Recently, ABA receptors and group A 2C-type protein phosphatases were shown to govern the ABA signaling pathway. Moreover, recent studies have suggested that there are interactions between the major ABA signaling pathway and other signaling factors in stress-response and seed development. The control of the expression of ABA signaling factors may improve tolerance to environmental stresses.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- ABC transporter:
-
ATP-binding cassette transporter
- ABI1/2/3/4/5:
-
ABA insensitive 1/2/3/4/5
- ABRE:
-
ABA-responsive element
- AHG1/3:
-
ABA hypersensitive germination 1/3
- AP2/ERF:
-
APETALA 2/ethylene-responsive element binding factor
- AREB:
-
ABRE-binding protein
- CRT:
-
C-repeat
- CBF:
-
CRT binding factor
- CE:
-
Coupling element
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- CPK:
-
Calcium-dependent protein kinase
- DRE:
-
Dehydration-responsive element
- DREB:
-
DRE-binding protein
- GA:
-
Gibberellin
- HAB1/2:
-
Homology to ABA 1/2
- HSP:
-
Heat shock protein
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- LEA:
-
Late embryogenesis abundant
- NAC:
-
NAM, ATAF, and CUC
- PYR1:
-
Pyrabactin resistance 1
- PYL:
-
PYR1-like
- SnRK2:
-
SNF1-related protein kinase 2
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
- PP2C:
-
2C-type protein phosphatase
- RCAR1:
-
Regulatory component of ABA receptor 1
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
References
Acevedo-Hernandez GJ, Leon P, Herrera-Estrella LR (2005) Sugar and ABA responsiveness of a minimal RBCS light-responsive unit is mediated by direct binding of ABI4. Plant J 43:506–519
Antoni R, Gonzalez-Guzman M, Rodriguez L, Rodrigues A, Pizzio GA, Rodriguez PL (2012) Selective inhibition of clade A phosphatases type 2C by PYR/PYL/RCAR abscisic acid receptors. Plant Physiol 158:970–980
Bensmihen S, Rippa S, Lambert G, Jublot D, Pautot V, Granier F, Giraudat J, Parcy F (2002) The homologous ABI5 and EEL transcription factors function antagonistically to fine-tune gene expression during late embryogenesis. Plant Cell 14:1391–1403
Bensmihen S, Giraudat J, Parcy F (2005) Characterization of three homologous basic leucine zipper transcription factors (bZIP) of the ABI5 family during Arabidopsis thaliana embryo maturation. J Exp Bot 56:597–603
Bhaskara GB, Nguyen TT, Verslues PE (2012) Unique drought resistance functions of the highly ABA-induced clade A protein phosphatase 2Cs. Plant Physiol 160:379–395
Bossi F, Cordoba E, Dupre P, Mendoza MS, Roman CS, Leon P (2009) The Arabidopsis ABA-INSENSITIVE (ABI) 4 factor acts as a central transcription activator of the expression of its own gene, and for the induction of ABI5 and SBE2.2 genes during sugar signaling. Plant J 59:359–374
Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Lauriere C (2004) Identification of nine sucrose nonfermenting 1-related protein kinases 2 activated by hyperosmotic and saline stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 279:41758–41766
Brocard-Gifford IM, Lynch TJ, Finkelstein RR (2003) Regulatory networks in seeds integrating developmental, abscisic acid, sugar, and light signaling. Plant Physiol 131:78–92
Bucholc M, Ciesielski A, Goch G, Anielska-Mazur A, Kulik A, Krzywinska E, Dobrowolska G (2011) SNF1-related protein kinases 2 are negatively regulated by a plant-specific calcium sensor. J Biol Chem 286:3429–3441
Chakrabortee S, Boschetti C, Walton LJ, Sarkar S, Rubinsztein DC, Tunnacliffe A (2007) Hydrophilic protein associated with desiccation tolerance exhibits broad protein stabilization function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:18073-18078
Chan Z (2012) Expression profiling of ABA pathway transcripts indicates crosstalk between abiotic and biotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Genomics 100:110–115
Chen YH, Hu L, Punta M, Bruni R, Hillerich B, Kloss B, Rost B, Love J, Siegelbaum SA, Hendrickson WA (2010) Homologue structure of the SLAC1 anion channel for closing stomata in leaves. Nature. 467:1074–1080
Choi HI, Park HJ, Park JH, Kim S, Im MY, Seo HH, Kim YW, Hwang I, Kim SY (2005) Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase AtCPK32 interacts with ABF4, a transcriptional regulator of abscisic acid-responsive gene expression, and modulates its activity. Plant Physiol 139:1750–1761
Cutler SR, Rodriguez PL, Finkelstein RR, Abrams SR (2010) Abscisic acid: emergence of a core signaling network. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:651–679
Dupeux F, Santiago J, Betz K, Twycross J, Park SY, Rodriguez L, Gonzalez-Guzman M, Jensen MR, Krasnogor N, Blackledge M, Holdsworth M, Cutler SR, Rodriguez PL, Marquez JA (2011) A thermodynamic switch modulates abscisic acid receptor sensitivity. EMBO J 30:4171–4184
Endo A, Koshiba T, Kamiya Y, Nambara E (2008) Vascular system is a node of systemic stress responses: competence of the cell to synthesize abscisic acid and its responsiveness to external cues. Plant Signal Behav 3:1138–1140
Fan J, Hill L, Crooks C, Doerner P, Lamb C (2009) Abscisic acid has a key role in modulating diverse plant-pathogen interactions. Plant Physiol 150:1750–1761
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SS, Rock CD (2002) Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell 14 Suppl: S15–S45
Finkelstein R, Lynch T, Reeves W, Petitfils M, Mostachetti M (2011) Accumulation of the transcription factor ABA-insensitive (ABI)4 is tightly regulated post-transcriptionally. J Exp Bot 62:3971–3979
Fujii H, Zhu JK (2009) Arabidopsis mutant deficient in 3 abscisic acid-activated protein kinases reveals critical roles in growth, reproduction, and stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:8380–8385
Fujii H, Verslues PE, Zhu JK (2007) Identification of two protein kinases required for abscisic acid regulation of seed germination, root growth, and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:485–494
Fujii H, Chinnusamy V, Rodrigues A, Rubio S, Antoni R, Park SY, Cutler SR, Sheen J, Rodriguez PL, Zhu JK (2009) In vitro reconstitution of an abscisic acid signalling pathway. Nature 462:660–664
Fujii H, Verslues PE, Zhu JK (2011) Arabidopsis decuple mutant reveals the importance of SnRK2 kinases in osmotic stress responses in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:1717–1722
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Maruyama K, Seki M, Hiratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, Tran LS, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2004) A dehydration-induced NAC protein, RD26, is involved in a novel ABA-dependent stress-signaling pathway. Plant J 39:863–876
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Noutoshi Y, Takahashi F, Narusaka Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Crosstalk between abiotic and biotic stress responses: a current view from the points of convergence in the stress signaling networks. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:436–442
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Satoh R, Maruyama K, Parvez MM, Seki M, Hiratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2005) AREB1 is a transcription activator of novel ABRE-dependent ABA signaling that enhances drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:3470–3488
Fujita Y, Nakashima K, Yoshida T, Katagiri T, Kidokoro S, Kanamori N, Umezawa T, Fujita M, Maruyama K, Ishiyama K, Kobayashi M, Nakasone S, Yamada K, Ito T, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009) Three SnRK2 protein kinases are the main positive regulators of abscisic acid signaling in response to water stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 50:2123–2132
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011) ABA-mediated transcriptional regulation in response to osmotic stress in plants. J Plant Res 124:509–525
Fujita Y, Yoshida T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2013) Pivotal role of the AREB/ABF-SnRK2 pathway in ABRE-mediated transcription in response to osmotic stress in plants. Physiol Plant 147:15–27
Furihata T, Maruyama K, Fujita Y, Umezawa T, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Abscisic acid-dependent multisite phosphorylation regulates the activity of a transcription activator AREB1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:1988–1993
Geiger D, Scherzer S, Mumm P, Stange A, Marten I, Bauer H, Ache P, Matschi S, Liese A, Al-Rasheid KA, Romeis T, Hedrich R (2009) Activity of guard cell anion channel SLAC1 is controlled by drought-stress signaling kinase-phosphatase pair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:21425–21430
Gonzalez-Guzman M, Pizzio GA, Antoni R, Vera-Sirera F, Merilo E, Bassel GW, Fernandez MA, Holdsworth MJ, Perez-Amador MA, Kollist H, Rodriguez PL (2012) Arabidopsis PYR/PYL/RCAR receptors play a major role in quantitative regulation of stomatal aperture and transcriptional response to abscisic acid. Plant Cell 24:2483–2496
Hirayama T, Shinozaki K (2007) Perception and transduction of abscisic acid signals: keys to the function of the versatile plant hormone ABA. Trends Plant Sci 12:343–351
Hobo T, Kowyama Y, Hattori T (1999) A bZIP factor, TRAB1, interacts with VP1 and mediates abscisic acid-induced transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:15348–15353
Johnson RR, Wagner RL, Verhey SD, Walker-Simmons MK (2002) The abscisic acid-responsive kinase PKABA1 interacts with a seed-specific abscisic acid response element-binding factor, TaABF, and phosphorylates TaABF peptide sequences. Plant Physiol 130:837–846
Kagaya Y, Hobo T, Murata M, Ban A, Hattori T (2002) Abscisic acid-induced transcription is mediated by phosphorylation of an abscisic acid response element binding factor, TRAB1. Plant Cell 14:3177–3189
Kang JY, Choi HI, Im MY, Kim SY (2002) Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper proteins that mediate stress-responsive abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 14:343–357
Kang J, Hwang JU, Lee M, Kim YY, Assmann SM, Martinoia E, Lee Y (2010) PDR-type ABC transporter mediates cellular uptake of the phytohormone abscisic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:2355–2360
Kim S, Kang JY, Cho DI, Park JH, Kim SY (2004) ABF2, an ABRE-binding bZIP factor, is an essential component of glucose signaling and its overexpression affects multiple stress tolerance. Plant J 40:75–87
Kim TH, Bohmer M, Hu H, Nishimura N, Schroeder JI (2010) Guard cell signal transduction network: advances in understanding abscisic acid, CO2, and Ca2+ signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:561–591
Kim JS, Mizoi J, Yoshida T, Fujita Y, Nakajima J, Ohori T, Todaka D, Nakashima K, Hirayama T, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011a) An ABRE promoter sequence is involved in osmotic stress-responsive expression of the DREB2A gene, which encodes a transcription factor regulating drought-inducible genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 52:2136–2146
Kim TH, Hauser F, Ha T, Xue S, Bohmer M, Nishimura N, Munemasa S, Hubbard K, Peine N, Lee BH, Lee S, Robert N, Parker JE, Schroeder JI (2011b) Chemical genetics reveals negative regulation of abscisic acid signaling by a plant immune response pathway. Curr Biol 21:990–997
Kim H, Hwang H, Hong JW, Lee YN, Ahn IP, Yoon IS, Yoo SD, Lee S, Lee SC, Kim BG (2012) A rice orthologue of the ABA receptor, OsPYL/RCAR5, is a positive regulator of the ABA signal transduction pathway in seed germination and early seedling growth. J Exp Bot 63:1013–1024
Klingler JP, Batelli G, Zhu JK (2010) ABA receptors: the START of a new paradigm in phytohormone signalling. J Exp Bot 61:3199–3210
Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto S, Minami H, Kagaya Y, Hattori T (2004) Differential activation of the rice sucrose nonfermenting1-related protein kinase2 family by hyperosmotic stress and abscisic acid. Plant Cell 16:1163–1177
Kobayashi Y, Murata M, Minami H, Yamamoto S, Kagaya Y, Hobo T, Yamamoto A, Hattori T (2005) Abscisic acid-activated SNRK2 protein kinases function in the gene-regulation pathway of ABA signal transduction by phosphorylating ABA response element-binding factors. Plant J 44:939–949
Kuromori T, Miyaji T, Yabuuchi H, Shimizu H, Sugimoto E, Kamiya A, Moriyama Y, Shinozaki K (2010) ABC transporter AtABCG25 is involved in abscisic acid transport and responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:2361–2366
Kuromori T, Sugimoto E, Shinozaki K (2011) Arabidopsis mutants of AtABCG22, an ABC transporter gene, increase water transpiration and drought susceptibility. Plant J 67:885–894
Lee KH, Piao HL, Kim HY, Choi SM, Jiang F, Hartung W, Hwang I, Kwak JM, Lee IJ (2006) Activation of glucosidase via stress-induced polymerization rapidly increases active pools of abscisic acid. Cell 126:1109–1120
Lee SC, Lan W-Z, Buchanan BB, Luan S (2009) A protein kinase-phosphatase pair interacts with an ion channel to regulate ABA signaling in plant guard cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:21419–21424
Lee SJ, Kang JY, Park HJ, Kim MD, Bae MS, Choi HI, Kim SY (2010) DREB2C interacts with ABF2, a bZIP protein regulating abscisic acid-responsive gene expression, and its overexpression affects abscisic acid sensitivity. Plant Physiol 153:716–727
Lopez-Molina L, Mongrand S, Chua NH (2001) A postgermination developmental arrest checkpoint is mediated by abscisic acid and requires the ABI5 transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4782–4787
Lu QS, Paz JD, Pathmanathan A, Chiu RS, Tsai AY, Gazzarrini S (2010) The C-terminal domain of FUSCA3 negatively regulates mRNA and protein levels, and mediates sensitivity to the hormones abscisic acid and gibberellic acid in Arabidopsis. Plant J 64:100–113
Luerssen H, Kirik V, Herrmann P, Misera S (1998) FUSCA3 encodes a protein with a conserved VP1/AB13-like B3 domain which is of functional importance for the regulation of seed maturation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 15:755–764
Lynch T, Erickson BJ, Finkelstein RR (2012) Direct interactions of ABA-insensitive(ABI)-clade protein phosphatase(PP)2Cs with calcium-dependent protein kinases and ABA response element-binding bZIPs may contribute to turning off ABA response. Plant Mol Biol 80:647–658
Ma Y, Szostkiewicz I, Korte A, Moes D, Yang Y, Christmann A, Grill E (2009) Regulators of PP2C phosphatase activity function as abscisic acid sensors. Science 324:1064–1068
Martinez-Andujar C, Ordiz MI, Huang Z, Nonogaki M, Beachy RN, Nonogaki H (2011) Induction of 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase in Arabidopsis thaliana seeds enhances seed dormancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:17225–17229
Maruyama K, Todaka D, Mizoi J, Yoshida T, Kidokoro S, Matsukura S, Takasaki H, Sakurai T, Yamamoto YY, Yoshiwara K, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2012) Identification of cis-acting promoter elements in cold- and dehydration-induced transcriptional pathways in Arabidopsis, rice, and soybean. DNA Res 19:37–49
Mauch-Mani B, Mauch F (2005) The role of abscisic acid in plant-pathogen interactions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:409–414
Melcher K, Ng LM, Zhou XE, Soon FF, Xu Y, Suino-Powell KM, Park SY, Weiner JJ, Fujii H, Chinnusamy V, Kovach A, Li J, Wang Y, Peterson FC, Jensen DR, Yong EL, Volkman BF, Cutler SR, Zhu JK, Xu HE (2009) A gate-latch-lock mechanism for hormone signalling by abscisic acid receptors. Nature 462:602–608
Miyazono K, Miyakawa T, Sawano Y, Kubota K, Kang HJ, Asano A, Miyauchi Y, Takahashi M, Zhi Y, Fujita Y, Yoshida T, Kodaira KS, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Tanokura M (2009) Structural basis of abscisic acid signalling. Nature 462:609–614
Mizoguchi M, Umezawa T, Nakashima K, Kidokoro S, Takasaki H, Fujita Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2010) Two closely related subclass II SnRK2 protein kinases cooperatively regulate drought-inducible gene expression. Plant Cell Physiol 51:842–847
Mustilli AC, Merlot S, Vavasseur A, Fenzi F, Giraudat J (2002) Arabidopsis OST1 protein kinase mediates the regulation of stomatal aperture by abscisic acid and acts upstream of reactive oxygen species production. Plant Cell 14:3089–3099
Nakabayashi K, Okamoto M, Koshiba T, Kamiya Y, Nambara E (2005) Genome-wide profiling of stored mRNA in Arabidopsis thaliana seed germination: epigenetic and genetic regulation of transcription in seed. Plant J 41:697–709
Nakamura S, Lynch TJ, Finkelstein RR (2001) Physical interactions between ABA response loci of Arabidopsis. Plant J 26:627–635
Nakashima K, Fujita Y, Katsura K, Maruyama K, Narusaka Y, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulation of ABI3- and ABA-responsive genes including RD29B and RD29A in seeds, germinating embryos, and seedlings of Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 60:51–68
Nakashima K, Fujita Y, Kanamori N, Katagiri T, Umezawa T, Kidokoro S, Maruyama K, Yoshida T, Ishiyama K, Kobayashi M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009a) Three Arabidopsis SnRK2 protein kinases, SRK2D/SnRK2.2, SRK2E/SnRK2.6/OST1 and SRK2I/SnRK2.3, involved in ABA signaling are essential for the control of seed development and dormancy. Plant Cell Physiol 50:1345–1363
Nakashima K, Ito Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009b) Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiol 149:88–95
Nakashima K, Takasaki H, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2012) NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819:97–103
Nambara E, Marion-Poll A (2005) Abscisic acid biosynthesis and catabolism. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:165–185
Narusaka Y, Nakashima K, Shinwari ZK, Sakuma Y, Furihata T, Abe H, Narusaka M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Interaction between two cis-acting elements, ABRE and DRE, in ABA-dependent expression of Arabidopsis rd29A gene in response to dehydration and high-salinity stresses. Plant J 34:137–148
Negi J, Matsuda O, Nagasawa T, Oba Y, Takahashi H, Kawai-Yamada M, Uchimiya H, Hashimoto M, Iba K (2008) CO2 regulator SLAC1 and its homologues are essential for anion homeostasis in plant cells. Nature 452:483–486
Nishimura N, Hitomi K, Arvai AS, Rambo RP, Hitomi C, Cutler SR, Schroeder JI, Getzoff ED (2009) Structural mechanism of abscisic acid binding and signaling by dimeric PYR1. Science 326:1373–1379
Niu X, Helentjaris T, Bate NJ (2002) Maize ABI4 binds coupling element1 in abscisic acid and sugar response genes. Plant Cell 14:2565–2575
Okamoto M, Tanaka Y, Abrams SR, Kamiya Y, Seki M, Nambara E (2009) High humidity induces abscisic acid 8′-hydroxylase in stomata and vasculature to regulate local and systemic abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 149:825–834
Park SY, Fung P, Nishimura N, Jensen DR, Fujii H, Zhao Y, Lumba S, Santiago J, Rodrigues A, Chow TF, Alfred SE, Bonetta D, Finkelstein R, Provart NJ, Desveaux D, Rodriguez PL, McCourt P, Zhu JK, Schroeder JI, Volkman BF, Cutler SR (2009) Abscisic acid inhibits type 2C protein phosphatases via the PYR/PYL family of START proteins. Science 324:1068–1071
Pilot G, Lacombe B, Gaymard F, Cherel I, Boucherez J, Thibaud JB, Sentenac H (2001) Guard cell inward K+ channel activity in Arabidopsis involves expression of the twin channel subunits KAT1 and KAT2. J Biol Chem 276:3215–3221
Piskurewicz U, Jikumaru Y, Kinoshita N, Nambara E, Kamiya Y, Lopez-Molina L (2008) The gibberellic acid signaling repressor RGL2 inhibits Arabidopsis seed germination by stimulating abscisic acid synthesis and ABI5 activity. Plant Cell 20:2729–2745
Raghavendra AS, Gonugunta VK, Christmann A, Grill E (2010) ABA perception and signalling. Trends Plant Sci 15:395–401
Reeves WM, Lynch TJ, Mobin R, Finkelstein RR (2011) Direct targets of the transcription factors ABA-Insensitive(ABI)4 and ABI5 reveal synergistic action by ABI4 and several bZIP ABA response factors. Plant Mol Biol 75:347–363
Santiago J, Dupeux F, Round A, Antoni R, Park SY, Jamin M, Cutler SR, Rodriguez PL, Marquez JA (2009) The abscisic acid receptor PYR1 in complex with abscisic acid. Nature 462:665–668
Sato A, Sato Y, Fukao Y, Fujiwara M, Umezawa T, Shinozaki K, Hibi T, Taniguchi M, Miyake H, Goto DB, Uozumi N (2009) Threonine at position 306 of the KAT1 potassium channel is essential for channel activity and is a target site for ABA-activated SnRK2/OST1/SnRK2.6 protein kinase. Biochem J 424:438–448
Schachtman DP, Goodger JQ (2008) Chemical root to shoot signaling under drought. Trends Plant Sci 13:281–287
Singh A, Giri J, Kapoor S, Tyagi AK, Pandey GK (2010) Protein phosphatase complement in rice: genome-wide identification and transcriptional analysis under abiotic stress conditions and reproductive development. BMC Genomics 11:435
Sirichandra C, Gu D, Hu HC, Davanture M, Lee S, Djaoui M, Valot B, Zivy M, Leung J, Merlot S, Kwak JM (2009) Phosphorylation of the Arabidopsis AtrbohF NADPH oxidase by OST1 protein kinase. FEBS Lett 583:2982–2986
Soon FF, Ng LM, Zhou XE, West GM, Kovach A, Tan MH, Suino-Powell KM, He Y, Xu Y, Chalmers MJ, Brunzelle JS, Zhang H, Yang H, Jiang H, Li J, Yong EL, Cutler S, Zhu JK, Griffin PR, Melcher K, Xu HE (2012) Molecular mimicry regulates ABA signaling by SnRK2 kinases and PP2C phosphatases. Science 335:85–88
Stone SL, Kwong LW, Yee KM, Pelletier J, Lepiniec L, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (2001) LEAFY COTYLEDON2 encodes a B3 domain transcription factor that induces embryo development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11806–11811
Tran LS, Nakashima K, Sakuma Y, Simpson SD, Fujita Y, Maruyama K, Fujita M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2004) Isolation and functional analysis of Arabidopsis stress-inducible NAC transcription factors that bind to a drought-responsive cis-element in the early responsive to dehydration stress 1 promoter. Plant Cell 16:2481–2498
Umezawa T, Sugiyama N, Mizoguchi M, Hayashi S, Myouga F, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Ishihama Y, Hirayama T, Shinozaki K (2009) Type 2C protein phosphatases directly regulate abscisic acid-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:17588–17593
Umezawa T, Nakashima K, Miyakawa T, Kuromori T, Tanokura M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2010) Molecular basis of the core regulatory network in ABA responses: sensing, signaling and transport. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1821–1839
Uno Y, Furihata T, Abe H, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid-dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11632–11637
Vahisalu T, Kollist H, Wang YF, Nishimura N, Chan WY, Valerio G, Lamminmaki A, Brosche M, Moldau H, Desikan R, Schroeder JI, Kangasjarvi J (2008) SLAC1 is required for plant guard cell S-type anion channel function in stomatal signalling. Nature 452:487–491
Weiner JJ, Peterson FC, Volkman BF, Cutler SR (2010) Structural and functional insights into core ABA signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:495–502
Wilkinson S, Davies WJ (2010) Drought, ozone, ABA and ethylene: new insights from cell to plant to community. Plant Cell Environ 33:510–525
Wind JJ, Peviani A, Snel B, Hanson J, Smeekens SC (2012) ABI4: versatile activator and repressor. Trends Plant Sci 148:1938–1952
Xiang Y, Tang N, Du H, Ye H, Xiong L (2008) Characterization of OsbZIP23 as a key player of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family for conferring abscisic acid sensitivity and salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol 148:1938–1952
Xue T, Wang D, Zhang S, Ehlting J, Ni F, Jakab S, Zheng C, Zhong Y (2008) Genome-wide and expression analysis of protein phosphatase 2C in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Genomics. 9:550
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Yasuda M, Ishikawa A, Jikumaru Y, Seki M, Umezawa T, Asami T, Maruyama-Nakashita A, Kudo T, Shinozaki K, Yoshida S, Nakashita H (2008) Antagonistic interaction between systemic acquired resistance and the abscisic acid-mediated abiotic stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:1678–1692
Yin P, Fan H, Hao Q, Yuan X, Wu D, Pang Y, Yan C, Li W, Wang J, Yan N (2009) Structural insights into the mechanism of abscisic acid signaling by PYL proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:1230–1236
Yoshida R, Hobo T, Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Takahashi F, Aronso J, Ecker JR, Shinozaki K (2002) ABA-activated SnRK2 protein kinase is required for dehydration stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1473–1483
Yoshida R, Umezawa T, Mizoguchi T, Takahashi S, Takahashi F, Shinozaki K (2006) The regulatory domain of SRK2E/OST1/SnRK2.6 interacts with ABI1 and integrates abscisic acid (ABA) and osmotic stress signals controlling stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 281:5310–5318
Yoshida T, Fujita Y, Sayama H, Kidokoro S, Maruyama K, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2010) AREB1, AREB2, and ABF3 are master transcription factors that cooperatively regulate ABRE-dependent ABA signaling involved in drought stress tolerance and require ABA for full activation. Plant J 61:672–685
Zhang X, Garreton V, Chua NH (2005) The AIP2 E3 ligase acts as a novel negative regulator of ABA signaling by promoting ABI3 degradation. Genes Dev 19:1532–1543
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Maki Katsuhara, Okayama University, Japan and Dr. Satoshi Tobita of JIRCAS for helpful comments. We thank Masami Toyoshima for skillful editorial assistance. Research in our laboratory was supported by the Program for Promotion of Basic and Applied Researches for Innovations in Bio-oriented Industry (BRAIN); the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF); the Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS) of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST)/Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA); Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Kumar.
A contribution to the Special Issue: Plant Hormone Signaling.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakashima, K., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. ABA signaling in stress-response and seed development. Plant Cell Rep 32, 959–970 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1418-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1418-1