Abstract
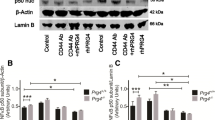
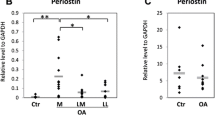
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of hyaluronic acid (HA) on the expression of osteopontin (OPN) and CD44 mRNA of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) in the patients with osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee. FLS were obtained from the knees of 10 patients with OA. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (Q-PCR) was used to assess the expression of the OPN mRNA and CD44 mRNA. The relative OPN mRNA expression in HA group (6.47 ± 2.30-fold) was significantly higher than in the control group (P = 0.045, P < 0.05), while in HYL group (0.65 ± 0.21-fold) it was lower than in the control group (P = 0.037, P < 0.05), and the difference in OPN mRNA expression between HA group and HYL group also showed statistically significant (P = 0.001, P < 0.05); however, there was no significant difference between each group of the relative CD44 mRNA expression (P > 0.05). Our study showed that HA can upregulate OPN mRNA expression in OA fibroblast-like synoviocytes, and the high expression of OPN mRNA in OA may be a result of increased HA level of OA synovitis; however, HA cannot affect the CD44 mRNA expression in OA fibroblast-like synoviocytes, and the high expression of CD44 mRNA in OA may be not a result of increased HA level of OA synovitis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malemud CJ, Islam N, Haqqi TM (2003) Pathophysiological mechanisms in osteoarthritis lead to novel therapeutic strategies. Cells Tissues Organs 174:34–48
Dahl LB, Dahl IM, Engstro m-Laurent A, Granath K (1985) Concentration and molecular weight of sodium hyaluronate in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other arthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis 44:817–822
Xu G, Nie H, Li N, Zheng W, Zhang D, Feng G (2005) Role of osteopontin in amplification and perpetuation of rheumatoid synovitis. J Clin Invest 115:1060–1067
Gao SG, Li KH, Zeng KB, Tu M, Xu M, Lei GH (2010) Elevated osteopontin level of synovial fluid and articular cartilage is associated with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthr Cartil 18:82–87
Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B (1990) CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell 61:1303–1313
Weber GF, Ashkar S, Glimcher MJ, Cantor H (1996) Receptor-ligand interaction between CD44 and osteopontin (Eta-1). Science 271:509–512
Dunn S, Kolomytkin OV, Waddell DD, Marino AA (2009) Hyaluronan-binding receptors: possible involvement in osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol 19:151–155
Stebulis JA, Rossetti RG, Atez FJ, Zurier RB (2005) Fibroblast-like synovial cells derived from synovial fluid. J Rheumatol 32:301–306
Matsui Y, Iwasaki N, Kon S, Takahashi D, Morimoto J, Matsui Y, Denhardt DT, Rittling S, Minami A, Uede T (2009) Accelerated development of aging-associated and instability-induced osteoarthritis in osteopontin-deficient mice. Arthr Rheum 60:2362–2371
Attur MG, Dave MN, Stuchin S, Kowalski AJ, Steiner G, Abramson SB, Denhardt DT, Amin AR (2001) Osteopontin: an intrinsic inhibitor of inflammation in cartilage. Arthr Rheum 44:578–584
Larkin J, Renukaradhya GJ, Sriram V, Du W, Gervay-Hague J, Brutkiewicz RR (2006) CD44 differentially activates mouse NK T cells and conventional T cells. J Immunol 177:268–279
Clark RA, Alon R, Springer TA (1972) CD44 and hyaluronan-dependent rolling interactions of lymphocytes on tonsillar stroma. J Cell Biol 134:1075–1087
de la Motte CA, Hascall VC, Drazba J, Bandyopadhyay SK, Strong SA (2003) Mononuclear leukocytes bind to specific hyaluronan structures on colon mucosal smooth muscle cells treated with polyinosinic acid: polycytidylic acid: inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor is crucial to structure and function. Am J Pathol 163:121–133
Mori H, Tomari T, Koshikawa N, Kajita M, Itoh Y, Sato H, Tojo H, Yana I, Seiki M (2002) CD44 directs membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase to lemellipodia by associating with its hemopexin-like domain. EMBO J 21:3949–3959
Mikecz K, Dennis K, Shi M, Kim JH (1999) Modulation of hyaluronan receptor (CD44) function in vivo in a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheum 42:659–668
Neidhart M, Gay RE, Gay S (2000) Anti–interleukin-1 and anti-CD44 interventions producing significant inhibition of cartilage destruction in an in vitro model of cartilage invasion by rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Arthr Rheum 43:1719–1728
Weigel JA, Raymond RC, McGary C, Singh A, Weigel PH (2003) A blocking antibody to the hyaluronan receptor for endocytosis (HARE) inhibits hyaluronan clearance by perfused liver. J Biol Chem 14:9808–9812
Stern R, Kogan G, Jedrzejas MJ, Soltés L (2007) The many ways to cleave hyaluronan. Biotechnol Adv 25:537–557
Kim MS, Park MJ, Moon EJ, Kim SJ, Lee CH, Yoo H, Shin SH, Song ES, Lee SH (2005) Hyaluronic acid induces osteopontin via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway to enhance the motility of human glioma cells. Cancer Res 65:686–691
Martínez-Sanz E, Ossipov DA, Hilborn J, Larsson S, Jonsson KB, Varghese OP (2011) Bone reservoir: injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel for minimal invasive bone augmentation. J Control Release 152:232–240
Xu C, Wang Y, Yu X, Chen X, Li X, Yang X, Li S, Zhang X, Xiang AP (2009) Evaluation of human mesenchymal stem cells response to biomimetic bioglass-collagen-hyaluronic acid-phosphatidylserine composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A 88:264–273
Mendes RM, Silva GA, Lima MF, Calliari MV, Almeida AP, Alves JB, Ferreira AJ (2008) Sodium hyaluronate accelerates the healing process in tooth sockets of rats. Arch Oral Biol 53:1155–1162
Kim J, Kim IS, Cho TH, Kim HC, Yoon SJ, Choi J, Park Y, Sun K, Hwang SJ (2010) In vivo evaluation of MMP sensitive high-molecular weight HA-based hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A 95:673–681
Gao C, Guo H, Downey L, Marroquin C, Wei J, Kuo PC (2003) Osteopontin-dependent CD44v6 expression and cell adhesion in HepG2. Carcinogenesis 24:1871–1878
Cook AC, Chambers AF, Turley EA, Tuck AB (2006) Osteopontin induction of hyaluronan synthase 2 expression promotes breast cancer malignancy. J Biol Chem 281:24381–24389
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grants from the National 863 project of China (2011AA030101), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 30300396), the Provincial Science Foundation of Hunan (NO. 09JJ3048), the Graduate degree thesis Innovation Foundation of Hunan Province (CX-2010B102), and National Clinical Key Department Construction Projects of China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, FJ., Gao, SG., Cheng, L. et al. The effect of hyaluronic acid on osteopontin and CD44 mRNA of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Rheumatol Int 33, 79–83 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2339-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2339-3