Abstract
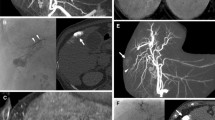
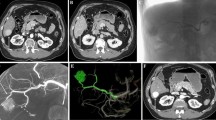
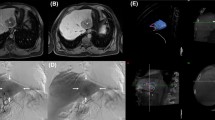
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the detectability of corona enhancement around the hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by dual-phase cone-beam computed tomography during hepatic arteriography (CBCTHA). Dual-phase CBCTHA was performed for 71 HCC lesions (mean ± SD 1.7 ± 0.9 cm), including seven presenting a nodule-in-nodule appearance and nine hypervascular pseudolesions. The first scan was performed during injection of 30–40 ml half-diluted contrast material at a rate of 1.5–2 ml/s through the hepatic artery. Scanning was initiated 7 s after the beginning of contrast material injection. The second scan was started 30 s after the end of the first scan. Detectability of corona enhancement on second-phase CBCTHA was evaluated. Thickness of corona enhancement was also analyzed as thin (≤2 mm) or thick (>2 mm). Corona enhancement was detected in 63 (88.7%) of 71 tumors (1.8 ± 0.9 cm), but it was not detected in eight tumors (1.0 ± 0.2 cm). Thin corona enhancement was seen in 18 tumors (1.2 ± 0.5 cm), and thick corona enhancement was seen in 45 tumors (2.0 ± 0.9 cm). There was a significant difference in tumor diameter between tumors with and those without corona enhancement (P = 0.0157) and between thin and thick corona enhancement (P = 0.001). In all seven early-stage tumors, corona enhancement was demonstrated around the hypervascular focus within the hypovascular tumor portion. None of the nine pseudolesions showed any corona enhancement. Dual-phase CBCTHA depicted corona enhancement in 88.7% of hypervascular HCC lesions. This technique may improve the diagnostic accuracy of HCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ueda K, Matsui O, Kawamori Y et al (1998) Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation of hemodynamics with dynamic CT during hepatic arteriography. Radiology 206:161–166
Ueda K, Matsui O, Kawamori Y et al (1998) Differentiation of hypervascular hepatic pseudolesions from hepatocellular carcinoma: value of single-level dynamic CT during hepatic arteriography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22:703–708
Inoue E, Fujita M, Hosomi N et al (1998) Double phase CT arteriography of the whole liver in the evaluation of hepatic tumors. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22:64–68
Matsui O, Ueda K, Kobayashi S et al (2002) Intra- and perinodular hemodynamics of hepatocellular carcinoma: CT observation during intra-arterial contrast injection. Abdom Imaging 27:147–156
Kitao A, Zen Y, Matsui O et al (2009) Hepatocarcinogenesis: multistep changes of drainage vessels at CT during arterial portography and hepatic arteriography—radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiology 252:605–614
Hirota S, Nakao N, Yamamoto S et al (2006) Cone-beam CT with flat-panel-detector digital angiography system: early experience in abdominal interventional procedures. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29:1034–1038
Kakeda S, Korogi Y, Ohnari N et al (2008) Usefulness of cone-beam CT with flat panel detectors in conjunction with catheter angiography for transcatheter arterial embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18:1508–1516
Miyayama S, Matsui O, Yamashiro M et al (2009) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma by CT during arterial portography using a cone-beam CT technology: comparison with conventional CTAP. Abdom Imaging 34:502–506
Miyayama S, Yamashiro M, Okuda M et al (2009) Usefulness of cone-beam computed tomography during ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for small hepatocellular carcinomas that cannot be demonstrated on angiography. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32:255–264
Terayama N, Matsui O, Ueda K et al (2002) Peritumoral rim enhancement of liver metastasis: hemodynamics observed on single-level dynamic CT during hepatic arteriography and histopathologic correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:975–980
Kita R, Nishikawa H, Matsuo H et al (2007) A case of nodule-in-nodule type HCC presenting corona enhancement within the outer tumor on single-level dynamic CT during hepatic arteriography. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkaishi 104:837–839 (in Japanese)
Miyayama S, Matsui O, Yamashiro M et al (2007) Iodized oil accumulation in the hypovascular tumor portion of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma after ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Hepatol Int 1:451–459
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyayama, S., Yamashiro, M., Okuda, M. et al. Detection of Corona Enhancement of Hypervascular Hepatocellular Carcinoma by C-Arm Dual-Phase Cone-Beam CT During Hepatic Arteriography. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34, 81–86 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-010-9835-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-010-9835-9