Abstract
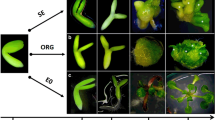
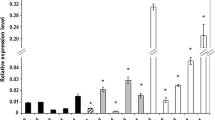
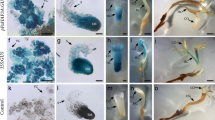
The expression pattern of the LEC2 gene during somatic embryogenesis (SE) in Arabidopsis explants (immature zygotic embryos) induced in vitro was followed, using real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR). The analysis revealed differential expression of LEC2 transcripts within a 30 days time course of somatic embryo development. A significant auxin-dependent upregulation of the LEC2 gene was found to be associated with the induction phase of SE. In contrast to embryogenic culture the level of LEC2 expression was noticeably lower in non-embryogenic callus of Col-0 and hormonal mutants (cbp20 and axr4-1) with low SE-efficiency. The study with 35S::LEC2-GR transgenic plants showed that overexpression of LEC2 can compensate for the auxin requirement, and that transgenic explants formed somatic embryos when cultured in vitro under auxin-free conditions. However, unlike in auxin-induced SE, intense callus formation preceded the embryogenic response triggered via LEC2 overexpression, suggesting an indirect pathway of morphogenesis. Moreover, a negative interaction between auxin treatment and LEC2 overexpression in terms of SE efficiency was observed, as transgenic explants cultured on auxin medium displayed a significantly reduced level of embryogenic potential. The study provides further experimental evidence that in the determination of the embryogenic response in Arabidopsis somatic cells, a close link exists between auxin and the LEC2 activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- DEX:
-
Dexamethasone
- E:
-
Induction medium
- IZE:
-
Immature zygotic embryo
- SAM:
-
Shoot apical meristem
- SE:
-
Somatic embryogenesis
- SLS:
-
Shoot-like structures
- ZE:
-
Zygotic embryogenesis
References
Baud S, Mendoza MS, To A, Harscoët E, Lepiniec L, Dubreucq B (2007) WRINKLED1 specifies the regulatory action of LEAFY COTYLEDON2 towards fatty acid metabolism during seed maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 50:825–838
Boutilier K, Offringa R, Sharma VK, Kieft H, Ouellet T, Zhang L, Hattori J, Liu C-M, van Lammeren AAM, Miki BLA, Custers JBM, van Lookeren Compagne MM (2002) Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryonic growth. Plant Cell 14:1737–1749
Braybrook SA, Harada JJ (2008) LECs go crazy in embryo development. Trends Plant Sci 13:624–630
Braybrook SA, Stone SL, Park S, Bui AQ, Le BH, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (2006) Genes directly regulated by LEAFY COTYLEDON2 provide insight into the control of embryo maturation and somatic embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:3468–3473
Che P, Love TM, Frame BR, Wang K, Carriquiry AL, Howell SH (2006) Gene expression pattern during somatic embryo development and germination in maize Hi II callus cultures. Plant Mol Biol 62:1–14
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Curaba J, Moritz T, Blervaque R, Parcy F, Raz V, Herzog M, Vachon G (2004) AtGA3ox2, a key gene responsible for bioactive gibberellin biosynthesis, is regulated during embryogenesis by LEAFY COTYLEDON2 and FUSCA3 in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 136:3660–3669
Dharmasiri S, Swarup R, Mockaitis K, Dharmasiri N, Singh SK, Kowalchyk M, Marchant A, Mills S, Sandberg G, Bennett MJ, Estelle M (2006) AXR4 is required for localization of the auxin influx facilitator AUX1. Science 312:218–220
Feher A, Pasternak TP, Dudits D (2003) Transition of somatic plant cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74:201–228
Gaj MD (2001a) Direct somatic embryogenesis as a rapid and efficient system for in vitro regeneration of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 64:39–46
Gaj MD (2001b) Somatic embryogenesis in in vitro cultures of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. (in Polish with English summary) Monograph of Silesian University, No. 1970. Silesian University, Katowice, Poland
Gaj MD (2004) Factors influencing somatic embryogenesis induction and plant regeneration with particular reference to Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Growth Regul 43:27–47
Gaj MD, Zhang S, Harada JJ, Lemaux PG (2005) LEAFY COTYLEDON genes are essential for induction of somatic embryogenesis of Arabidopsis. Planta 222:977–988
Gaj MD, Trojanowska A, Ujczak A, Mędrek M, Kozioł A, Garbaciak B (2006) Hormone-response mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. impaired in somatic embryogenesis. Plant Growth Regul 49:183–197
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirement of suspension culture of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Gill R, Saxena PK (1993) Somatic embryogenesis in Nicotiana tabacum L.: induction by thidiazuron of direct embryo differentiation from culture leaf disc. Plant Cell Rep 12:154–159
Giraudat J, Hauge BM, Valon C, Smalle J, Parcy F, Goodman HM (1992) Isolation of the Arabidopsis ABI3 gene by positional cloning. Plant Cell 4:1251–1261
Harada JJ (2001) Role of Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON genes in seed development. J Plant Physiol 158:405–409
Harding EW, Tang W, Nichols KW, Fernandez DE, Perry SE (2003) Expression and maintenance of embryogenic potential is enhanced through constitutive expression of AGAMOUS-Like15. Plant Physiol 133:653–663
Hecht V, Vielle-Calzada J-P, Hartog MV, Schmidt ED, Boutilier K, Grossniklaus U, de Vries SC (2001) The Arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE1 gene is expressed in developing ovules and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in culture. Plant Physiol 127:803–816
Henderson JT, Li HCH, Rider SD, Mordhorst AP, Romero-Severson J, Cheng JCH, Robey J, Sung ZR, de Vries SC, Ogas J (2004) PICKLE acts through the plant to repress expression of embryonic traits and may play a role in gibberellin-dependent responses. Plant Physiol 134:995–1005
Hobbie L, Estelle M (1995) The axr4 auxin-resistant mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana define a gene important for root gravitropism and lateral root initiation. Plant J 7:211–220
Ikeda-Iwai M, Umehara M, Satoh S, Kamada H (2003) Stress-induced somatic embryogenesis in vegetative tissues of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 34:107–114
Jimenez VM (2005) Involvement of plant hormones and plant growth regulators on in vitro somatic embryogenesis. Plant Growth Regul 47:91–110
Kikuchi A, Sanuki N, Higashi K, Koshiba T, Kamada H (2006) Abscisic acid and stress treatment are essential for acquisition of embryogenic competence by carrot somatic cells. Planta 223:637–645
Kim S, Yang J-Y, Xu J, Jang I-Ch, Prigge MJ, Chua N-H (2008) Two cap-binding proteins CBP20 and CBP80 are involved in processing primary microRNAs. Plant Cell Physiol 49:1634–1644
Kmieciak M, Simpson CG, Lewandowska D, Brown JW, Jarmolowski A (2002) Cloning and characterization of two subunits of Arabidopsis thaliana nuclear cap-binding complex. Gene 283:171–183
Kroj T, Savino G, Valon C, Giraudat J, Parcy F (2003) Regulation of storage protein gene expression in Arabidopsis. Development 130:6065–6073
Kurczyńska EU, Gaj MD, Ujczak A, Mazur E (2007) Histological analysis of direct somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Planta 266:619–628
Liscum E, Reed JW (2002) Genetics of Aux/IAA and ARF action in plant growth and development. Plant Mol Biol 49:387–400
Luerssen H, Kirik V, Herrmann P, Misèra S (1998) FUSCA3 encodes a protein with a conserved VP1/ABI3-like B3 domain which is of functional importance for the regulation of seed maturation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 15:755–764
Malik MR, Wang F, Dirpaul JM, Zhou N, Polowick PL, Ferrie AMR, Krochko JE (2007) Transcript profiling and identification of molecular markers for early microspore embryogenesis in Brassica napus. Plant Physiol 144:134–154
Michalczuk L, Cooke TJ, Cohen JD (1992) Auxin level at different stages of carrot somatic embryogenesis. Phytochemistry 31:1097–1103
Murashige T, Skoog FA (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Ogas J, Cheng J-C, Sung ZR, Somerville C (1997) Cellular differentiation regulated by gibberellin in the Arabidopsis thaliana pickle mutant. Science 277:91–94
Padmanabhan K, Cantliffe DJ, Koch KE (2001) Auxin-regulated gene expression and embryogenic competence in callus cultures of sweetpotato. Ipomea batatas (L.) Lam. Plant Cell Rep 20:187–192
Papp I, Mur LA, Dalmadi A, Dulai S, Koncz C (2004) A mutation in Cap Binding Protein 20 gene confers drought tolerance to Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 55:679–686
Perry SE, Nichols KW, Fernandez DE (1996) The MADS domain protein AGL15 localizes to nucleus during early stages of seed development. Plant Cell 8:1977–1989
Perry SE, Lehti MD, Fernandez DE (1999) The MADS-domain protein AGAMOUS-Like 15 accumulates in embryonic tissues with diverse origins. Plant Physiol 120:121–129
Rashid SZ, Yamaji N, Masaharu K (2007) Shoot formation from root tip region: a developmental alteration by WUS in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 26:1449–1455
Ribnicky DM, Cohen JD, Hu WS, Cooke TJ (2002) An auxin surge following fertilization in carrots: a mechanism for regulating plant totipotency. Planta 214:505–509
Rider SD, Henderson JT, Jerome RE, Edenberg HJ, Romero-Severson J, Ogas J (2003) Coordinate repression of regulators of embryonic identity by PICKLE during germination in Arabidopsis. Plant J 35:33–43
Rose RJ, Nolan KE (2006) Genetic regulation of somatic embryogenesis with particular reference to Arabidopsis thaliana and Medicago truncatula. In vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 42:473–481
Sablowski RW, Meyerowitz EM (1998) A homolog of NO APICAL MERISTEM is an immediate target of the floral homeotic genes APETALA3/PISTILLATA. Cell 92:93–103
Santos-Mendoza SM, Dubreucq B, Miquel M, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2005) LEAFY COTYLEDON2 activation is sufficient to trigger the accumulation of oil and seed specific mRNAs in Arabidopsis leaves. FEBS Lett 579:4666–4670
Santos-Mendoza M, Dubreucq B, Baud S, Parcy F, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2008) Deciphering gene regulatory network that control seed development and maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 54:608–620
Schmidt EDL, Guzzo F, Toonen MAJ, de Vries SC (1997) A leucine-rich repeat containing receptor-like kinase marks somatic plant cells competent to form embryos. Development 124:2049–2062
Sharma SK, Millam S, Hedley PE, McNicol J, Bryan GJ (2008) Molecular regulation of somatic embryogenesis in potato: an auxin led perspective. Plant Mol Biol 68:185–201
Singla B, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2007) Analysis of expression profile of selected genes expressed during auxin-induced somatic embryogenesis in leaf base system of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and their possible interactions. Plant Mol Biol 65:677–692
Srinivisan C, Liu Z, Heidmann I, Supena EDJ, Fukuoka H, Joosen R, Lambalk J, Angenent G, Scorza R, Custers JBM, Boutilier K (2007) Heterologous expression of the BABY BOOM AP2/ERF transcription factor enhances the regeneration capacity of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Planta 225:341–351
Stasolla C, van Zyl L, Egertsdotter U, Craig D, Liu W, Sederoff RR (2003) The effect of polyethylene glycol on gene expression of developing white spruce somatic embryos. Plant Physiol 131:49–60
Stasolla C, Bozhkov PV, Chu TM, van Zyl L, Egertsdotter U, Suarez MF, Craig D, Wolfinger RD, von Arnold S, Sederoff RR (2004) Variation in transcript abundance during somatic embryogenesis in gymnosperms. Tree Physiol 24:1073–1085
Stone SL, Kwong LW, Yee KM, Pelletier J, Lepiniec L, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (2001) LEAFY COTYLEDON2 encodes B3 domain transcription factor that induces embryo development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11806–11811
Stone SL, Braybrook SA, Paula SL, Kwong LW, Meuser J, Pelletier J, Hsieh T-F, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (2008) Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON2 induces maturation traits and auxin activity: implications for somatic embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:3151–3156
Thellin O, Zorzi W, Lakaye B, De Borman B, Coumans B, Hennen G, Grisar T, Igout A, Heinen E (1999) Housekeeping genes as internal standards: use and limits. J Biotechnol 75:291–295
Thibaud-Nissen F, Shealy RT, Khanna A, Vodkin LO (2003) Clustering of microarray data reveals transcript patterns associated with somatic embryogenesis in soybean. Plant Physiol 132:118–136
Thomas C, Bronner R, Molinier J, Prinsen E, van Onckelen H, Hahne G (2002) Immuno-cytochemical localization of indole-3-acetic acid during induction of somatic embryogenesis in cultured sunflower embryos. Planta 215:577–583
To A, Valon C, Savino G, Guilleminot J, Devic M, Giraudat J, Parcy F (2006) A network of local and redundant gene regulation governs Arabidopsis seed maturation. Plant Cell 18:1642–1651
van Zyl L, Bozhkov PV, Clapham DH, Sederoff RR, von Arnold S (2003) Up, down and up again is a signature global gene expression pattern at the beginning of gymnosperm embryogenesis. Gene Expr Patterns 3:83–91
Wang H, Caruso LV, Downie AB, Perry SE (2004) The embryo MADS domain protein AGAMOUS-Like15 directly regulates expression of a gene encoding an enzyme involved in gibberellin metabolism. Plant Cell 16:1206–1219
Wang H, Guo J, Lambert KN, Lin Y (2007) Developmental control of Arabidopsis seed oil biosynthesis. Planta 226:773–783
Zeng F, Zhang X, Zhu L, Tu L, Guo X, Nie Y (2006) Isolation and characterization of genes associated to cotton somatic embryogenesis by suppression subtractive hybridization and macroarray. Plant Mol Biol 60:167–183
Zimmerman JL (1993) Somatic embryogenesis: a model for early development in higher plants. Plant Cell 5:1411–1423
Zuo J, Niu QW, Frugis G, Chua NH (2002) The WUSCHEL gene promotes vegetative-to-embryonic transition in Arabidopsis. Plant J 30:349–359
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by grant Nr N301 079 31/2006 from the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Rose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ledwoń, A., Gaj, M.D. LEAFY COTYLEDON2 gene expression and auxin treatment in relation to embryogenic capacity of Arabidopsis somatic cells. Plant Cell Rep 28, 1677–1688 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-009-0767-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-009-0767-2