Abstract.
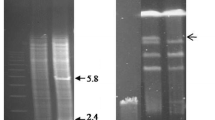
A genomic library from Burkholderia cepacia IS-16 was constructed in Escherichia coli by partial Sau3AI digestion of the chromosomal DNA, with the plasmid vector Bluescript SK. This library was screened for clones able to grow as green stained colonies on selective medium developed for detecting phosphatase-positive colonies. Three green-stained clones (pFS1, pFS2, and pFS3) carried recombinant plasmids harboring DNA inserts of 5.0, 8.0, and 0.9 kb, respectively. DNA hybridization experiments demonstrated the presence of overlapping DNA fragments in the three clones and that these three clones were all derived from Burkholderia cepacia IS-16 genomic DNA. DNA sequence analysis, together with polyacrylamide gels of proteins encoded by E. coli containing pFS3, suggested that the isolated 0.9-kb DNA fragment encodes the functional portion of a phosphate transport protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 October 1999 / Accepted: 10 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, H., Rossolini, G., Gonzalez, T. et al. Isolation of a Gene from Burkholderia cepacia IS-16 Encoding a Protein That Facilitates Phosphatase Activity. Curr Microbiol 40, 362–366 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002840010071
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002840010071