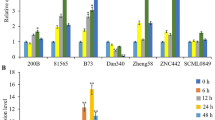
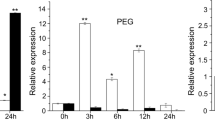
Abstract
NAC proteins are plant-specific transcription factors that play essential roles in stress responses. However, only little information regarding stress-related NAC genes is available in maize. In this study, a maize NAC gene, ZmSNAC1, was cloned and functionally characterized. Expression analysis revealed that ZmSNAC1 was strongly induced by low temperature, high-salinity, drought stress, and abscisic acid (ABA) treatment, but downregulated by salicylic acid treatment. Subcellular localization experiments in Arabidopsis protoplast cells indicated that ZmSNAC1 was localized in the nucleus. Transactivation assays demonstrated that ZmSNAC1 functioned as a transcriptional activator. Overexpression of ZmSNAC1 in Arabidopsis led to hypersensitivity to ABA and osmotic stress at the germination stage, but enhanced tolerance to dehydration compared to wild-type seedlings. These results suggest that ZmSNAC1 functions as a stress-responsive transcription factor in positive modulation of abiotic stress tolerance, and may have applications in the engineering of drought-tolerant crops.
Key message ZmSNAC1 functioned as a stress-responsive transcription factor in response to abiotic stresses, and might be useful for crop tolerance improvement.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- NAC:
-
NAM, ATAF1/2 and CUC2
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- MeJA:
-
Methyl jasmonic acid
- SNAC:
-
Stress responsive NAC
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- 2, 4-D:
-
2, 4 Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- CaMV:
-
Cauliflower mosaic virus
- UTR:
-
Untranslated regions
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeats
References
Aida M, Ishida T, Fukaki H, Fujisawa H, Tasaka M (1997) Genes involved in organ separation in Arabidopsis: an analysis of the cup-shaped cotyledon mutant. Plant Cell 9:841–857
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Delessert C, Kazan K, Wilson IW, Van Der Straeten D, Manners J, Dennisand ES, Dolferus R (2005) The transcription factor ATAF2 represses the expression of pathogenesis-related genes in Arabidopsis. Plant J 43:745–757
Duval M, Hsieh TF, Kim SY, Thomas TL (2002) Molecular characterization of AtNAM: a member of the Arabidopsis NAC domain superfamily. Plant Mol Biol 50:237–248
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Maruyama K, Seki M, Hiratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, Tran LS, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2004) A dehydration-induced NAC protein, RD26, is involved in a novel ABA-dependent stress-signaling pathway. Plant J 39:863–876
Gao F, Xiong AS, Peng RH, Jin XF, Xu J, Zhu B, Chen JM, Yao QH (2010) OsNAC52, a rice NAC transcription factor, potentially responds to ABA and confers drought tolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 100:255–262
Hao YJ, Wei W, Song QX, Chen HW, Zhang YQ, Wang F, Zou HF, Lei G, Tian AG, Zhang WK, Ma B, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2011) Soybean NAC transcription factors promote abiotic stress tolerance and lateral root formation in transgenic plants. Plant J 68:302–313
Hu HH, Dai MQ, Yao JL, Xiao BZ, Li XH, Zhang QF, Xiong LZ (2006) Overexpressing a NAM, ATAF, and CUC (NAC) transcription factor enhances drought resistance and salt tolerance in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 35:12987–12992
Hu HH, You J, Fang YJ, Zhu XY, Qi ZY, Xiong LZ (2008) Characterization of transcription factor gene SNAC2 conferring cold and salt tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 67:169–181
Jeong JS, Kim YS, Baek KH, Jung H, Ha Sun-Hwa, Choi YD, Kim M, Reuzeau C, Kim JK (2010) Root-specific expression of OsNAC10 improves drought tolerance and grain yield in rice under field drought conditions. Plant Physiol 153:185–197
Kikuchi K, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Yoshida TK, Nagato Y, Matsusoka M, Hirano HY (1999) Molecular analysis of the NAC gene family in rice. Mol Gen Genet 262:1047–1051
Lata C, Prasad M (2011) Role of DREBs in regulation of abiotic stress responses in plants. J Exp Bot 62:4731–4748
Le DT, Nishiyama R, Watanabe Y, Watanabe Y, Mochida K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K, Tran LS (2011) Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of the plant-specific NAC transcription factor family in soybean during development and dehydration stress. DNA Res 18:263–276
Liu ZJ, Shao FX, Tang GY, Shan L, Bi YP (2009) Cloning and characterization of a transcription factor ZmNAC1 in maize (Zea mays). Hereditas (Beijing) 31:199–205
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆DDCt method. Methods 25:402–408
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nakashima K, Ito Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009) Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiol 149:88–95
Nakashima K, Takasaki H, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011) NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819:97–103
Nuruzzaman M, Manimekalai R, Sharoni AM, Satoh K, Kondoh H, Ooka H, Kikuchi S (2010) Genome-wide analysis of NAC transcription factor family in rice. Gene 465:30–44
Olsen AN, Ernst HA, Leggio LL, Skriver K (2005) NAC transcription factors: structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends Plant Sci 10:79–87
Ooka H, Satoh K, Doi K, Nagata T, Otomo Y, Murakami K (2003) Comprehensive analysis of NAC family genes in Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana. DNA Res 10:239–247
Qin F, Kakimoto M, Sakuma Y, Maruyama K, Osakabe Y, Tran LS, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2007) Regulation and functional analysis of ZmDREB2A in response to drought and heat stresses in Zea mays L. Plant J 50:54–69
Qin F, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011) Achievements and challenges in understanding plant abiotic stress responses and tolerance. Plant Cell Physiol 52:1569–1582
Riechmann JL, Heard J, Martin G, Reuber L, Jiang CZ, Keddie J, Pineda O, Ratcliffe OJ, Samaha RR, Adam L, Creelman R, Pilgrim M, Broun P, Zhang JZ, Ghandehari D, Sherman BK, Yu GL (2000) Arabidopsis transcription factors, genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 290:2105–2110
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Selth LA, Dogra SC, Rasheed MS, Healy H, Randles JW, Rezaian MA (2005) A NAC domain protein interacts with tomato leaf curl virus replication accessory protein and enhances viral replication. Plant Cell 17:311–325
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2007) Gene networks involved in drought stress response and tolerance. J Exp Bot 58:221–227
Song SY, Chen Y, Chen J, Dai XY, Zhang WH (2011) Physiological mechanisms underlying OsNAC5-dependent tolerance of rice plants to abiotic stress. Planta 234:331–345
Souer E, van Houwelingen A, Kloos D, Mol J, Koes R (1996) The no apical meristem gene of Petunia is required for pattern formation in embryos and flowers and is expressed at meristem and primordia boundaries. Cell 85:159–170
Takasaki H, Maruyama K, Kidokoro S, Ito Y, Fujita Y, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Nakashima K (2010) The abiotic stress-responsive NAC-type transcription factor OsNAC5 regulates stress-inducible genes and stress tolerance in rice. Mol Genet Gen 284:173–183
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (b) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTALX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tran LS, Nakashima K, Sakuma Y, Simpson SD, Fujita Y, Maruyama K, Fujita M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2004) Isolation and functional analysis of Arabidopsis stress inducible NAC transcription factors that bind to a drought responsive cis-element in the early responsive to dehydration stress. Plant Cell 16:2481–2498
Tran LS, Nishiyama R, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2010) Potential utilization of NAC transcription factors to enhance abiotic stress tolerance in plants by biotechnological approach. GM Crops 1:32–39
Verslues PE, Agarwal M, Katiyar-Agarwal S, Zhu JH, Zhu JK (2006) Methods and concepts in quantifying resistance to drought, salt and freezing, abiotic stresses that affect plant water status. Plant J 45:523–539
Verza NC, Figueira TRS, Sousa SM, Arruda P (2010) Transcription factor profiling identifies an aleurone-preferred NAC family member involved in maize seed development. Ann Appl Biol 158:115–129
Xia N, Zhang G, Sun YF, Zhu L, Xu LS, Chen XM, Liu B, Yu YT, Wang XJ, Huang LL, Kang ZS (2010) TaNAC8, a novel NAC transcription factor gene in wheat, responds to stripe rust pathogen infection and abiotic stresses. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 74:394–402
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Yokotani N, Ichikawa T, Kondou Y, Matsui M, Hirochika H, Iwabuchi M, Oda K (2009) Tolerance to various environmental stresses conferred by the salt-responsive rice gene ONAC063 in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 229:1065–1075
Yoon HK, Kim SG, Kim SY, Park CM (2008) Regulation of leaf senescence by NTL9-mediated osmotic stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cells 25:438–445
Zhang H, Jin J, Tang L, Zhao Y, Gu X, Luo J (2011) PlantTFDB 2.0: update and improvement of the comprehensive plant transcription factor database. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D1114–D1117
Zheng XN, Chen B, Lu GJ, Han B (2009) Overexpression of a NAC transcription factor enhances rice drought and salt tolerance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:985–989
Zimmermann R, Werr W (2005) Pattern formation in the monocot embryo as revealed by NAM and CUC3 orthologues from Zea mays L. Plant Mol Biol 58:669–685
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Feng Qin (Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for providing the pGreen-GFP-N vector and Dr. Fang-pu Han (Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for using Zeiss LSM 710 confocal laser scanning system. We really appreciate the anonymous reviewers’ helpful comments and suggestions. This work was partly supported by grants provided by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2012AA10A306, 2009CB118400) and China Natural Science Foundation (U1138304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by K. Wang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, M., Ying, S., Zhang, DF. et al. A maize stress-responsive NAC transcription factor, ZmSNAC1, confers enhanced tolerance to dehydration in transgenic Arabidopsis . Plant Cell Rep 31, 1701–1711 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1284-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1284-2