Abstract
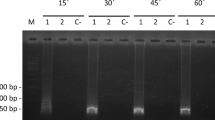
We successfully established a detection method which exhibited a markedly higher sensitivity than previously developed detection methods for Nosema bombycis by combining glass beads, FTA card, and LAMP. Spores of N. bombycis were first broken by acid-washed glass beads; the DNA was subsequently extracted and purified with the FTA card, and LAMP was performed using primers (LSU296) designed based on the sequence of the LSU rRNA of N. bombycis. The minimum detection concentration was 10 spores/mL. When this method was used to detect pebrine disease in silkworm egg, the detection rate for 500 silkworm eggs, in which only one egg was infected with N. bombycis, was 100 % under our optimized conditions. If the number of eggs in the sample increased to 800 or 1,000, the sample was divided into two equal portions, and the eggs were smashed with glass beads after the addition of 1 mL of TE buffer. The liquid in two tubes was later mixed and applied to the FTA card, and the detection rates were 100 %. Furthermore, the LAMP method established in our study could detect N. bombycis infection in silkworm 24 h earlier than microscopy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bing YY, Sun XH, An CL (2005) Biology and experimental detection of microsporidia. Parasit Dis Foreign Med Sci 32:166–169
Cai SF, He XY, He XK et al (2011) A protocol for fast and efficient preparation of genomic DNA and total proteins of Nosema bombycis. Sci Seric 37:1019–1024
Didier ES, Vossbrinck CR, Baker MD et al (1995) Identification and characterization of three Encephalitozoon cuniculi strains. Parasitology 111:411–421
Ellington A (1998) Preparation and analysis of DNA. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE (eds) Short protocols in molecular biology. China Scientific Press, Beijing, pp 29–71
Guo LD, Hyde KD, Liew EC (2001) Detection and taxonomic placement of endophytic fungi within frond tissues of Livistona chinensis based on rDNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 20:1–13
Hamiduzzaman MM, Guzman-Novoa E, Goodwin PH (2010) A multiplex PCR assay to diagnose and quantify Nosema infections in honey bees (Apis mellifera). J Invertebr Pathol 105:151–155
Hatakeyama Y, Hayasaka S (2003) A new method of pebrine inspection of silkworm egg using multiprimer PCR. J Invertebr Pathol 82:148–151
Huang SK, Lu XM, Wang FW et al (2004) Comparative study on spore surface proteins of two microsporidia and their infectivity to silkworm Bombyx mori. Sci Seric 30:157–162
Huang WF, Tsai SJ, Lo CF et al (2004) The novel organization and complete sequence of the ribosomal RNA gene of Nosema bombycis. Fungal Genet Biol 41:473–481
Jiang KY, Zhu Y, Liu WX et al (2012) Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for the detection of F5 Fimbriae gene in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Curr Microbiol 65:633–638
Keeler SP, Ferro PJ, Brown JD et al (2012) Use of FTA sampling cards for molecular detection of avian influenza virus in wild birds. Avian Dis 56:200–207
Kokoskin E, Gyorkos TW, Camus A et al (1994) Modified technique for efficient detection of microsporidia. J Clin Microbiol 32:1074–1075
Liu JP, Cao Y, Smith JE (2004) Studies on the application of PCR molecular diagnosis to silkworms with simulated pebrine disease. Sci Agric Sin 37:1925–1931
Liu JP, Cao Y, Smith JE (2004) Studies on the application of PCR molecular diagnosis to silkworms eggs and moth with simulated pebrine disease. Sci Agric Sin 30:367–370
Lee SH, Joung M, Yoon S et al (2010) Multiplex PCR detection of waterborne intestinal protozoa: microsporidia, Cyclospora, and Cryptosporidium. Korean J Parasitol 48:297–301
Liu HD, Pan GQ, Song SH et al (2008) Multiple rDNA units distributed on all chromosomes of Nosema bombycis. J Invertebr Pathol 99:235–238
Maikai BV, Umoh JU, Lawal IA et al (2012) Molecular characterizations of Cryptosporidium, Giardia, and Enterocytozoon in humans in Kaduna State, Nigeria. Exp Parasitol 131:452–456
Njiru ZK, Mikosza AS, Armstrong T et al (2008) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method for rapid detection of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2:e147
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H et al (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28:e63
Orlandi PA, Lampel KA (2000) Extraction-free, filter-based template preparation for rapid and sensitive PCR detection of pathogenic parasitic protozoa. J Clin Microbiol 38:2271–2277
Pan ZH, Gong CL, Zheng XJ et al (2007) Study on the detection sensitivity of PCR method for silkworm Nosema bombycis DNA. J Chang Inst Technol 21:51–54
Pan MH, Wan YC, Lu C (2001) Studies on the methods for preparing DNA of different species of microsporidia. J Southwest Agric Univ 23(111–112):116
Pan ZH, Zheng XJ, Xue ZY et al (2005) The method for extraction of Nosema bombycis DNA from silkworm eggs with pebrine. Sci Seric 31:486–489
Raynaud L, Delbac F, Broussolle V et al (1998) Identification of Encephalitozoon intestinalis in travelers with chronic diarrhea by specific PCR amplification. J Clin Microbiol 36:37–40
Sorel N, Guillot E, Thellier M et al (2003) Development of an immunomagnetic separation–polymerase chain reaction (IMS–PCR) assay specific for Enterocytozoon bieneusi in water samples. J Appl Microbiol 94:273–279
Sanders JL, Kent ML (2011) Development of a sensitive assay for the detection of Pseudoloma neurophilia in laboratory populations of the zebrafish Danio rerio. Dis Aquat Org 96:145–156
Singh P, Mirdha BR, Ahuja V et al (2013) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for rapid detection of Entamoeba histolytica in amoebic liver abscess. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:27–32
Subrungruang I, Mungthin M, Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr P et al (2004) Evaluation of DNA extraction and PCR methods for detection of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 42:3490–3494
Stine SW, Vladich FD, Pepper IL et al (2005) Development of a method for the concentration and recovery of microsporidia from tap water. J Environ Sci Health 40:913–925
Taniuchi M, Verweij JJ, Sethabutr O et al (2011) Multiplex polymerase chain reaction method to detect Cyclospora, Cystoisospora, and Microsporidia in stool samples. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 71:386–390
Widmer G, Akiyoshi DE (2010) Host-specific segregation of ribosomal nucleotide sequence diversity in the microsporidian Enterocytozoon bieneusi. Infect Genet Evol 10:122–128
Wolk DM, Schneider SK, Wengenack NL et al (2002) Real-time PCR method for detection of Encephalitozoon intestinalis from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 40:3922–3928
Xu YJ, Takvorian P, Cali A et al (2006) Identification of a new spore wall protein from Encephalitozoon cuniculi. Infect Immun 74:239–247
Zhang FY, Shi YH, Jiang K et al (2012) Sensitive and rapid detection of two toxic microalgae Alexandrium by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Acta Oceanol Sin 31:139–146
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the earmarked fund for the China Agriculture Research System. We are grateful to all who provided the means for us to access the free software used in our study, as cited in this article. We thank all of our partners and lab members for their kind help and criticism.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, W., Shen, Z., Tang, X. et al. Detection of Nosema bombycis by FTA Cards and Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP). Curr Microbiol 69, 532–540 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0619-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0619-3