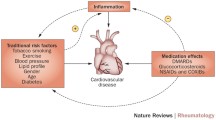
Abstract
New pathophysiological insights are now available on comorbidities in rheumatic diseases (RDs). Several nationwide studies point to the fact that comorbid diabetes mellitus (DM) increases the risk of adverse outcomes in patients with various RDs. Genetic factors, intensity of systemic inflammation, anti-inflammatory potential of therapeutic agents, and duration of RDs have been insufficiently explored in the context of comorbidities. Some disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) have demonstrated a potential to improve the glycemic control while glucocorticoids (GCs) have worsened it, particularly in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Anti-TNFalpha agents in combination with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) have been associated with a reduced risk of DM in patients with RA, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), Sjögren syndrome (SS), and SLE. Better understanding of confounding factor of currently available antirheumatic therapies in patients with DM and RDs will pave the way for a tailored approach, limiting the severity of clinical manifestations and reducing the mortality risk.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dadonienė J, Charukevič G, Jasionytė G, Staškuvienė K, Miltinienė D (2021) Mortality in inflammatory rheumatic diseases: lithuanian national registry data and systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(23):12338
Ahmed S, Gasparyan AY, Zimba O (2021) Comorbidities in rheumatic diseases need special consideration during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rheumatol Int 41(2):243–256
Matsunaga M, Lim E, Davis J, Chen JJ (2021) Dietary quality associated with self-reported diabetes, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis among younger and older US adults: a cross-sectional study using NHANES 2011–2016. Nutrients 13(2):545
Kong R, Sun L, Li H, Wang D (2022) The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis of rheumatic disease. Autoimmunity 55(1):1–7
Ding S, Xu S, Ma Y, Liu G, Jang H, Fang J (2019) Modulatory mechanisms of the NLRP3 inflammasomes in diabetes. Biomolecules 9(12):850
Mehta P, Gasparyan AY, Zimba O, Kitas GD, Yessirkepov M (2022) Interplay of diabetes mellitus and rheumatic diseases amidst the COVID-19 pandemic: influence on the risk of infection, outcomes, and immune responses. Clin Rheumatol 41(12):3897–3913
Szabłowski M, Okruszko MA, Pochodowicz K, Abramowicz P, Konstantynowicz J, Bossowski A et al (2022) Coincidence of juvenile idiopathic arthritis and type 1 diabetes: a case-based review. Rheumatol Int 42(2):371–378
Pablos JL, Galindo M, Carmona L, Lledó A, Retuerto M, Blanco R et al (2020) Clinical outcomes of hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and chronic inflammatory and autoimmune rheumatic diseases: a multicentric matched cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 79(12):1544–1549
Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Blackmore H, Kitas GD (2011) Writing a narrative biomedical review: considerations for authors, peer reviewers, and editors. Rheumatol Int 31:1409–1417
Nicolau J, Lequerré T, Bacquet H, Vittecoq O (2017) Rheumatoid arthritis, insulin resistance, and diabetes. Joint Bone Spine 84(4):411–416
Xie W, Yang X, Ji L, Zhang Z (2020) Incident diabetes associated with hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, biologics and glucocorticoids in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 50(4):598–607
Cacciapaglia F, Spinelli FR, Bartoloni E, Bugatti S, Erre GL, Fornaro M et al (2023) Clinical features of diabetes mellitus on rheumatoid arthritis: data from the cardiovascular obesity and rheumatic disease (CORDIS) study group. J Clin Med 12(6):2148
Roberts MJ, Leonard AN, Bishop NC, Moorthy A (2022) Lifestyle modification and inflammation in people with axial spondyloarthropathy-A scoping review. Musculoskeletal Care 20(3):516–528
Emamifar A, Jensen Hansen IM (2018) The influence of thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus, primary hyperparathyroidism, vitamin B12 deficiency and other comorbid autoimmune diseases on treatment outcome in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an exploratory cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore) 97(21):e10865
Li W, Bi S, Liang Y, Zhu H (2022) Construction of rheumatoid arthritis risk prediction and medical image applications from rheumatoid factor levels. Comput Math Methods Med 2022:8617467
Emamifar A, Levin K, Jensen Hansen IM (2017) Patients with newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis are at increased risk of diabetes mellitus: an observational cohort study. Acta Reumatol Port 42(4):310–317
Panopoulos S, Tektonidou M, Drosos AA, Liossis SN, Dimitroulas T, Garyfallos A et al (2018) Prevalence of comorbidities in systemic sclerosis versus rheumatoid arthritis: a comparative, multicenter, matched-cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 20(1):267
Cacciapaglia F, Spinelli FR, Piga M, Erre GL, Sakellariou G, Manfredi A et al (2022) Estimated 10-year cardiovascular risk in a large Italian cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients: data from the cardiovascular obesity and rheumatic disease (CORDIS) study group. Eur J Intern Med 96:60–65
Avouac J, Elhai M, Forien M, Sellam J, Eymard F, Molto A et al (2021) Influence of inflammatory and non-inflammatory rheumatic disorders on the clinical and biological profile of type-2 diabetes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 60(8):3598–3606
Arias de la Rosa I, Escudero-Contreras A, Rodríguez-Cuenca S, Ruiz-Ponce M, Jiménez-Gómez Y, Ruiz-Limón P et al (2018) Defective glucose and lipid metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis is determined by chronic inflammation in metabolic tissues. J Intern Med 284(1):61–77
Ruscitti P, Cipriani P, Liakouli V, Iacono D, Pantano I, Margiotta DPE et al (2021) Occurrence and predictive factors of high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis: findings from a 3-year, multicentre, prospective, observational study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 39(5):995–1002
Ruscitti P, Ursini F, Cipriani P, Ciccia F, Liakouli V, Carubbi F et al (2017) Prevalence of type 2 diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis: results from a cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore) 96(34):e7896
Eddy Warman N, Baharuddin H, Abdul Rahman TH, Ismail N, Ch’Ng SS, Rosman A, Abdul Ghani R (2022) High prevalence of undiagnosed impaired glucose tolerance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. SAGE Open Med 10:20503121221088090
Al-Sari UA (2022) Rheumatoid arthritis as a predisposing factor for increased risk of diabetes mellitus incidence. Wiad Lek 75(10):2329–2333. https://doi.org/10.36740/WLek202210103
Li G, Chi W, Bai B, Li Y, Wei T, Fu L (2019) Dose−response associations between metabolic indexes and the risk of comorbid type 2 diabetes mellitus among rheumatoid arthritis patients from Northern China: a case−control study. BMJ Open 9(7):e028011
Thomas K, Lazarini A, Kaltsonoudis E, Drosos A, Papalopoulos I, Sidiropoulos P et al (2018) Multicenter cross-sectional study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Greece: results from a cohort of 2.491 patients. Mediterr J Rheumatol 29(1):27–37
Di Muzio C, Cipriani P, Ruscitti P (2022) Rheumatoid arthritis treatment options and type 2 diabetes: unravelling the association. BioDrugs 36(6):673–685
Paul SK, Montvida O, Best JH, Gale S, Pethö-Schramm A, Sarsour K (2021) Association of biological antirheumatic therapy with risk for type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study in incident rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ Open 11(6):e042246
Lurati A, Laria A, Mazzocchi D, Re KA, Marrazza MG, Faggioli PM et al (2021) Improvement of HbA1c in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and rheumatoid arthritis treated with bDMARDs. Open Access Rheumatol 13:73–78
Desai RJ, Dejene S, Jin Y, Liu J, Kim SC (2020) Comparative risk of diabetes mellitus in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying drugs: a cohort study. ACR Open Rheumatol 2(4):222–231
Lin C, Ji H, Cai X, Yang W, Lv F, Ji L (2020) The association between the biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and the incidence of diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol Res 161:105216
Nam SH, Kim M, Kim YJ, Ahn SM, Hong S, Lee CK et al (2022) Risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus associated with antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a nationwide population study. J Clin Med 11(8):2109
Youssef J, Novosad SA, Winthrop KL (2015) Infection risk and safety of corticosteroid use. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 42(1):157–176
Movahedi M, Beauchamp ME, Abrahamowicz M, Ray DW, Michaud K, Pedro S et al (2016) Risk of incident diabetes mellitus associated with the dosage and duration of oral glucocorticoid therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68(5):1089–1098
Lillegraven S, Greenberg JD, Reed GW, Saunders K, Curtis JR, Harrold L et al (2019) Immunosuppressive treatment and the risk of diabetes in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 14(1):e0210459
Huang JF, Wu QN, Zheng XQ, Sun XL, Wu CY, Wang XB et al (2020) The characteristics and mortality of osteoporosis, osteomyelitis, or rheumatoid arthritis in the diabetes population: a retrospective study. Int J Endocrinol 2020:8821978
Costello RE, Marsden A, Movahedi M, Lunt M, Humphreys JH, Emsley R et al (2021) Correction to: The effect of glucocorticoid therapy on mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and concomitant type II diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Rheumatol 5(1):11
Lee CY, Tai CJ, Tsai YF, Kuan YH, Lee CH, Huang KH (2019) Prescribing trend of antirheumatic drugs in taiwan and risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a nationwide cohort study. Biomed Res Int 2019:7987529
Ozen G, Dell’Aniello S, Pedro S, Michaud K, Suissa S (2023) Reduction of cardiovascular disease and mortality versus risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus with statin use in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 75(3):597–607
Li K, Ji X, Seeley R, Lee WC, Shi Y, Song F et al (2022) Impaired glucose metabolism underlies articular cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. FASEB J 36(6):e22377
Kuusalo L, Felson DT, Wang N, Lewis CE, Torner J, Nevitt MC et al (2021) Metabolic osteoarthritis - relation of diabetes and cardiovascular disease with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 29(2):230–234
Kendzerska T, King LK, Lipscombe L, Croxford R, Stanaitis I, Hawker GA (2018) The impact of hip and knee osteoarthritis on the subsequent risk of incident diabetes: a population-based cohort study. Diabetologia 61(11):2290–2299
Mendy A, Park J, Vieira ER (2018) Osteoarthritis and risk of mortality in the USA: a population-based cohort study. Int J Epidemiol 47(6):1821–1829
Duclos M (2016) Osteoarthritis, obesity and type 2 diabetes: the weight of waist circumference. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 59(3):157–160
Courties A, Sellam J (2016) Osteoarthritis and type 2 diabetes mellitus: what are the links? Diabetes Res Clin Pract 122:198–206
Castano Betancourt MC, Morais CL, Vannucci Nunes Lipay M, Aragão J, de Azevedo E, Souza Munhoz M, Gomes Machado E et al (2019) Gender differences in the effect of diabetes mellitus and its treatment on osteoarthritic pain. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 7(1):e000736
Hawker GA, Croxford R, Bierman AS, Harvey P, Ravi B, Kendzerska T et al (2017) Osteoarthritis-related difficulty walking and risk for diabetes complications. Osteoarthr Cartil 25(1):67–75
Williams MF, London DA, Husni EM, Navaneethan S, Kashyap SR (2016) Type 2 diabetes and osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Diabetes Complic 30(5):944–950
Lu CH, Chung CH, Lee CH, Hsieh CH, Hung YJ, Lin FH et al (2018) Combination COX-2 inhibitor and metformin attenuate rate of joint replacement in osteoarthritis with diabetes: a nationwide, retrospective, matched-cohort study in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 13(1):e0191242
He M, Lu B, Opoku M, Zhang L, Xie W, Jin H et al (2022) Metformin prevents or delays the development and progression of osteoarthritis: new insight and mechanism of action. Cells 11(19):3012
Gao N, Kong M, Li X, Wei D, Zhu X, Hong Z et al (2022) Systemic lupus erythematosus and cardiovascular disease: a mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol 13:908831
Lin YJ, Chien CC, Ho CH, Chen HA, Chen CY (2022) Increased risk of type 2 diabetes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a nationwide cohort study in Taiwan. Medicine (Baltimore) 101(51):e32520
Castro LL, Lanna CCD, Ribeiro ALP, Telles RW (2018) Recognition and control of hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 37(10):2693–2698
García-Carrasco M, Mendoza-Pinto C, Munguía-Realpozo P, Etchegaray-Morales I, Vélez-Pelcastre SK, Méndez-Martínez S et al (2023) Insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 23(4):503–514
García-Dorta A, Quevedo-Abeledo JC, Rua-Figueroa Í, de Vera-González AM, González-Delgado A, Medina-Vega L et al (2021) Beta-cell function is disrupted in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 60(8):3826–3833
Alvarez-Payares JC, Ribero D, Rodríguez L, Builes CE, Prieto C, Arango C et al (2022) Late systemic lupus erythematosus-associated insulin resistance syndrome: a rare cause of de novo diabetes mellitus. Case Rep Med 2022:4655804
Hanai S, Kobayashi Y, Ichijo M, Ito R, Kobayashi K, Nakagomi D (2021) Antidiabetic effects of hydroxychloroquine in two Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Diabetol Int 13(2):447–451
Shaharir SS, Gafor AH, Said MS, Kong NC (2015) Steroid-induced diabetes mellitus in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: analysis from a Malaysian multi-ethnic lupus cohort. Int J Rheum Dis 18(5):541–547
Chen YM, Lin CH, Lan TH, Chen HH, Chang SN, Chen YH et al (2015) Hydroxychloroquine reduces risk of incident diabetes mellitus in lupus patients in a dose-dependent manner: a population-based cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 54(7):1244–1249
Sciascia S, Mompean E, Radin M, Roccatello D, Cuadrado MJ (2017) Rate of adverse effects of medium- to high-dose glucocorticoid therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review of randomized control trials. Clin Drug Investig 37(6):519–524
Salmasi S, Sayre EC, Antonio Aviña-Zubieta J, Esdaile JM, De Vera MA (2021) Adherence to antimalarial therapy and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a population-based study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 73(5):702–706
Levinson D, Abugroun A, Osinski K (2022) Hydroxychloroquine lowers the risk for diabetes mellitus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Diabetes Epidemiol Manag 8:100089
Jiang MY, Hwang JC, Feng IJ (2018) Impact of diabetes mellitus on the risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci Rep 8(1):6008
Hansen RB, Falasinnu T, Faurschou M, Jacobsen S, Simard JF (2023) Risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and diabetes mellitus: a Danish nationwide cohort study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.25091
Gau SY, Leong PY, Lin CL, Tsou HK, Wei JC (2021) Higher Risk for sjögren’s syndrome in patients with fibromyalgia: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Front Immunol 12:640618
Su YJ, Leong PY, Wang YH, Wei JC (2022) Sjögren syndrome is a hidden contributor of macrovascular and microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Rheum Dis 25(10):1176–1185
Chen TH, Lai TY, Wang YH, Chiou JY, Hung YM, Wei JC (2019) Hydroxychloroquine was associated with reduced risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus in patients with Sjögren syndrome. QJM 112(10):757–762
Kim J, Kim YS, Park SH (2021) Metformin as a treatment strategy for Sjögren’s syndrome. Int J Mol Sci 22(13):7231
Matsubara Y, Nakamura Y, Tamura N, Kameda H, Otomo K, Kishimoto M et al (2022) A nationwide questionnaire survey on the prevalence of ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in Japan. Mod Rheumatol 32(5):960–967
Ferraz-Amaro I, Rueda-Gotor J, Genre F, Corrales A, Blanco R, Portilla V et al (2021) Potential relation of cardiovascular risk factors to disease activity in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 13:1759720X211033755
Chen HH, Yeh SY, Chen HY, Lin CL, Sung FC, Kao CH (2014) Ankylosing spondylitis and other inflammatory spondyloarthritis increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in an Asian population. Rheumatol Int 34(2):265–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2927-5
Exarchou S, Lie E, Lindström U, Askling J, Forsblad-d’Elia H, Turesson C et al (2016) Mortality in ankylosing spondylitis: results from a nationwide population-based study. Ann Rheum Dis 75(8):1466–1472
Wang CR, Tsai HW (2021) Anti- and non-tumor necrosis factor-α-targeted therapies effects on insulin resistance in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. World J Diabetes 12(3):238–260
Chen HH, Chen DY, Lin CC, Chen YM, Lai KL, Lin CH (2017) Association between use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and diabetes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, or psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis: a nationwide, population-based cohort study of 84,989 patients. Ther Clin Risk Manag 13:583–592
van der Houwen TB, van Hagen PM, van Laar JAM (2022) Immunopathogenesis of Behçet’s disease and treatment modalities. Semin Arthritis Rheum 52:151956
Gheita TA, El-Latif EA, El-Gazzar II, Samy N, Hammam N, Abdel Noor RA et al (2019) Behçet’s disease in Egypt: a multicenter nationwide study on 1526 adult patients and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 38(9):2565–2575
Alharthy F, Almaqati AS, Alsulami S, Ahmad A (2023) Behçet’s disease in Saudi Arabia: clinical and demographic characteristics. Cureus 15(2):e34867
Jung JH, Han KD, Lee YB, Park YG (2022) Behçet’s disease is associated with multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis: a Korean population-based study. Dermatology 238(1):86–91
Chen T, Shao X, Li H, Chen Y, Liu L, Zhong J, Chen J (2023) Association of Behçet’s disease with the risk of metabolic syndrome and its components: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-023-01044-x
Tufan A, Lachmann HJ (2020) Familial Mediterranean fever, from pathogenesis to treatment: a contemporary review. Turk J Med Sci 50(SI-2):1591–1610
Gicchino MF, Iafusco D, Zanfardino A, Del Giudice EM, Olivieri AN (2021) A case report of a boy suffering from type 1 diabetes mellitus and familial Mediterranean fever. Ital J Pediatr 47(1):127
Anwar GM, Fouad HM, Abd El-Hamid A, Mahmoud F, Musa N, Lotfi H et al (2015) A study of familial Mediterranean Fever (MEFV) gene mutations in Egyptian children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Med Genet 58(1):31–34
Baş F, Kabataş-Eryilmaz S, Günöz H, Darendeliler F, Küçükemre B, Bundak R et al (2009) Type 1 diabetes mellitus associated with autoimmune thyroid disease, celiac disease and familial Mediterranean fever: case report. Turk J Pediatr 51(2):183–186
Kharouf F, Tsemach-Toren T, Ben-Chetrit E (2022) IL-1 inhibition in familial Mediterranean fever: clinical outcomes and expectations. Clin Exp Rheumatol 40(8):1567–1574
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: FY, ZO. Writing—original draft: FY, ZO. Writing—review & editing: FY, ZO, KM, ZA, MY. Approval—FY, ZO, KM, ZA, MY.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fedorchenko, Y., Mahmudov, K., Abenov, Z. et al. Diabetes mellitus in rheumatic diseases: clinical characteristics and treatment considerations. Rheumatol Int 43, 2167–2174 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-023-05453-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-023-05453-9