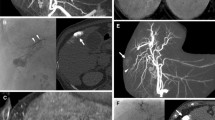
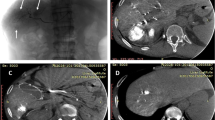
Abstract
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) is an imaging modality that provides computed tomographic images using a rotational C-arm equipped with a flat panel detector as part of the Angiography suite. The aim of this technique is to provide additional information to conventional 2D imaging to improve the performance of interventional liver oncology procedures (intraarterial treatments such as chemoembolization or selective internal radiation therapy, and percutaneous tumor ablation). CBCT provides accurate tumor detection and targeting, periprocedural guidance, and post-procedural evaluation of treatment success. This technique can be performed during intraarterial or intravenous contrast agent administration with various acquisition protocols to highlight liver tumors, liver vessels, or the liver parenchyma. The purpose of this review is to present an extensive overview of published data on CBCT in interventional oncology of the liver, for both percutaneous ablation and intraarterial procedures.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Racadio JM, Babic D, Homan R, et al. Live 3D Guidance in the Interventional Radiology Suite. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189(6):W357–64.
Orth RC, Wallace MJ, Kuo MD. Technology Assessment Committee of the Society of Interventional R C-arm cone-beam CT: general principles and technical considerations for use in interventional radiology. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008;19(6):814–20.
Wallace MJ, Kuo MD, Glaiberman C, et al. Three-dimensional C-arm cone-beam CT: applications in the interventional suite. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;20(7 Suppl):S523–37.
Morimoto M, Numata K, Kondo M, et al. C-arm cone beam CT for hepatic tumor ablation under real-time 3D imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194(5):W452–4.
Iwazawa J, Ohue S, Hashimoto N, Mitani T. Ablation margin assessment of liver tumors with intravenous contrast-enhanced C-arm computed tomography. World J Radiol. 2012;4(3):109–14.
Cazzato RL, Buy X, Alberti N, Fonck M, Grasso RF, Palussiere J. Flat-panel cone-beam CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of very small (≤1.5 cm) liver tumors: technical note on a preliminary experience. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2015;38(1):206–12.
Abdel-Rehim M, Ronot M, Sibert A, Vilgrain V. Assessment of liver ablation using cone beam computed tomography. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(2):517–24.
Tacher V, Radaelli A, Lin M, Geschwind JF. How I do it: cone-beam CT during transarterial chemoembolization for liver cancer. Radiology. 2015;274(2):320–34.
Pellerin O, Lin M, Bhagat N, Shao W, Geschwind JF. Can C-arm cone-beam CT detect a micro-embolic effect after TheraSphere radioembolization of neuroendocrine and carcinoid liver metastasis? Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013;28(6):459–65.
Louie JD, Kothary N, Kuo WT, et al. Incorporating cone-beam CT into the treatment planning for yttrium-90 radioembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;20(5):606–13.
Lucatelli P, Corona M, Argiro R, et al. Impact of 3D rotational angiography on liver embolization procedures: review of technique and applications. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2015;38(3):523–35.
Koelblinger C, Schima W, Berger-Kulemann V, et al. C-arm CT during hepatic arteriography tumour-to-liver contrast: intraindividual comparison of three different contrast media application protocols. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(4):938–42.
Loffroy R, Lin M, Rao P, et al. Comparing the detectability of hepatocellular carcinoma by C-arm dual-phase cone-beam computed tomography during hepatic arteriography with conventional contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2012;35(1):97–104.
Lee IJ, Chung JW, Yin YH, et al. Cone-beam CT hepatic arteriography in chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: angiographic image quality and its determining factors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014;25(9):1369–79 quiz 79- e1.
Bruix J. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011;53(3):1020–2.
European Association for the Study of the L, European Organisation For R, Treatment Of C. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56(4):908–43.
Vogl TJ, Naguib NN, Zangos S, Eichler K, Hedayati A, Nour-Eldin NE. Liver metastases of neuroendocrine carcinomas: interventional treatment via transarterial embolization, chemoembolization and thermal ablation. Eur J Radiol. 2009;72(3):517–28.
Steward MJ, Warbey VS, Malhotra A, Caplin ME, Buscombe JR. Yu D Neuroendocrine tumors: role of interventional radiology in therapy. RadioGraphics. 2008;28(4):1131–45.
Martin RCG, Joshi J, Robbins K, Tomalty D, O’Hara R, Tatum C. Transarterial chemoembolization of metastatic colorectal carcinoma with drug-eluting beads, irinotecan (DEBIRI): multi-institutional registry. J Oncol. 2009;2009:1–6.
Zechlinski JJ, Rilling WS. Transarterial therapies for the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Interv Radiol. 2013;30(1):21–7.
Lammer J, Malagari K, Vogl T, et al. Prospective randomized study of doxorubicin-eluting-bead embolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: results of the PRECISION V study. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2010;33(1):41–52.
Martin R, Geller D, Espat J, et al. Safety and efficacy of trans arterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads in hepatocellular cancer: a systematic review. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012;59(113):255–60.
Lencioni R, De Baere T, Burrel M, et al. Transcatheter Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Doxorubicin-loaded DC Bead (DEBDOX): technical recommendations. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2011;35(5):980–5.
Bouvier A, Ozenne V, Aubé C, et al. Transarterial chemoembolisation: effect of selectivity on tolerance, tumour response and survival. Eur Radiol. 2011;21(8):1719–26.
Golfieri R, Cappelli A, Cucchetti A, et al. Efficacy of selective transarterial chemoembolization in inducing tumor necrosis in small (<5 cm) hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology. 2011;53(5):1580–9.
Kakeda S, Korogi Y, Ohnari N, et al. Usefulness of cone-beam volume CT with flat panel detectors in conjunction with catheter angiography for transcatheter arterial embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007;18(12):1508–16.
Tognolini A, Louie JD, Hwang GL, Hofmann LV, Sze DY, Kothary N. Utility of C-arm CT in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transhepatic arterial chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(3):339–47.
Miyayama S, Yamashiro M, Hashimoto M, et al. Comparison of local control in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma ≤6 cm with or without intraprocedural monitoring of the embolized area using cone-beam computed tomography. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2014;37(2):388–95.
Iwazawa J, Ohue S, Hashimoto N, Muramoto O, Mitani T. Survival after C-arm CT-assisted chemoembolization of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(12):3985–92.
Hirota S, Nakao N, Yamamoto S, et al. Cone-beam CT with flat-panel-detector digital angiography system: early experience in abdominal interventional procedures. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2006;29(6):1034–8.
Meyer BC, Frericks BB, Albrecht T, Wolf KJ, Wacker FK. Contrast-enhanced abdominal angiographic CT for intra-abdominal tumor embolization: a new tool for vessel and soft tissue visualization. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2007;30(4):743–9.
Meyer BC, Frericks BB, Voges M, et al. Visualization of hypervascular liver lesions During TACE: comparison of angiographic C-arm CT and MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;190(4):W263–9.
Miyayama S, Matsui O, Yamashiro M, et al. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma by CT during arterial portography using a cone-beam CT technology: comparison with conventional CTAP. Abdom Imaging. 2009;34(4):502–6.
Miyayama S, Yamashiro M, Okuda M, et al. Usefulness of cone-beam computed tomography during ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for small hepatocellular carcinomas that cannot be demonstrated on angiography. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2009;32(2):255–64.
Iwazawa J, Ohue S, Hashimoto N, Abe H, Hamuro M, Mitani T. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of angiographic C-arm CT and MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;195(4):882–7.
Lin M, Loffroy R, Noordhoek N, et al. Evaluating tumors in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) using dual-phase cone-beam CT. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2011;20(5):276–81.
Higashihara H, Osuga K, Onishi H, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of C-arm CT during selective transcatheter angiography for hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with intravenous contrast-enhanced, biphasic, dynamic MDCT. Eur Radiol. 2012;22(4):872–9.
Miyayama S, Yamashiro M, Hashimoto M, et al. Identification of small hepatocellular carcinoma and tumor-feeding branches with cone-beam CT guidance technology during transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24(4):501–8.
Tacher V, Lin M, Chao M, et al. Semiautomatic volumetric tumor segmentation for hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison between C-arm cone beam computed tomography and MRI. Acad Radiol. 2013;20(4):446–52.
Schernthaner RE, Lin M, Duran R, Chapiro J, Wang Z, Geschwind JF. Delayed-phase cone-beam ct improves detectability of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma during conventional transarterial chemoembolization. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2014. doi:10.1007/s00270-014-1026-7.
Lee IJ, Chung JW, Yin YH, et al. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) hepatic arteriography in chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: performance depicting tumors and tumor feeders. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s00270-015-1055-x.
Miyayama S, Yamashiro M, Okuda M, et al. Detection of corona enhancement of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma by C-arm dual-phase cone-beam CT during hepatic arteriography. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2011;34(1):81–6.
Paul J, Mbalisike EC, Vogl TJ. Ultrafast cone-beam computed tomography imaging and postprocessing data during image-guided therapeutic practice. Eur Radiol. 2014;24(11):2866–75.
Iwazawa J, Ohue S, Mitani T, et al. Identifying feeding arteries during TACE of hepatic tumors: comparison of C-arm CT and digital subtraction angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192(4):1057–63.
Minami Y, Yagyu Y, Murakami T, Kudo M. Tracking navigation imaging of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma using three-dimensional cone-beam CT angiography. Liver Cancer. 2014;3(1):53–61.
Virmani S, Ryu RK, Sato KT, et al. Effect of C-arm angiographic CT on transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007;18(10):1305–9.
Miyayama S, Yamashiro M, Hashimoto M, et al. Blood supply of the main bile duct from the caudate artery and medial subsegmental artery of the hepatic artery: evaluation using images obtained during transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 2013;43(11):1175–81.
Deschamps F, Solomon SB, Thornton RH, et al. Computed analysis of three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography angiography for determination of tumor-feeding vessels during chemoembolization of liver tumor: a pilot study. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2010. doi:10.1007/s00270-010-9846-6.
Wang X, Shah RP, Maybody M, et al. Cystic artery localization with a three-dimensional angiography vessel tracking system compared with conventional two-dimensional angiography. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;22(10):1414–9.
Kim HC, Chung JW, An S, et al. Left inferior phrenic artery feeding hepatocellular carcinoma: angiographic anatomy using C-arm CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(4):W288–94.
Kim HC, Chung JW, Lee IJ, et al. Intercostal artery supplying hepatocellular carcinoma: demonstration of a tumor feeder by C-arm CT and multidetector row CT. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2011;34(1):87–91.
Forner A, Ayuso C, Varela M, et al. Evaluation of tumor response after locoregional therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma: are response evaluation criteria in solid tumors reliable? Cancer. 2009;115(3):616–23.
Lencioni R, Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30(1):52–60.
Kwan SW, Fidelman N, Ma E, Kerlan RK Jr, Yao FY. Imaging predictors of the response to transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a radiological-pathological correlation. Liver Transpl. 2012;18(6):727–36.
Shim JH, Han S, Shin YM, et al. Optimal measurement modality and method for evaluation of responses to transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma based on enhancement criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24(3):316–25.
Loffroy R, Lin M, Yenokyan G, et al. Intraprocedural C-arm dual-phase cone-beam CT: can it be used to predict short-term response to TACE with drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma? Radiology. 2013;266(2):636–48.
Jeon UB, Lee JW, Choo KS, et al. Iodized oil uptake assessment with cone-beam CT in chemoembolization of small hepatocellular carcinomas. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(46):5833–7.
Sun JH, Wang LG, Bao HW, et al. Usefulness of C-arm angiographic computed tomography for detecting iodized oil retention during transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Int Med Res. 2010;38(4):1259–65.
Iwazawa J, Ohue S, Kitayama T, Sassa S, Mitani T. C-arm CT for assessing initial failure of iodized oil accumulation in chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(2):W337–42.
Peynircioglu B, Hizal M, Cil B, et al. Quantitative liver tumor blood volume measurements by a C-arm CT post-processing software before and after hepatic arterial embolization therapy: comparison with MDCT perfusion. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2015;21(1):71–7.
Riaz A, Kulik LM, Mulcahy MF, Lewandowski RJ, Salem R. Yttrium-90 radioembolization in the management of liver malignancies. Semin Oncol. 2010;37(2):94–101.
Denys A, Pracht M, Duran R, et al. How to prepare a patient for transarterial radioembolization? A practical guide. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s00270-015-1071-x.
Mahnken AH, Spreafico C, Maleux G, Helmberger T, Jakobs TF. Standards of practice in transarterial radioembolization. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2013;36(3):613–22.
Kim YS, Rhim H, Cho OK, Koh BH, Kim Y. Intrahepatic recurrence after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of the pattern and risk factors. Eur J Radiol. 2006;59(3):432–41.
Nakazawa T, Kokubu S, Shibuya A, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation between local tumor progression after ablation and ablative margin. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(2):480–8.
Mulier S, Ni Y, Jamart J, Ruers T, Marchal G, Michel L. Local recurrence after hepatic radiofrequency coagulation: multivariate meta-analysis and review of contributing factors. Ann Surg. 2005;242(2):158–71.
Clasen S, Pereira PL. Magnetic resonance guidance for radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008;27(2):421–33.
Solomon SB, Silverman SG. Imaging in interventional oncology. Radiology. 2010;257(3):624–40.
Crocetti L, Della Pina C, Cioni D, Lencioni R. Peri-intraprocedural imaging: US, CT, and MRI. Abdom Imaging. 2011;36(6):648–60.
Guibal A, Bertin C, Egels S, Savier E, Grenier PA, Lucidarme O. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) follow-up after radiofrequency ablation or cryoablation of focal liver lesions: treated-area patterns and their changes over time. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(5):1392–400.
Hakime A, Deschamps F, De Carvalho EG, Teriitehau C, Auperin A, De Baere T. Clinical evaluation of spatial accuracy of a fusion imaging technique combining previously acquired computed tomography and real-time ultrasound for imaging of liver metastases. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2011;34(2):338–44.
Iwazawa J, Hashimoto N, Mitani T, Ohue S. Fusion of intravenous contrast-enhanced C-arm CT and pretreatment imaging for ablation margin assessment of liver tumors: a preliminary study. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2012;22(4):251–3.
Kothary N, Abdelmaksoud MH, Tognolini A, et al. Imaging guidance with C-arm CT: prospective evaluation of its impact on patient radiation exposure during transhepatic arterial chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;22(11):1535–43.
Schulz B, Heidenreich R, Heidenreich M, et al. Radiation exposure to operating staff during rotational flat-panel angiography and C-arm cone beam computed tomography (CT) applications. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(12):4138–42.
Suzuki S, Yamaguchi I, Kidouchi T, Yamamoto A, Masumoto T, Ozaki Y. Evaluation of effective dose during abdominal three-dimensional imaging for three flat-panel-detector angiography systems. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2011;34(2):376–82.
Kwok YM, Irani FG, Tay KH, Yang CC, Padre CG, Tan BS. Effective dose estimates for cone beam computed tomography in interventional radiology. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(11):3197–204.
Schegerer AA, Lechel U, Ritter M, Weisser G, Fink C, Brix G. Dose and image quality of cone-beam computed tomography as compared with conventional multislice computed tomography in abdominal imaging. Invest Radiol. 2014;49(10):675–84.
Suk Oh J, Jong Chun H, Gil Choi B, Giu Lee H. Transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads in hepatocellular carcinoma: usefulness of contrast saturation features on cone-beam computed tomography imaging for predicting short-term tumor response. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24(4):483–9.
Chen R, Geschwind JF, Wang Z, Tacher V, Lin M. Quantitative assessment of lipiodol deposition after chemoembolization: comparison between cone-beam CT and multidetector CT. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24(12):1837–44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Does not apply.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bapst, B., Lagadec, M., Breguet, R. et al. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) in the Field of Interventional Oncology of the Liver. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39, 8–20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-015-1180-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-015-1180-6