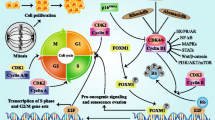
Abstract
Abnormalities in the cell cycle are responsible for the majority of human neoplasias. Most abnormalities occur due to hyperphosphorylation of the tumor suppressor gene Rb by the key regulators of the cell cycle, the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Thus, a pharmacological CDK inhibitor may be useful in the prevention and/or treatment of human neoplasms. Flavopiridol is a flavonoid with interesting preclinical properties: (1) potent CDK inhibitory activity; (2) it depletes cyclin D1 and vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA by transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms, respectively; (3) it inhibits positive elongation factor B, leading to transcription "halt"; and (4) it induces apoptosis in several preclinical models. The first phase I trial of a CDK inhibitor, flavopiridol, has been completed. Dose-limiting toxicities included secretory diarrhea and proinflammatory syndrome. Antitumor activity was observed in some patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and renal, colon, and prostate cancers. Concentrations between 300 and 500 nM—necessary to inhibit CDK—were achieved safely. Phase II trials with infusional flavopiridol and phase I infusional trials in combination with standard chemotherapy are being completed with encouraging results. A novel phase I trial of 1-h flavopiridol administration was recently completed. The maximum tolerated doses using flavopiridol daily for 5, 3, and 1 consecutive days are 37.5, 50, and 62.5 mg/m2 per day. Dose-limiting toxicities include vomiting, neutropenia, proinflammatory syndrome, and diarrhea. Plasma flavopiridol concentrations achieved were in the range 1.5–3.5 μM. Phase II/III trials using this 1-h schedule in several tumor types including non-small-cell lung cancer, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, mantle cell lymphoma, and head and neck cancer are being conducted worldwide. UCN-01, the second CDK modulator that has entered clinical trials, has unique preclinical properties: (1) it inhibits protein kinase C (PKC) activity; (2) it promotes cell-cycle arrest by accumulation in p21/p27; (3) it induces apoptosis in several preclinical models; and (4) it abrogates the G2 checkpoint by inhibition of chk1. The last of these represents a novel strategy to combine UCN-01 with DNA-damaging agents. In the initial UCN-01 clinical trial (continuous infusion for 72 h), a prolonged half-life of about 600 h (100 times longer than in preclinical models) was observed. The maximum tolerated dose was 42.5 mg/m2 per day for 3 days. Dose-limiting toxicities were nausea/vomiting, hypoxemia, and symptomatic hyperglycemia. One patient with melanoma achieved a partial response (8 months). Another patient with refractory anaplastic large-cell lymphoma had no evidence of disease at >4 years. Bone marrow and tumor samples obtained from some patients revealed loss in adducin phosphorylation, a substrate of PKC. Phase I trials with shorter infusions are being completed. In summary, the first two CDK modulators have shown encouraging results in early clinical trials. A question that remains unanswered is "Which is the best schedule for combination with standard antitumor agents?" Moreover, it is still unclear which pharmacodynamic endpoint reflects loss of CDK activity in tissue samples from patients in these trials. Despite these caveats, we feel that CDKs are sensible targets for cancer therapy and that there are several small-molecule CDK modulators in clinical trials with encouraging results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J, Palombella VJ, Elliott PJ (2000) Proteasome inhibition: a new strategy in cancer treatment. Invest New Drugs 18:109
Akinaga S, Gomi K, Morimoto M, Tamaoki T, Okabe M (1991) Antitumor activity of UCN-01, a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C, in murine and human tumor models. Cancer Res 51:4888
Akinaga S, Nomura K, Gomi K, Okabe M (1993) Enhancement of antitumor activity of mitomycin C in vitro and in vivo by UCN-01, a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 32:183
Akinaga S, Nomura K, Gomi K, Okabe M (1994) Effect of UCN-01, a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C, on the cell-cycle distribution of human epidermoid carcinoma, A431 cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 33:273
Akiyama T, Yoshida T, Tsujita T, Shimizu M, Mizukami T, Okabe M, Akinaga S (1997) G1 phase accumulation induced by UCN-01 is associated with dephosphorylation of Rb and CDK2 proteins as well as induction of CDK inhibitor p21/Cip1/WAF1/Sdi1 in p53-mutated human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Cancer Res 57:1495
Akiyama T, Shimizu M, Okabe M, Tamaoki T, Akinaga S (1999) Differential effects of UCN-01, staurosporine and CGP 41 251 on cell cycle progression and CDC2/cyclin B1 regulation in A431 cells synchronized at M phase by nocodazole. Anticancer Drugs 10:67
Arguello F, Alexander M, Sterry J, Tudor G, Smith E, Kalavar N, Greene J, Koss W, Morgan D, Stinson S, Siford T, Alvord W, Labansky R, Sausville E (1998) Flavopiridol induces apoptosis of normal lymphoid cells, causes immunosuppression, and has potent antitumor activity in vivo against human and leukemia xenografts. Blood 91:2482
Baratte B, Meijer L, Galaktionov K, Beach D (1992) Screening for antimitotic compounds using the cdc25 tyrosine phosphatase, an activator of the mitosis-inducing p34cdc2/cyclin Bcdc13 protein kinase. Anticancer Res 12:873
Bennett S, Mani S, O'Reilly S, Wright J, Schilsky R, Vokes E, Grochow L (1999) Phase II trial of flavopiridol in metastatic colorectal cancer: preliminary results (abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol
Bible KC, Kaufmann SH (1996) Flavopiridol: a cytotoxic flavone that induces cell death in noncycling A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 56:4856
Bible KC, Kaufmann SH (1997) Cytotoxic synergy between flavopiridol (NSC 649890, L86-8275) and various antineoplastic agents: the importance of sequence of administration. Cancer Res 57:3375
Blanchard JL, Epstein DM, Boisclair MD, Rudolph J, Pal K (1999) Dysidiolide and related gamma-hydroxy butenolide compounds as inhibitors of the protein tyrosine phosphatase, CDC25. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9:2537
Bonfanti M, Taverna S, Salmona M, D'Incalci M, Broggini M (1997) p21WAF1-derived peptides linked to an internalization peptide inhibit human cancer cell growth. Cancer Res 57:1442
Brooks EE, Gray NS, Joly A, Kerwar SS, Lum R, Mackman RL, Norman TC, Rosete J, Rowe M, Schow SR, Schultz PG, Wang X, Wick MM, Shiffman D (1997) CVT-313, a specific and potent inhibitor of CDK2 that prevents neointimal proliferation. J Biol Chem 272:29207
Brusselbach S, Nettelbeck DM, Sedlacek HH, Muller R (1998) Cell cycle-independent induction of apoptosis by the anti-tumor drug flavopiridol in endothelial cells. Int J Cancer 77:146
Bunch RT, Eastman A (1996) Enhancement of cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity by 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01), a new G2-checkpoint inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res 2:791
Bunch RT, Eastman A (1997) 7-Hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) causes redistribution of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and abrogates cisplatin-induced S-phase arrest in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell Growth Differ 8:779
Buquet-Fagot C, Lallemand F, Montagne M, Mester J (1997) Effects of olomucine, a selective inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases, on cell cycle progression in human cancer cell lines. Anticancer Drugs 8:623
Busby EC, Leistritz DF, Abraham RT, Karnitz LM, Sarkaria JN (2000) The radiosensitizing agent 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) inhibits the DNA damage checkpoint kinase hChk1. Cancer Res 60:2108
Byrd JC, Shinn C, Waselenko JK, Fuchs EJ, Lehman TA, Nguyen PL, Flinn IW, Diehl LF, Sausville E, Grever MR (1998) Flavopiridol induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via activation of caspase-3 without evidence of bcl-2 modulation or dependence on functional p53. Blood 92:3804
Cagnoli M, Barbieri F, Bruzzo C, Alama A (1998) Control of cyclin D1 expression by antisense oligonucleotides in three ovarian cancer cell lines. Gynecol Oncol 70:372
Carlson B, Pearlstein R, Naik R, Sedlacek H, Sausville E, Worland P (1996) Inhibition of CDK2, CDK4 and CDK7 by flavopiridol and structural analogs (abstract 101). Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res
Carlson BA, Dubay MM, Sausville EA, Brizuela L, Worland PJ (1996) Flavopiridol induces G1 arrest with inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 2 and CDK4 in human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 56:2973
Carlson B, Lahusen T, Singh S, Loaiza-Perez A, Worland PJ, Pestell R, Albanese C, Sausville EA, Senderowicz AM (1999) Downregulation of cyclin D1 by transcriptional repression in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells induced by flavopiridol. Cancer Res 59:4634
Chao SH, Fujinaga K, Marion JE, Taube R, Sausville EA, Senderowicz AM, Peterlin BM, Price DH (2000) Flavopiridol inhibits P-TEFb and blocks HIV-1 replication. J Biol Chem 275:28345
Chen X, Lowe M, Keyomarsi K (1999) UCN-01-mediated G1 arrest in normal but not tumor breast cells is pRb-dependent and p53-independent. Oncogene 18:5691
Chen YN, Sharma SK, Ramsey TM, Jiang L, Martin MS, Baker K, Adams PD, Bair KW, Kaelin WG (1999) Selective killing of transformed cells by cyclin/cyclin-dependent kinase 2 antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:4325
Chiarugi V, Magnelli L, Cinelli M, Basi G (1994) Apoptosis and the cell cycle. Cell Mol Biol Res 40:603
Chien M, Astumian M, Liebowitz D, Rinker-Schaeffer C, Stadler W (1999) In vitro evaluation of flavopiridol, a novel cell cycle inhibitor, in bladder cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 44:81
Chintala SK, Fueyo J, Gomez-Manzano C, Venkaiah B, Bjerkvig R, Yung WK, Sawaya R, Kyritsis AP, Rao JS (1997) Adenovirus-mediated p16/CDKN2 gene transfer suppresses glioma invasion in vitro. Oncogene 15:2049
Choi YH, Lee SJ, Nguyen P, Jang JS, Lee J, Wu ML, Takano E, Maki M, Henkart PA, Trepel JB (1997) Regulation of cyclin D1 by calpain protease. J Biol Chem 272:28479
Colas P, Cohen B, Jessen T, Grishina I, McCoy J, Brent R (1996) Genetic selection of peptide aptamers that recognize and inhibit cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature 380:548
Cordon-Cardo C (1995) Mutations of cell cycle regulators. Biological and clinical implications for human neoplasia. Am J Pathol 147:545
Craig C, Wersto R, Kim M, Ohri E, Li Z, Katayose D, Lee SJ, Trepel J, Cowan K, Seth P (1997) A recombinant adenovirus expressing p27Kip1 induces cell cycle arrest and loss of cyclin-Cdk activity in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 14:2283
De Azevedo WF, Mueller-Dieckmann HJ, Schulze-Gahmen U, Worland PJ, Sausville E, Kim SH (1996) Structural basis for specificity and potency of a flavonoid inhibitor of human CDK2, a cell cycle kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:2735
De Azevedo WF, Leclerc S, Meijer L, Havlicek L, Strnad M, Kim SH (1997) Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by purine analogues: crystal structure of human CDK2 complexed with roscovitine. Eur J Biochem 243:518
Dees E, O'Reilly S, Figg W, Elza-Brown K, Aylesworth C, Carducci M, Byrd J, Grever M, Donehower R (2000) A phase I and pharmacologic study of UCN-01, a protein kinase C inhibitor (abstract 2342). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol
DeGregori J, Leone G, Ohtani K, Miron A, Nevins JR (1995) E2F-1 accumulation bypasses a G1 arrest resulting from the inhibition of G1 cyclin-dependent kinase activity. Genes Dev 9:2873
DelSal G, Loda M, Pagano M (1996) Cell cycle and cancer: critical events at the G1 restriction point. Crit Rev Oncog 7:127
Dodo K, Takahashi M, Yamada Y, Sugimoto Y, Hashimoto Y, Shirai R (2000) Synthesis of a novel class of cdc25A inhibitors from vitamin D3. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10:615
Drees M, Dengler WA, Roth T, Labonte H, Mayo J, Malspeis L, Grever M, Sausville EA, Fiebig H (1997) Flavopiridol (L86-8275): selective antitumor activity in vitro and activity in vivo for prostate carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 3:273
Driscoll B, Buckley S, Barsky L, Weinberg K, Anderson KD, Warburton D (1999) Abrogation of cyclin D1 expression predisposes lung cancer cells to serum deprivation-induced apoptosis. Am J Physiol 276:L679
Eastham JA, Hall SJ, Sehgal I, Wang J, Timme TL, Yang G, Connell-Crowley L, Elledge SJ, Zhang WW, Harper JW (1995) In vivo gene therapy with p53 or p21 adenovirus for prostate cancer. Cancer Res 55:5151
Edwards MC, Wong C, Elledge SJ (1998) Human cyclin K, a novel RNA polymerase II-associated cyclin possessing both carboxy-terminal domain kinase and Cdk-activating kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol 18:4291
Eicher SA, Clayman GL, Liu TJ, Shillitoe EJ, Storthz KA, Roth JA, Lotan R (1996) Evaluation of topical gene therapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in an organotypic model. Clin Cancer Res 2:1659
Elledge SJ (1996) Cell cycle checkpoints: preventing an identity crisis. Science 274:1664
Fahraeus R, Paramio JM, Ball KL, Lain S, Lane DP (1996) Inhibition of pRb phosphorylation and cell-cycle progression by a 20-residue peptide derived from p16CDKN2/INK4A. Curr Biol 6:84
Fingert HJ, Pu AT, Chen ZY, Googe PB, Alley MC, Pardee AB (1988) In vivo and in vitro enhanced antitumor effects by pentoxifylline in human cancer cells treated with thiotepa. Cancer Res 48:4375
Fowler L, Dong L, Bowes RC, van de Water B, Stevens JL, Jaken S (1998) Transformation-sensitive changes in expression, localization, and phosphorylation of adducins in renal proximal tubule epithelial cells. Cell Growth Differ 9:177
Fredersdorf S, Burns J, Milne AM, Packham G, Fallis L, Gillett CE, Royds JA, Peston D, Hall PA, Hanby AM, Barnes DM, Shousha S, O'Hare MJ, Lu X (1997) High level expression of p27(kip1) and cyclin D1 in some human breast cancer cells: inverse correlation between the expression of p27(kip1) and degree of malignancy in human breast and colorectal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:6380
Fuse E, Tanii H, Kurata N, Kobayashi H, Shimada Y, Tamura T, Sasaki Y, Tanigawara Y, Lush RD, Headlee D, Figg W, Arbuck SG, Senderowicz AM, Sausville EA, Akinaga S, Kuwabara T, Kobayashi S (1998) Unpredicted clinical pharmacology of UCN-01 caused by specific binding to human alpha1-acid glycoprotein. Cancer Res 58:3248
Gansauge S, Gansauge F, Ramadani M, Stobbe H, Rau B, Harada N, Beger HG (1997) Overexpression of cyclin D1 in human pancreatic carcinoma is associated with poor prognosis. Cancer Res 57:1634
Gius DR, Ezhevsky SA, Becker-Hapak M, Nagahara H, Wei MC, Dowdy SF (1999) Transduced p16INK4a peptides inhibit hypophosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle progression prior to activation of Cdk2 complexes in late G1. Cancer Res 59:2577
Grana X, Reddy EP (1995) Cell cycle control in mammalian cells: role of cyclins, cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs), growth suppressor genes and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs). Oncogene 11:211
Grana X, De Luca A, Sang N, Fu Y, Claudio PP, Rosenblatt J, Morgan DO, Giordano A (1994) PITALRE, a nuclear CDC2-related protein kinase that phosphorylates the retinoblastoma protein in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:3834
Graves PR, Yu L, Schwarz JK, Gales J, Sausville EA, O'Connor PM, Piwnica-Worms H (2000) The Chk1 protein kinase and the Cdc25C regulatory pathways are targets of the anticancer agent UCN-01. J Biol Chem 275:5600
Gray NS, Wodicka L, Thunnissen AM, Norman TC, Kwon S, Espinoza FH, Morgan DO, Barnes G, LeClerc S, Meijer L, Kim SH, Lockhart DJ, Schultz PG (1998) Exploiting chemical libraries, structure, and genomics in the search for kinase inhibitors. Science 281:533
Gray N, Detivaud L, Doerig C, Meijer L (1999) ATP-site directed inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases. Curr Med Chem 6:859
Gray-Bablin J, Rao S, Keyomarsi K (1997) Lovastatin induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in human breast cells occurs in a cell cycle-independent fashion. Cancer Res 57:604
Harper J, Elledge S (1996) Cdk inhibitors in development and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 6:56
Hartwell LH, Kastan MB (1994) Cell cycle control and cancer. Science 266:1821
Hashemolhosseini S, Nagamine Y, Morley SJ, Desrivieres S, Mercep L, Ferrari S (1998) Rapamycin inhibition of the G1 to S transition is mediated by effects on cyclin D1 mRNA and protein stability. J Biol Chem 273:14424
Hsueh CT, Kelsen D, Schwartz GK (1998) UCN-01 suppresses thymidylate synthase gene expression and enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in a sequence-dependent manner. Clin Cancer Res 4:2201
Husain A, Yan XJ, Rosales N, Aghajanian C, Schwartz GK, Spriggs DR (1997) UCN-01 in ovary cancer cells: effective as a single agent and in combination with cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) independent of p53 status. Clin Cancer Res 3:2089
Innocenti F, Stadler W, Iyer L, Vokes EE, Ratain MJ (2000) Flavopiridol-induced diarrhea is related to the systemic metabolism of flavopiridol to its glucuronide (abstract 694). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol
Jin X, Nguyen D, Zhang WW, Kyritsis AP, Roth JA (1995) Cell cycle arrest and inhibition of tumor cell proliferation by the p16INK4 gene mediated by an adenovirus vector. Cancer Res 55:3250
Jones CB, Clements MK, Wasi S, Daoud SS (2000) Enhancement of camptothecin-induced cytotoxicity with UCN-01 in breast cancer cells: abrogation of S/G(2) arrest. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 45:252
Kaldis P, Russo AA, Chou HS, Pavletich NP, Solomon MJ (1998) Human and yeast Cdk-activating kinases (CAKs) display distinct substrate specificities. Mol Biol Cell 9:2545
Kasten MM, Giordano A (1998) pRb and the CDKs in apoptosis and the cell cycle. Cell Death Differ 5:132
Katayose Y, Kim M, Rakkar AN, Li Z, Cowan KH, Seth P (1997) Promoting apoptosis: a novel activity associated with the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Cancer Res 57:5441
Kaur G, Stetler-Stevenson M, Sebers S, Worland P, Sedlacek H, Myers C, Czech J, Naik R, Sausville E (1992) Growth inhibition with reversible cell cycle arrest of carcinoma cells by flavone L86-8275. J Natl Cancer Inst 84:1736
Kawakami K, Futami H, Takahara J, Yamaguchi K (1996) UCN-01, 7-hydroxyl-staurosporine, inhibits kinase activity of cyclin-dependent kinases and reduces the phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product in A549 human lung cancer cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 219:778
Kent LL, Hull-Campbell NE, Lau T, Wu JC, Thompson SA, Nori M (1999) Characterization of novel inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 260:768
Kerr JS, Wexler RS, Mousa SA, Robinson CS, Wexler EJ, Mohamed S, Voss ME, Devenny JJ, Czerniak PM, Gudzelak A, Slee AM (1999) Novel small molecule alpha v integrin antagonists: comparative anti-cancer efficacy with known angiogenesis inhibitors. Anticancer Res 19:959
Kitagawa M, Okabe T, Ogino H, Matsumoto H, Suzuki-Takahashi I, Kokubo T, Higashi H, Saitoh S, Taya Y, Yasuda H (1993) Butyrolactone I, a selective inhibitor of cdk2 and cdc2 kinase. Oncogene 8:2425
Konig A, Schwartz GK, Mohammad RM, Al-Katib A, Gabrilove JL (1997) The novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol downregulates Bcl-2 and induces growth arrest and apoptosis in chronic B-cell leukemia lines. Blood 90:4307
Kornmann M, Arber N, Korc M (1998) Inhibition of basal and mitogen-stimulated pancreatic cancer cell growth by cyclin D1 antisense is associated with loss of tumorigenicity and potentiation of cytotoxicity to cisplatinum. J Clin Invest 101:344
Lahusen J, Loaiza-Perez A, Sausville EA, Senderowicz AM (2000) Flavopiridol-induced apoptosis is associated with p38 and MEK activation and is prevented by caspase and MAPK inhibitors (abstract 2202). Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res
Lee HR, Chang TH, Tebalt MJ, Senderowicz AM, Szabo E (1999) Induction of differentiation accompanies inhibition of CDK2 in a non-small cell lung cancer cell line. Int J Oncol 15:161
Lees JA, Saito M, Vidal M, Valentine M, Look T, Harlow E, Dyson N, Helin K (1993) The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol 13:7813
Losiewicz MD, Carlson BA, Kaur G, Sausville EA, Worland PJ (1994) Potent inhibition of CDC2 kinase activity by the flavonoid L86-8275. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 201:589
Lowe SW, Bodis S, Bardeesy N, McClatchey A, Remington L, Ruley HE, Fisher DE, Jacks T, Pelletier J, Housman DE (1994) Apoptosis and the prognostic significance of p53 mutation. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 59:419
MacLachlan TK, Sang N, Giordano A (1995) Cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases and CDK inhibitors: implications in cell cycle control and cancer. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 5:127
Marchetti A, Buttitta F, Merlo G, Diella F, Pellegrini S, Pepe S, Macchiarini P, Chella A, Angeletti CA, Callahan R (1993) p53 alterations in non-small cell lung cancers correlate with metastatic involvement of hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes. Cancer Res 53:2846
Meijer L (2000) Cyclin-dependent kinases inhibitors as potential anticancer, antineurodegenerative, antiviral and antiparasitic agents. Drug Resist Updates 3:83
Meijer L, Kim SH (1997) Chemical inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases. Methods Enzymol 283:113
Meijer L, Borgne A, Mulner O, Chong JP, Blow JJ, Inagaki N, Inagaki M, Delcros JG, Moulinoux JP (1997) Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, CDK2 and CDK5. Eur J Biochem 243:527
Meikrantz W, Schlegel R (1996) Suppression of apoptosis by dominant negative mutants of cyclin-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem 271:10205
Melillo G, Sausville EA, Cloud K, Lahusen T, Varesio L, Senderowicz AM (1999) Flavopiridol, a protein kinase inhibitor, down-regulates hypoxic induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human monocytes. Cancer Res 59:5433
Michalides R, van Veelen N, Hart A, Loftus B, Wientjens E, Balm A (1995) Overexpression of cyclin D1 correlates with recurrence in a group of forty-seven operable squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res 55:975
Muise-Helmericks RC, Grimes HL, Bellacosa A, Malstrom SE, Tsichlis PN, Rosen N (1998) Cyclin D expression is controlled post-transcriptionally via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 273:29864
Pardee AB (1994) Multiple molecular levels of cell cycle regulation. J Cell Biochem 54:375
Pardee S (1974) A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 71:1286
Park S, Cheon J, Lee Y, Park Y, Lee K, Lee C, Lee S (1996) A specific inhibitor of cyclin-dependent protein kinases, CDC2 and CDK2. Mol Cell 6:679
Parker B, Kaur G, Nieves-Neira W, Taimi M, Kolhagen G, Shimizu T, Pommier Y, Sausville E, Senderowicz AM (1998) Early induction of apoptosis in hematopoietic cell lines after exposure to flavopiridol. Blood 91:458
Patel V, Senderowicz AM, Pinto D, Igishi T, Raffeld M, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ensley JF, Sausville EA, Gutkind JS (1998) Flavopiridol, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, suppresses the growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas by inducing apoptosis. J Clin Invest 102:1674
Patel V, Lahusen T, Sy T, Sausville EA, Gutkind JS, Senderowicz AM (2002) Perifosine, a novel alkylphospholipid, induces p21(WAF1) expression in squamous carcinoma cells through a p53-independent pathway, leading to loss in cyclin-dependent kinase activity and cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res 62:1401
Patel V, Lahusen T, Leethanakul C, Igishi T, Kremer C, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ensley JF, Sausville EA, Gutkind JS, Senderowicz AM (2002) Antitumor activity of UCN-01 in carcinomas of the head and neck is associated with altered expression of cyclin D3 and p27(KIP1). Clin Cancer Res 8:3549
Paulovich A, Toczyski D, Hartwell L (1997) When checkpoints fail. Cell 88:315
Peng J, Zhu Y, Milton JT, Price DH (1998) Identification of multiple cyclin subunits of human P-TEFb. Genes Dev 12:755
Pines J (1994) The cell cycle kinases. Semin Cancer Biol 5:305
Pines J (1995) Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: theme and variations. Adv Cancer Res 66:181
Pollack IF, Kawecki S, Lazo JS (1996) Blocking of glioma proliferation in vitro and in vivo and potentiating the effects of BCNU and cisplatin: UCN-01, a selective protein kinase C inhibitor. J Neurosurg 84:1024
Rickert P, Seghezzi W, Shanahan F, Cho H, Lees E (1996) Cyclin C/CDK8 is a novel CTD kinase associated with RNA polymerase II. Oncogene 12:2631
Roberge M, Tudan C, Hung SM, Harder KW, Jirik FR, Anderson H (1994) Antitumor drug fostriecin inhibits the mitotic entry checkpoint and protein phosphatases 1 and 2A. Cancer Res 54:6115
Rosania GR, Merlie J, Gray N, Chang YT, Schultz PG, Heald R (1999) A cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor inducing cancer cell differentiation: biochemical identification using Xenopus egg extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:4797
Sandig V, Brand K, Herwig S, Lukas J, Bartek J, Strauss M (1997) Adenovirally transferred p16INK4/CDKN2 and p53 genes cooperate to induce apoptotic tumor cell death. Nat Med 3:313
Sarkaria JN, Busby EC, Tibbetts RS, Roos P, Taya Y, Karnitz LM, Abraham RT (1999) Inhibition of ATM and ATR kinase activities by the radiosensitizing agent, caffeine. Cancer Res 59:4375
Sato S, Fujita N, Tsuruo T (2002) Interference with PDK1-Akt survival signaling pathway by UCN-01 (7-hydroxystaurosporine). Oncogene 21:1727
Sausville EA, Lush RD, Headlee D, Smith AC, Figg WD, Arbuck SG, Senderowicz AM, Fuse E, Tanii H, Kuwabara T, Kobayashi S (1998) Clinical pharmacology of UCN-01: initial observations and comparison to preclinical models. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol [Suppl] 42:S54
Sausville EA, Arbuck SG, Messmann R, Headlee D, Bauer KS, Lush RM, Murgo A, Figg WD, Lahusen T, Jaken S, Jing X, Roberge M, Fuse E, Kuwabara T, Senderowicz AM (2001) Phase I trial of 72-hour continuous infusion UCN-01 in patients with refractory neoplasms. J Clin Oncol 19:2319
Schrump DS, Matthews W, Chen GA, Mixon A, Altorki NK (1998) Flavopiridol mediates cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in esophageal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 4:2885
Schultz C, Link A, Leost M, Zaharevitz DW, Gussio R, Sausville EA, Meijer L, Kunick C (1999) Paullones, a series of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: synthesis, evaluation of CDK1/cyclin B inhibition, and in vitro antitumor activity. J Med Chem 42:2909
Schutte B, Nieland L, van Engeland M, Henfling ME, Meijer L, Ramaekers FC (1997) The effect of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor olomoucine on cell cycle kinetics. Exp Cell Res 236:4
Schwartz G, Farsi K, Maslak P, Kelsen D, Spriggs D (1997) Potentiation of apoptosis by flavopiridol in mitomycin-C-treated gastric and breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 3:1467
Schwartz G, Kaubisch A, Saltz L, Ilson D, O'Reilly E, Barazzuol J, Endres S, Soltz M, Tong W, Spriggs D, Kelsen D (1999) Phase I trial of sequential paclitaxel and the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol (abstract 3215). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol
Schwartz GK, O'Reilly E, Ilson D, Saltz L, Sharma S, Tong W, Maslak P, Stoltz M, Eden L, Perkins P, Endres S, Barazzoul J, Spriggs D, Kelsen D (2002) Phase I study of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol in combination with paclitaxel in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 20:2157
Sedlacek HH, Czech J, Naik R, Kaur G, Worland P, Losiewicz M, Parker B, Carlson B, Smith A, Senderowicz A, Sausville E (1996) Flavopiridol (L86-8275, NSC-649890), a new kinase inhibitor for tumor therapy. Int J Oncol 9:1143
Senderowicz AM (1999) Flavopiridol: the first cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor in human clinical trials. Invest New Drugs 17:313
Senderowicz AM (2000) Small molecule modulators of cyclin-dependent kinases for cancer therapy. Oncogene 19:6600
Senderowicz AM (2001) Cyclin-dependent kinase modulators: a novel class of cell cycle regulators for cancer therapy. In: Giaccone G, Schilsky R, Sondel P (eds) Cancer chemotherapy and biological response modifiers (annual 19). Elsevier Science, Oxford
Senderowicz AM (2001) Cyclin-dependent kinase modulators: a novel class of cell cycle regulators for cancer therapy. Cancer Chemother Biol Response Modif 19:165
Senderowicz AM (2001) Development of cyclin-dependent kinase modulators as novel therapeutic approaches for hematological malignancies. Leukemia 15:1
Senderowicz AM (2002) The cell cycle as a target for cancer therapy: basic and clinical findings with the small molecule inhibitors flavopiridol and UCN-01. Oncologist 7:12
Senderowicz AM, Sausville EA (2000) Preclinical and clinical development of cyclin-dependent kinase modulators. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:376
Senderowicz AM, Headlee D, Stinson S, Lush RM, Tompkins A, Brawley O, Bergan R, Figg WD, Smith A, Sausville EA (1996) Phase I trial of a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol in patients with refractory neoplasms. In: 9th National Cancer Institute–European Organization for Research on Treatment of Cancer Symposium Proceedings. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, p 77
Senderowicz AM, Headlee D, Stinson SF, Lush RM, Kalil N, Villalba L, Hill K, Steinberg SM, Figg WD, Tompkins A, Arbuck SG, Sausville EA (1998) Phase I trial of continuous infusion flavopiridol, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in patients with refractory neoplasms. J Clin Oncol 16:2986
Senderowicz AM, Headlee D, Lush R, Bauer K, Figg W, Murgo AS, Arbuck S, Inoue K, Kobashi S, Kuwabara T, Sausville E (1998) Phase I trial of infusional UCN-01, a novel protein kinase inhibitor, in patients with refractory neoplasms. In: 10th National Cancer Institute–European Organization for Research on Treatment of Cancer Symposium Proceedings. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, p 78
Senderowicz AM, Headlee D, Lush R, Bauer K, Figg W, Murgo AS, Arbuck S, Inoue K, Kobashi S, Kuwabara T, Sausville E (1999) Phase I trial of infusional UCN-01, a novel protein kinase inhibitor, in patients with refractory neoplasms (abstract 1547). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol
Senderowicz AM, Messmann R, Arbuck S, Headlee D, Zhai S, Murgo A, Melillo G, Figg WD, Sausville EA (2000) A phase I trial of 1 hour infusion of flavopiridol (Fla), a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced neoplasms (abstract 796). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol
Seynaeve CM, Stetler-Stevenson M, Sebers S, Kaur G, Sausville EA, Worland PJ (1993) Cell cycle arrest and growth inhibition by the protein kinase antagonist UCN-01 in human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 53:2081
Seynaeve CM, Kazanietz MG, Blumberg PM, Sausville EA, Worland PJ (1994) Differential inhibition of protein kinase C isozymes by UCN-01, a staurosporine analogue. Mol Pharmacol 45:1207
Shao RG, Cao CX, Shimizu T, O'Connor PM, Kohn KW, Pommier Y (1997) Abrogation of an S-phase checkpoint and potentiation of camptothecin cytotoxicity by 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) in human cancer cell lines, possibly influenced by p53 function. Cancer Res 57:4029
Shapiro G, Patterson A, Lynch C, Lucca J, Anderson I, Boral A, Elias A, Lu H, Salgia R, Skarin A, Panek-Clark C, McKenna R, Rabin M, Vasconcelles M, Eder P, Supko J, Lynch T, Rollins B (1999) A phase II trial of flavopiridol in patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer (abstract 4126). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol
Shapiro GI, Koestner DA, Matranga CB, Rollins BJ (1999) Flavopiridol induces cell cycle arrest and p53-independent apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 5:2925
Sherr CJ (1996) Cancer cell cycles. Science 274:1672
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1999) CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 13:1501
Shimizu E, Zhao MR, Nakanishi H, Yamamoto A, Yoshida S, Takada M, Ogura T, Sone S (1996) Differing effects of staurosporine and UCN-01 on RB protein phosphorylation and expression of lung cancer cell lines. Oncology 53:494
Shimizu T, O'Connor P, Kohn KW, Pommier Y (1995) Unscheduled activation of cyclin B1/Cdc2 kinase in human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL60 cells undergoing apoptosis induced by DNA damage. Cancer Res 55:228
Spitz FR, Nguyen D, Skibber JM, Cusack J, Roth JA, Cristiano RJ (1996) In vivo adenovirus-mediated p53 tumor suppressor gene therapy for colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 16:3415
Stadler WM, Vogelzang NJ, Amato R, Sosman J, Taber D, Liebowitz D, Vokes EE (2000) Flavopiridol, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in metastatic renal cancer: a University of Chicago Phase II Consortium study. J Clin Oncol 18:371
Sugiyama K, Shimizu M, Akiyama T, Tamaoki T, Yamaguchi K, Takahashi R, Eastman A, Akinaga S (2000) UCN-01 selectively enhances mitomycin C cytotoxicity in p53 defective cells which is mediated through S and/or G(2) checkpoint abrogation. Int J Cancer 85:703
Takahashi I, Kobayashi E, Asano K, Yoshida M, Nakano H (1987) UCN-01, a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C from Streptomyces. J Antibiot 40:1782
Takahashi I, Saitoh Y, Yoshida M, Sano H, Nakano H, Morimoto M, Tamaoki T (1989) UCN-01 and UCN-02, new selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. II. Purification, physico-chemical properties, structural determination and biological activities. J Antibiot 42:571
Tamaoki T (1991) Use and specificity of staurosporine, UCN-01, and calphostin C as protein kinase inhibitors. Methods Enzymol 201:340
Tamura T, Sasaki Y, Minami H, Fujii H, Ito K, Igarashi T, Kamiya Y, Kurata T, Ohtsu T, Onozawa Y, Yamamoto N, Yamamoto N, Watanabe Y, Tanigaara Y, Fuse E, Kuwabara T, Kobayahsi S, Shimada Y (1999) Phase I study of UCN-01 by 3-hour infusion (abstract 1145). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol
Tan AR, Headlee D, Messmann R, Sausville EA, Arbuck SG, Murgo AJ, Melillo G, Zhai S, Figg WD, Swain SM, Senderowicz AM (2002) Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of flavopiridol administered as a daily 1-hour infusion in patients with advanced neoplasms. J Clin Oncol 20:4074
Tassan JP, Schultz SJ, Bartek J, Nigg EA (1994) Cell cycle analysis of the activity, subcellular localization, and subunit composition of human CAK (CDK-activating kinase). J Cell Biol 127:467
Testa JR, Bellacosa A (2001) AKT plays a central role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10983
Thomas JP, Tutsch KD, Cleary JF, Bailey HH, Arzoomanian R, Alberti D, Simon K, Feierabend C, Binger K, Marnocha R, Dresen A, Wilding G (2002) Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic trial of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 50:465
Tsuchida E, Urano M (1997) The effect of UCN-01 (7-hydroxystaurosporine), a potent inhibitor of protein kinase C, on fractionated radiotherapy or daily chemotherapy of a murine fibrosarcoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 39:1153
Usuda J, Saijo N, Fukuoka K, Fukumoto H, Kuh HJ, Nakamura T, Koh Y, Suzuki T, Koizumi F, Tamura T, Kato H, Nishio K (2000) Molecular determinants of UCN-01-induced growth inhibition in human lung cancer cells. Int J Cancer 85:275
Walker DH (1998) Small-molecule inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases: molecular tools and potential therapeutics. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 227:149
Wang C, Fu M, Mani S, Wadler S, Senderowicz AM, Pestell RG (2001) Histone acetylation and the cell-cycle in cancer. Front Biosci 6:D610
Wang MB, Billings KR, Venkatesan N, Hall FL, Srivatsan ES (1998) Inhibition of cell proliferation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines with antisense cyclin D1. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119:593
Wang Q, Worland PJ, Clark JL, Carlson BA, Sausville EA (1995) Apoptosis in 7-hydroxystaurosporine-treated T lymphoblasts correlates with activation of cyclin-dependent kinases 1 and 2. Cell Growth Differ 6:927
Wang Q, Fan S, Eastman A, Worland PJ, Sausville EA, O'Connor P (1996) UCN-01: a potent abrogator of G2 checkpoint function in cancer cells with disrupted p53. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:956
Warbrick E, Lane DP, Glover DM, Cox LS (1995) A small peptide inhibitor of DNA replication defines the site of interaction between the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Curr Biol 5:275
Wei P, Garber ME, Fang SM, Fischer WH, Jones KA (1998) A novel CDK9-associated C-type cyclin interacts directly with HIV-1 Tat and mediates its high-affinity, loop-specific binding to TAR RNA. Cell 92:451
Weinberg RA (1995) The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 81:323
Werner J, Kelsen D, Karpeh M, Inzeo D, Barazzuol J, Sugarman A, Schwartz GK (1998) The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol is an active and unexpectedly toxic agent in advanced gastric cancer (abstract 1247). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol
Wilcken NR, Sarcevic B, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (1996) Differential effects of retinoids and antiestrogens on cell cycle progression and cell cycle regulatory genes in human breast cancer cells. Cell Growth Differ 7:65
Wilson WH, Sorbara L, Figg WD, Mont EK, Sausville E, Warren KE, Balis FM, Bauer K, Raffeld M, Senderowicz AM, Monks A (2000) Modulation of clinical drug resistance in a B cell lymphoma patient by the protein kinase inhibitor 7-hydroxystaurosporine: presentation of a novel therapeutic paradigm. Clin Cancer Res 6:415
Worland PJ, Kaur G, Stetler-Stevenson M, Sebers S, Sartor O, Sausville EA (1993) Alteration of the phosphorylation state of p34cdc2 kinase by the flavone L86-8275 in breast carcinoma cells. Correlation with decreased H1 kinase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 46:1831
Wright J, Blatner GL, Cheson BD (1998) Clinical trials referral resource. Clinical trials of flavopiridol. Oncology (Huntingt) 12:1018,1023
Yu JT, Foster RG, Dean DC (2001) Transcriptional repression by RB-E2F and regulation of anchorage-independent survival. Mol Cell Biol 21:3325
Yu L, Orlandi L, Wang P, Orr M, Senderowicz AM, Sausville EA, Silvestrini RA, O'Connor P (1998) UCN-01 abrogates G2 arrest through a cdc2-dependent pathway that involves inactivation of the Wee1Hu kinase. J Biol Chem 273:33455
Zaharevitz DW, Gussio R, Leost M, Senderowicz AM, Lahusen T, Kunick C, Meijer L, Sausville EA (1999) Discovery and initial characterization of the paullones, a novel class of small-molecule inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases. Cancer Res 59:2566
Zhou Q, Stetler-Stevenson M, Steeg PS (1997) Inhibition of cyclin D expression in human breast carcinoma cells by retinoids in vitro. Oncogene 15:107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented at the 18th Bristol-Myers Squibb Nagoya International Cancer Treatment Symposium, "New Strategies for Novel Anticancer Drug Development", 8–9 November 2002, Nagoya, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senderowicz, A.M. Novel direct and indirect cyclin-dependent kinase modulators for the prevention and treatment of human neoplasms. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 52 (Suppl 1), 61–73 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-003-0624-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-003-0624-x