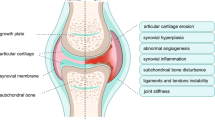
Abstract
The joint disease osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, which mainly affects the older people. OA is becoming one of the major non-fatal health burdens of the world. The etiology of OA is mostly unclear, and it cannot be cured totally. Osteopontin (OPN) is a multifunctional phosphoprotein, of which overexpression and high level of presence in synovial fluid and articular cartilage were found to be associated with OA progression. Usually, in OA progression, OPN plays important role as an intrinsic regulator. Recent studies have taken attempt to use this protein as a diagnostic marker of OA and use OPN as a target for the drug development against OA. This review summarizes the role of OPN in OA, with focusing on the mechanism of action, and also discussing the diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of OA related to OPN.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laslett LL, Quinn SJ, Winzenberg TM, Sanderson K, Cicuttini F, Jones G (2012) A prospective study of the impact of musculoskeletal pain and radiographic osteoarthritis on health related quality of life in community dwelling older people. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 13:168
Garriga XM (2014) Definition, etiology, classification and presentation forms. Aten Primaria 46(Suppl 1):3–10
Jones G (2013) Osteoarthritis: Where are we for pain and therapy in 2013? Aust Fam Physician 42(11):766–769
Neogi T (2013) The epidemiology and impact of pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 21(9):1145–1153
Martín AP (2014) Symptoms, localizations: knee, hip, hands, spine, other localizations. Aten Primaria 46(Suppl 1):11–17
Woolf AD, Pfleger B (2003) Burden of major musculoskeletal conditions. Bull World Health Organ 81(9):646–656
Murray CJ, Lopez AD (1996) Evidence-based health policy-lessons from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Science 274(5288):740–743
Brandt KD, Dieppe P, Radin E (2009) Etiopathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Med Clin North Am 93(1):1–24, xv
Leung GJ, Rainsford KD, Kean WF (2014) Osteoarthritis of the hand I: aetiology and pathogenesis, risk factors, investigation and diagnosis. J Pharm Pharmacol 66(3):339–346
de Rezende MU, de Campos GC, Pailo AF (2013) Current concepts in osteoarthritis. Acta Ortop Bras 21(2):120–122
Zhang W, Nuki G, Moskowitz RW, Abramson S, Altman RD, Arden NK, Bierma-Zeinstra S, Brandt KD, Croft P, Doherty M, Dougados M, Hochberg M, Hunter DJ, Kwoh K, Lohmander LS, Tugwell P (2010) OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis: part III: changes in evidence following systematic cumulative update of research published through January 2009. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 18(4):476–499
Vargas Negrín F, Medina Abellán MD, Hermosa Hernán JC, de Felipe Medina R (2014) Treatment of patients with osteoarthritis. Aten Primaria 46(Suppl 1):39–61
Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, Nolte S, Ackerman I, Fransen M, Bridgett L, Williams S, Guillemin F, Hill CL, Laslett LL, Jones G, Cicuttini F, Osborne R, Vos T, Buchbinder R, Woolf A, March L (2014) The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204763
Standal T, Borset M, Sundan A (2004) Role of osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone remodeling. Exp Oncol 26(3):179–184
Hasegawa M, Nakoshi Y, Iino T, Sudo A, Segawa T, Maeda M, Yoshida T, Uchida A (2009) Thrombin-cleaved osteopontin in synovial fluid of subjects with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 36(2):240–245
Yamaga M, Tsuji K, Miyatake K, Yamada J, Abula K, Ju YJ, Sekiya I, Muneta T (2012) Osteopontin level in synovial fluid is associated with the severity of joint pain and cartilage degradation after anterior cruciate ligament rupture. PLoS One 7(11):e49014
O’Regan A, Berman JS (2000) Osteopontin: a key cytokine in cell-mediated and granulomatous inflammation. Int J Exp Pathol 81(6):373–390
Gao SG, Li KH, Zeng KB, Tu M, Xu M, Lei GH (2010) Elevated osteopontin level of synovial fluid and articular cartilage is associated with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 18(1):82–87
Elsebaie H, Elchamy HA, Kaddah EA, Abdelfatta RG (2012) Osteopontin in patients with primary knee osteoarthritis: relation to disease severity. Life Sci J 9(4):3902–3909
Ohshima S, Kobayashi H, Yamaguchi N, Nishioka K, Umeshita-Sasai M, Mima T, Nomura S, Kon S, Inobe M, Uede T, Saeki Y (2002) Expression of osteopontin at sites of bone erosion in a murine experimental arthritis model of collagen-induced arthritis: possible involvement of osteopontin in bone destruction in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46(4):1094–1101
Jiang Y, Yao M, Liu Q, Zhou C (2013) OPN gene polymorphisms influence the risk of knee OA and OPN levels in synovial fluid in a Chinese population. Arthritis Res Ther 15(1):R3
Choi ST, Kim JH, Kang EJ, Lee SW, Park MC, Park YB, Lee SK (2008) Osteopontin might be involved in bone remodelling rather than in inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47(12):1775–1779
Wang KX, Denhardt DT (2008) Osteopontin: role in immune regulation and stress responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 19(5–6):333–345
Matsui Y, Iwasaki N, Kon S, Takahashi D, Morimoto J, Matsui Y, Denhardt DT, Rittling S, Minami A, Uede T (2009) Accelerated development of aging-associated and instability-induced osteoarthritis in osteopontin-deficient mice. Arthritis Rheum 60(8):2362–2371
Honsawek S, Tanavalee A, Sakdinakiattikoon M, Chayanupatkul M, Yuktanandana P (2009) Correlation of plasma and synovial fluid osteopontin with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis. Clin Biochem 42(9):808–812
Mohammed FI, El-Azeem MIA, KamalElDin AM (2012) Plasma and synovial fluid osteopontin levels in patients with knee osteoarthritis: relation to radiological grade. Egypt Rheumatol 34(3):131–136
Qin LF, Wang WC, Fang H, Mao XZ, Huang GL, Chen Y, Zhou HD, Shen Y, Qin LH, Peng D (2013) Expression of NF-κB and osteopontin of synovial fluid of patients with knee osteoarthritis. Asian Pac J Trop Med 6(5):379–382
Xu M, Zhang L, Zhao L, Gao S, Han R, Su D, Lei G (2013) Phosphorylation of osteopontin in osteoarthritis degenerative cartilage and its effect on matrix metalloprotease 13. Rheumatol Int 33(5):1313–1319
Pullig O, Weseloh G, Gauer S, Swoboda B (2000) Osteopontin is expressed by adult human osteoarthritic chondrocytes: protein and mRNA analysis of normal and osteoarthritic cartilage. Matrix Biol 19(3):245–255
Martínez-Calleja A, Velasquillo C, Vega-López M, Arellano-Jiménez MJ, Tsutsumi-Fujiyoshi VK, Mondragón-Flores R, Kouri-Flores JB (2014) Osteopontin expression and localization of Ca++ deposits in early stages of osteoarthritis in a rat model. Histol Histopathol [Epub ahead of print]
Zhang FJ, Gao SG, Cheng L, Tian J, Xu WS, Luo W, Song Y, Yang Y, Lei GH (2013) The effect of hyaluronic acid on osteopontin and CD44 mRNA of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Rheumatol Int 33(1):79–83
Dong X, Zheng Y, Liu HY (2013) The clinical significance of serum and joint fluid osteopontin, and thrombin-cleaved osteopontin levels in osteoarthritis. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 52(12):1023–1027
Buckwalter JA, Mankin HJ (1998) Articular cartilage: degeneration and osteoarthritis, repair, regeneration, and transplantation. Instr Course Lect 47:487–504
Monfort J, Garcia-Giralt N, López-Armada MJ, Monllau JC, Bonilla A, Benito P, Blanco FJ (2006) Decreased metalloproteinase production as a response to mechanical pressure in human cartilage: a mechanism for homeostatic regulation. Arthritis Res Ther 8(5):R149
Couchourel D, Aubry I, Delalandre A, Lavigne M, Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP, Lajeunesse D (2009) Altered mineralization of human osteoarthritic osteoblasts is attributable to abnormal type I collagen production. Arthritis Rheum 60(5):1438–1450
Garnero P, Ayral X, Rousseau JC, Christgau S, Sandell LJ, Dougados M, Delmas PD (2002) Uncoupling of type II collagen synthesis and degradation predicts progression of joint damage in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46(10):2613–2624
Singh A, Goel SC, Gupta KK, Kumar M, Arun GR, Patil H, Kumaraswamy V, Jha S (2014) The role of stem cells in osteoarthritis: an experimental study in rabbits. Bone Joint Res 3(2):32–37
Goldring SR, Goldring MB (2006) Clinical aspects, pathology and pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 6(4):376–378
Yumoto K, Ishijima M, Rittling SR, Tsuji K, Tsuchiya Y, Kon S, Nifuji A, Uede T, Denhardt DT, Noda M (2002) Osteopontin deficiency protects joints against destruction in anti-type II collagen antibody-induced arthritis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(7):4556–4561
Yamamoto N, Sakai F, Kon S, Morimoto J, Kimura C, Yamazaki H, Okazaki I, Seki N, Fujii T, Uede T (2003) Essential role of the cryptic epitope SLAYGLR within osteopontin in a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest 112(2):181–188
Yamamoto N, Nakashima T, Torikai M, Naruse T, Morimoto J, Kon S, Sakai F, Uede T (2007) Successful treatment of collagen-induced arthritis in non-human primates by chimeric anti-osteopontin antibody. Int Immunopharmacol 7(11):1460–1470
Fan K, Dai J, Wang H, Wei H, Cao Z, Hou S, Qian W, Wang H, Li B, Zhao J, Xu H, Yang C, Guo Y (2008) Treatment of collagen-induced arthritis with an anti-osteopontin monoclonal antibody through promotion of apoptosis of both murine and human activated T cells. Arthritis Rheum 58(7):2041–2052
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Grants from the National 863 Project of China (2011AA030101), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81201420, 81272034), the Young Teacher’s boosting project of the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities in Central South University (2012QNZT103, 2012QNZT095) and National Clinical Key Department Construction Projects of China.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, C., Gao, S. & Lei, G. Association of osteopontin with osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int 34, 1627–1631 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-3036-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-3036-9