Abstract
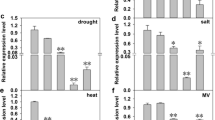
CaRma1H1, an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-localized hot pepper really interesting new genes (RING) E3 Ub ligase, was previously reported to be a positive regulator of drought stress responses. To address the possibility that CaRma1H1 can be used to improve tolerance to abiotic stress in crop plants, CaRma1H1 was constitutively expressed in transgenic tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) plants. CaRma1H1-overexpressing tomato plants (35S:CaRma1H1) exhibited greatly enhanced tolerance to high-salinity treatments compared with wild-type plants. Leaf chlorophyll and proline contents in CaRma1H1 overexpressors were 4.3- to 8.5-fold and 1.2- to 1.5-fold higher, respectively, than in wild-type plants after 300 mM NaCl treatment. Transgenic cotyledons developed and their roots elongated in the presence of NaCl up to 200 mM. In addition, 35S:CaRma1H1 lines were markedly more tolerant to severe drought stress than were wild-type plants. Detached leaves of CaRma1H1 overexpressors preserved water more efficiently than did wild-type leaves during a rapid dehydration process. The ER chaperone genes LePDIL1, LeBIP1, and LeCNX1 were markedly up-regulated in 35S:CaRma1H1 tomatoes compared with wild-type plants. Therefore, overexpression of CaRma1H1 may enhance tomato plant ER responses to drought stress by effectively removing nonfunctional ubiquitinated proteins. Collectively, constitutive expression of CaRma1H1 in tomatoes conferrred strongly enhanced tolerance to salt- and water-stress. This raises the possibility that CaRma1H1 may be useful for developing abiotic stress-tolerant tomato plants.
Key message CaRma1H1 increases drought tolerance in transgenic tomato plants.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- RING:
-
Really interesting new genes
- Ub:
-
Ubiquitin
References
Bae H, Kim SK, Cho SK, Kang BG, Kim WT (2011) Overexpression of OsRDCP1, a rice RING domain-containing E3 ubiquitin ligase, increased tolerance to drought stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci 180:775–782
Bhatnagar-Mathur P, Vadez V, Sharma K (2008) Transgenic approaches for abiotic stress tolerance in plants: retrospect and prospects. Plant Cell Rep 27:411–424
Boyer JS (1982) Plant productivity and environment. Science 218:443–448
Cho SK, Ryu MY, Seo DH, Kang BG, Kim WT (2011) The Arabidopsis RING E3 ubiquitin ligase AtAIRP2 plays combinatory roles with AtAIRP1 in ABA-mediated drought stress responses. Plant Physiol 157:2240–2257
Choi JY, Seo YS, Kim SJ, Kim WT, Shin JS (2011) Constitutive expression of CaXTH3, a hot pepper xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase, enhanced tolerance to salt and drought stresses without phenotypic defects in tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum cv. Dotaerang). Plant Cell Rep 30:869–877
Claussen W (2005) Proline as a measure of stress in tomato plants. Plant Sci 168:241–248
Cuartero J, Bolarin M, Asins M, Moreno V (2006) Increasing salt tolerance in the tomato. J Exp Bot 57:1045–1058
Cushman JC, Bohnert HJ (2000) Genomic approaches to plant stress tolerance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:117–124
Deikman J, Petracek M, Heard JH (2012) Drought tolerance through biotechnology: improving translation from the laboratory to farmers’ fields. Curr Opin Biotechnol 23:243–250
Foolad M (2004) Recent advances in genetics of salt tolerance in tomato. Plant Cell Tiss Org 76:101–119
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Noutoshi Y, Takahashi F, Narusaka Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Crosstalk between abiotic and biotic stress responses: a current view from the points of convergence in the stress signaling networks. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:436–442
Ko JH, Yang SH, Han KH (2006) Upregulation of an Arabidopsis RING-H2 gene, XERICO, confers drought tolerance through increased abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant J 47:343–355
Lee JH, Kim WT (2011) Regulation of abiotic stress signal transduction by E3 ubiquitin ligases in Arabidopsis. Mol Cells 31:201–208
Lee HK, Cho SK, Son O, Xu Z, Hwang IH, Kim WT (2009) Drought stress-induced Rma1H1, a RING membrane-anchor E3 ubiquitin ligase homolog, regulates aquaporin levels via ubiquitination in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell 21:622–641
Li H, Jiang H, Bu Q, Zhao Q, Sun J, Xie Q, Li C (2011) The Arabidopsis RING finger E3 ligase RHA2b acts additively with RHA2a in regulating abscisic acid signaling and drought response. Plant Physiol 156:550–563
Liu H, Zhang H, Yang Y, Li G, Yang Y, Wang X, Basnayake BM, Li D, Song F (2008) Functional analysis reveals pleiotropic effects of rice RING-H2 finger protein gene OsBIRF1 on regulation of growth and defense responses against abiotic and biotic stresses. Plant Mol Biol 68:17–30
Liu L, Cui F, Li Q, Yin B, Zhang H, Lin B, Wu Y, Xia R, Tang S, Xie Q (2011) The endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation is necessary for plant salt tolerance. Cell Res 21:957–969
Lyzenga WJ, Stone SL (2012) Abiotic stress tolerance mediated by protein ubiquitination. J Exp Bot 63:599–616
Park GG, Park JJ, Yoon J, Yu SN, An G (2010) A RING finger E3 ligase gene, Oryza sativa Delayed Seed Germination 1 (OsDSG1), controls seed germination and stress responses in rice. Plant Mol Biol 74:467–478
Ryu MY, Cho SK, Kim WT (2010) The Arabidopsis C3H2C3-type RING E3 ubiquitin ligase AtAIRP1 is a positive regulator of an ABA-dependent response to drought stress. Plant Physiol 154:1983–1997
Seo YS, Kim SJ, Harn CH, Kim WT (2011) Ectopic expression of apple fruit homogentisate phytyltransferase gene (MdHPT1) increases tocopherol in transgenic tomato (Solanum lycopersicum cv. Micro-Tom) leaves and fruits. Phytochemistry 72:321–329
Wang WX, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14
Yoo CY, Pence HE, Hasegawa PM, Mickelbart MV (2009) Regulation of transpiration to improve crop water use. Critical Rev Plant Sci 28:410–431
Zhang JX, Klueva NY, Wang Z, Wu R, Ho THD, Nguyen HT (2000) Genetic engineering for abiotic stress resistance in crop plants. In Vitro Cell Dev Pl 36:108–114
Zhang Y, Yang C, Li Y, Zheng N, Chen H, Zhao Q, Gao T, Guo H, Xie Q (2007) SDIR1 is a RING finger E3 ligase that positively regulates stress-responsive abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:1912–1929
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the National Center for GM Crops (Project No. PJ008152) of the Next Generation BioGreen 21 Program funded by the Rural Development Administration and the National Research Foundation (Project No. 2010-0000782), Republic of Korea, to W.T.K. and by a Grant from the Next Generation BioGreen21 Program (PJ008198) funded by the Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea, to J.S.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by J. R. Liu.
Y. S. Seo and J. Y. Choi contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, Y.S., Choi, J.Y., Kim, S.J. et al. Constitutive expression of CaRma1H1, a hot pepper ER-localized RING E3 ubiquitin ligase, increases tolerance to drought and salt stresses in transgenic tomato plants. Plant Cell Rep 31, 1659–1665 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1278-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1278-0