Abstract
Purpose
Oxaliplatin (L-OHP) is a third-generation, platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent and is widely used in gastroenterological cancer regimens. It is important to complete chemotherapy cycles to improve treatment efficacy for cancer patients. However, undesirable side effects, including acute and chronic neuropathies, and myelosuppression, lead to the discontinuation of chemotherapy in some treatment regimens. To predict and prevent the onset of side effects, and to establish appropriate dose adjustment, pharmacokinetic and toxicodynamic studies were performed to investigate the effects of L-OHP in rats.
Methods
Rats were administered intravenous L-OHP, once a week for 4 weeks, at doses of 3, 5, or 8 mg/kg. Pharmacokinetic profiles were observed on Day 1 and Day 22. Acute and chronic neuropathies were evaluated over 4 weeks; cold allodynia was evaluated using an acetone test and mechanical allodynia using the von Frey test. Hematological parameters were also investigated during the same period.
Results
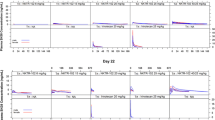
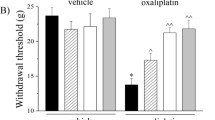
The mean AUC0-∞ values for L-OHP were 0.4 ± 0.2, 2.4 ± 0.4, and 3.5 ± 0.9 ng h/mL, increasing dose-dependently on Day 1. The accumulation of L-OHP on Day 22 was observed after repeated administration of L-OHP, as shown by mean AUC0-∞ values of 0.6 ± 0.2, 4.0 ± 1.0, and 14.1 ± 9.8 ng·h/mL, for the three doses. Cold allodynia was observed from Day 3 in the 5 and 8 mg/kg groups, and the extent of this response was dose-dependent. Mechanical allodynia was also observed from Day 10 in the 5 and 8 mg/kg groups. Moreover, the platelet count was the most sensitive among the hematological parameters.
Conclusion
These results provide useful experimental data for clinical cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, to establish a pharmacokinetic and toxicodynamic model of L-OHP for adequate dose adjustment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argyriou AA, Cavaletti G, Briani C et al (2013) Clinical pattern and association of oxaliplatin acute neurotoxicity: a prospective study in 170 patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer 119:438–444
Pasetto LM, D’Andrea MR, Rossia E, Monfardinia S (2006) Oxaliplatin-related neurotoxicity: how and why? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 59:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2006.01.001
Beonoit E, Brienza S, Dubois JM (2006) Oxaliplatin, an anticancer agent that affects both Na+ and K+ channels in frog peripheral myelinated axons. Gen Physiol Biophys 25:263–276
Kagiava A, Tsingotjidou A, Emmanouilides C, Theophilidis G (2008) The effects of oxaliplatin, an anticancer drug, on potassium channels of the peripheral myelinated nerve fibres of the adult rat. Neuro Toxicol 29: 1100 – 1006
Graham MA, Lockwood GF, Dennis Greenslade D, Brienza S, Bayssas M, Gamelin E (2000) Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin: a critical review. Clin Can Res 6:1205–1218
Grolleau F, Gamelin L, Boisdron-Celle M, Lapied B, Pelhate M, Gamelin E (2001) A possible explanation for a neurotoxic effect of the anticancer agent oxaliplatin on neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels. J Neurophysiol 85:2293–2297
Argyriou AA, Polychronopoulos P, Iconomou G, Koutras A, Makatsoris T, Gerolymos MK, Gourzis P, Assimakopoulos K, Kalofonos HP, Chroni E (2007) Incidence and characteristics of peripheral neuropathy during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for metastatic colon cancer. Acta Oncol 46:1131–1137. https://doi.org/10.1080/02841860701355055
Cavaletti G, Tredici G, Petruccioli MG, Dondè E, Tredici P, Marmiroli P, Minoia C, Ronchi A, Bayssas M, Etienne GG (2001) Effects of different schedules of oxaliplatin treatment on the peripheral nervous system of the rat. Eur J Cancer 37:2457–2463
McKeage MJ, Hsu T, Screnci D, Haddad G, Baguley BC (2001) Nucleolar damage correlates with neurotoxicity induced by different platinum drugs. Br J Cancer 85:1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2001.2024
Luo FR1, Wyrick SD, Chaney SG (1999) Comparative neurotoxicity of oxaliplatin, ormaplatin, and their biotransformation products utilizing a rat dorsal root ganglia in vitro explant culture model. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 44:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002800050941
Jamieson SM, Liu J, Connor B, McKeage MJ (2005) Oxaliplatin causes selective atrophy of a subpopulation of dorsal root ganglion neurons without inducing cell loss. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 56:391–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-004-0953-4
Nakayama G, Kodera Y, Yokoyama H, Okuda N, Watanabe T, Tanaka C, Iwata N, Ohashi N, Koike M, Fujiwara M, Nakao A (2011) Modified FOLFOX6 with oxaliplatin stop-and-go strategy and oral S-1 maintenance therapy in advanced colorectal cancer: CCOG-0704 study. Int J Clin Oncol 16: 506 – 11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-011-0214-6
Gamelin L, Boisdron-Celle M, Delva R, Guérin-Meyer V, Ifrah N, Morel A, Gamelin E (2004) Prevention of oxaliplatin-related neurotoxicity by calcium and magnesium infusions: a retrospective study of 161 patients receiving oxaliplatin combined with 5-Fluorouracil and leucovorin for advanced colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15:4055–4061. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0666
Gamelin L, Boisdron-Celle M, Morel A, Poirier AL, Berger V, Gamelin E, Tournigand C, de Gramont A (2008) Oxaliplatin-related neurotoxicity: interest of calcium-magnesium infusion and no impact on its efficacy. J Clin Oncol 26:1188–1190. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.15.3767
Shord SS, Bernard SA, Lindley C, Blodgett A, Mehta V, Churchel MA, Poole M, Pescatore SL, Luo FR, Chaney SG (2002) Oxaliplatin biotransformation and pharmacokinetics: a pilot study to determine the possible relationship to neurotoxicity. Anticancer Res 22:2301–2309
Beg MS, Komrokji RS, Ahmed K, Safa MM (2008) Oxaliplatin-induced immune mediated thrombocytopenia. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62:925–927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-007-0675-5
Curtis BR, Kaliszewski J, Marques MB, Saif MW, Nabelle L, Blank J, McFarland JG, Aster RH (2006) Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia resulting from sensitivity to oxaliplatin. Am J Hematol 81:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.20516
Toshiaki Watanabe T, Michio Itabash M, Yasuhiro Shimada Y, Shinji Tanaka S, Yoshinori Ito Y, Yoichi Ajioka Y et al (2010) Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (JSCCR) guidelines 2010 for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 17:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-011-0315-2 (Epub 2011 Oct 15)
Flatters SJ, Bennett GJ (2004) Ethosuximide reverses paclitaxel- and vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Pain 109: 150–161 10.1016/j.pain.2004.01.029
Di Cesare Mannelli L, Pacini A, Bonaccini L, Zanardelli M, Mello T, Ghelardini C (2013) Morphologic features and glial activation in rat oxaliplatin-dependent neuropathic pain. J Pain 14: 1585–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2013.08.002
Sakurai M, Egashira N, Kawashiri T, Yano T, Ikesue H, Oishi R (2009) Oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy in the rat: involvement of oxalate in cold hyperalgesia but not mechanical allodynia. Pain 147: 165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2009.09.003
Minakata K, Suzuki M, Nozawa H, Gonmori K, Watanabe K, Suzuki O (2006) Platinum levels in various tissues of a patient who died 181 days after cisplatin overdosing determined by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Forensic Toxicol 24:83–87
Argyriou AA, Bruna J, Marmiroli P, Cavaletti G (2011) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity (CIPN): an update. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 82:51–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2011.04.012
Di Cesare Mannelli L, Pacini A, Corti F, Boccella S, Luongo L, Esposito E, Cuzzocrea S, Maione S, Calignano A, Ghelardini C (2015) Antineuropathic profile of N-palmitoylethanolamine in a rat model of oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity. PLoS One 10:e0128080. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128080
Grothey A (2003) Oxaliplatin-safety profile: neurotoxicity. Semin Oncol 30(4 Suppl 15):5–13
Schmelz R, Lersch C (2002) Acute oxaliplatin-induced peripheral-nerve hyperexcitability. J Clin Oncol 20:3561–3562
Boughattas NA1, Hecquet B, Fournier C, Bruguerolle B, Trabelsi H, Bouzouita K, Omrane B, Lévi F (1994) Comparative pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin (L-OHP) and carboplatin (CBDCA) in mice with reference to circadian dosing time. Biopharm Drug Dispos 15: 761 – 73
Kiernan MC (2007) The pain with platinum: oxaliplatin and neuropathy. Eur J Cancer 43:2631–2633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2007.09.008
Saif MW, Reardon J (2005) Management of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy. Ther Clin Risk Manag 1: 249 – 58
Reddy SM, Vergo MT, Paice JA, Kwon N, Helenowski IB, Benson AB, Mulcahy MF, Nimeiri HS, Harden RN (2015) Quantitative sensory testing at baseline and during cycle 1 oxaliplatin infusion detects subclinical peripheral neuropathy and predicts clinically overt chronic neuropathy in gastrointestinal malignancies. Clin Colorectal Cancer 15:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clcc.2015.07.001
Jardim DL, Rodrigues CA, Novis YA, Rocha VG, Hoff PM (2012) Oxaliplatin-related thrombocytopenia. Ann Oncol 23:1937–1942. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mds074
Puchalski TA, Krzyzanski W, Blum RA, Jusko WJ (2001) Pharmacodynamic modeling of lansoprazole using an indirect irreversible response model. J Clin Pharmacol 41(3):251–258
Pachman D, Qin R, Seisler DK, Smith EMI, Beutler AS, Ta LE, Lafky JM, Wagner-Johnston ND, Ruddy KJ, Dakhil S, Staff NP, Grothey A, Loprinzi CL (2015) Clinical course of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy: results from the randomized phase III trial N08CB (Alliance). J Clin Oncol 33:3416–3422. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.58.8533
Acknowledgements
I would like to express the deepest appreciation to Professor Toshiyuki Sakaeda. Without his guidance and persistent help, this paper would not have been possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from JSPS KAKENHI, Grant number 15K08085.
Conflict of interest
Y. Ito declares that she has no conflict of interest. S. Kobuchi declares that he has no conflict of interest. R. Shimizu hat she has no conflict of interest. Y. Katsuyama that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Experiments were conducted in accordance with the Guidelines for Animal Experimentation, Kyoto Pharmaceutical University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, Y., Kobuchi, S., Shimizu, R. et al. Pharmacokinetic and toxicodynamic evaluation of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy and hematological toxicity in rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 81, 155–161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3485-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3485-4