Abstract
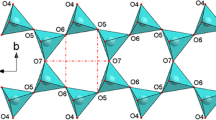
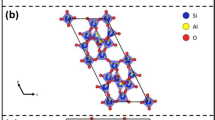
The elastic behavior and the structural evolution at high pressure of a natural phillipsite have been investigated by in situ single-crystal X-ray diffraction up to 9.44 GPa, using a diamond anvil cell and the nominally penetrating P-transmitting fluid methanol:ethanol:water (16:3:1) mix. Although no phase transition was observed within the P-range investigated, two different compressional regimes occur. Between 0.0001 and 2.0 GPa, the refined elastic parameters, calculated by a second-order Birch–Murnaghan equation of state (BM-EoS) fit, are V 0 = 1005(1) Å3, K 0 = 89(8) GPa for the unit-cell volume; a 0 = 9.914(7) Å, K a = 81(12) GPa for the a-axis; b 0 = 14.201(9) Å, K b = 50(5) GPa for the b-axis; and c 0 = 8.707(2) Å, K c = 107(8) GPa for the c-axis (K a :K b :K c ~1.62:1:2.14). Between 2.0 and 9.4 GPa, a P-induced change in the configuration of H2O molecules, coupled with a change in the tilting mechanisms of the framework tetrahedra, gives rise to a second compressional regime, in which the phillipsite structure is softer if compared to the first compressional range. In the second compressional regime, the refined elastic parameters, calculated by a second-order BM-EoS fit, are V 0 = 1098 (7) Å3, K 0 = 18.8(7) GPa for the unit-cell volume; a 0 = 10.07(3) Å, K a = 30(2) GPa for the a-axis; b 0 = 14.8(1) Å, K b = 11(1) GPa for the b-axis; and c 0 = 8.94(2) Å, K c = 21(1) GPa for the c-axis (K a :K b :K c ~2.72:1:1.90). The evolution of the monoclinic β angle with pressure shows two distinct trends in the two compressional regimes: with a negative slope between 0.0001 and 2.0 GPa, and a positive slope between 2.0 and 9.4 GPa. The mechanisms, at the atomic scale, that govern the two compressional regimes of the phillipsite structure are described.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agilent (2012) CrysAlis RED. Agilent Technologies Ltd, Yarnton
Angel RJ, Hazen RM, Downs RT (2000) High-temperature and high-pressure crystal chemistry. Rev Mineral Geochem 41:35–60
Angel RJ, Bujak M, Zhao J, Gatta GD, Jacobsen SD (2007) Effective hydrostatic limits of pressure media for high-pressure crystallographic studies. J Appl Crystallogr 40:26–32
Angel RJ, Alvaro M, Gonzalez-Platas J (2014) EosFit7c and a Fortran module (library) for equation of state calculations. Z Kristallogr 229:405–419
Armbruster T, Gunter ME (2001) Crystal structures of natural zeolites. Rev Mineral Geochem 45:1–57
Baerlocher C, McCusker LB, Olson DH (2007) Atlas of zeolite framework types, 6th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Danisi RM, Armbruster T, Nagashima M (2015) Structural intergrowth of merlinoite/phillipsite and its temperature-dependent dehydration behaviour: a single-crystal X-ray study. Mineral Mag 79:191–203
Galli E, Loschi Ghittoni AG (1972) The crystal chemistry of phillipsites. Am Mineral 57:1125–1145
Gatta GD, Lee Y (2007) Anisotropic elastic behaviour and structural evolution of zeolite phillipsite at high pressure: a synchrotron powder diffraction study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 105:239–250
Gatta GD, Lee Y (2014) Zeolites at high pressure: a review. Mineral Mag 78:267–291
Gatta GD, Comodi P, Zanazzi PF, Boffa Ballaran T (2005) Anomalous elastic behavior and high-pressure structural evolution of zeolite levyne. Am Mineral 90:645–652
Gatta GD, Nestola F, Boffa Ballaran T (2006) Elastic behavior, phase transition and pressure-induced structural evolution of analcime. Am Mineral 91:568–578
Gatta GD, Rotiroti N, Boffa Ballaran T, Pavese A (2008) Leucite at high-pressure: elastic behaviour, phase stability and petrological implications. Am Mineral 93:1588–1596
Gatta GD, Cappelletti P, Rotiroti N, Slebodnick C, Rinaldi R (2009a) New insights into the crystal structure and crystal chemistry of the zeolite phillipsite. Am Mineral 94:190–199
Gatta GD, Rotiroti N, Boffa Ballaran T, Sanchez-Valle C, Pavese A (2009b) Elastic behavior and phase stability of pollucite, a potential host for nuclear waste. Am Mineral 94:1137–1143
Gatta GD, Cappelletti P, Langella A (2010) Crystal-chemistry of phillipsites from the Neapolitan Yellow Tuff. Eur J Mineral 22:779–786
Gatta GD, Lotti P, Nestola F, Pasqual D (2012) On the high-pressure behavior of gobbinsite, the natural counterpart of the synthetic zeolite Na-P2. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 163:259–269
Gatta GD, Comboni D, Alvaro M, Lotti P, Càmara F, Domeneghetti MC (2014) Thermoelastic behavior and dehydration process of cancrinite. Phys Chem Miner 41:373–386
Gatta GD, Cappelletti P, de’ Gennaro B, Rotiroti N, Langella A (2015) New data on Cu-exchanged phillipsite: a multi-methodological study. Phys Chem Miner 42:723–733
Gottardi G, Galli E (1985) Natural zeolites. Minerals and rocks series. Springer, Berlin, p 409
Gualtieri AF, Caputo D, Colella C (1999a) Ion-exchange selectivity of phillipsite for Cs+ : a structural investigation using the Rietveld method. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 32:319–329
Gualtieri AF, Passaglia E, Galli E, Viani A (1999b) Rietveld structure refinement of Sr-exchanged phillipsites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 31:33–43
Gualtieri AF, Passaglia E, Galli E (2000) Rietveld structure refinement of natural and Na-, K-, Ca-, and Ba-exchanged phillipsites. In: Colella C, Mumpton FA (eds) Natural zeolites for the third millennium. De Frede, Naples, pp 93–110
Langella A, Cappelletti P, de’ Gennaro R (2001) Zeolites in closed hydrologic systems. Rev Mineral Geochem 45:235–260
Lotti P, Gatta GD, Comboni D, Merlini M, Pastero L, Hanfland M (2016) AlPO4-5 zeolite at high pressure: crystal–fluid interaction and elastic behaviour. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 228:158–167
Mao HK, Xu J, Bell PM (1986) Calibration of the ruby pressure gauge to 800-kbar under quasi-hydrostatic conditions. J Geophys Res 91:4673–4676
Passaglia E, Sheppard RA (2001) The crystal chemistry of zeolites. Rev Mineral Geochem 45:69–116
Passaglia E, Galli E, Gualtieri AF (2000) Natural zeolites for the third millennium. De Frede, Naples, pp 259–267
Petříček V, Dušek M, Palatinus L (2014) Crystallographic computing system JANA2006: general features. Z Kristallogr 229:345–352
Rinaldi R, Pluth JL, Smith JV (1974) Zeolites of the phillipsite family. Refinement of the crystal structure of phillipsite and harmotome. Acta Crystallogr B 30:2426–2433
Rinaldi R, Smith JV, Jung G (1975) Chemistry and paragenesis of faujasite, phillipsite, and offretite from Sasbach, Kaiserstuhl, Germany. Neues Jahrb Miner Mon 10:433–443
Rothkirch A, Gatta GD, Meyer M, Merkel S, Merlini M, Liermann H-P (2013) Single-crystal diffraction at the Extreme Conditions beamline P02.2: procedure for collecting and analyzing high-pressure single-crystal data. J Synchrotron Radiat 20:711–720
Sani A, Cruciani G, Gualtieri AF (2002) Dehydration dynamics of Ba-phillipsite: an in situ synchrotron powder diffraction study. Phys Chem Miner 29:351–361
Steinfink H (1962) The crystal structure of the zeolite phillipsite. Acta Crystallogr 15:644–651
Stuckenschmidt E, Fuess H, Kvick A (1990) Investigation of the structure of harmotome by X-ray (293 K, 100 K) and neutron-diffraction (15 K). Eur J Mineral 2:861–874
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Italian Ministry of Education, MIUR-Project: “Futuro in Ricerca 2012—ImPACT—RBFR12CLQD.” DESY—PETRA III (Hamburg) is thanked for the allocation of beamtime. Y. Lee is thanked for the sample of phillipsite from Richmond, Victoria, Australia. Two anonymous reviewers are thanked for their constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Comboni, D., Gatta, G.D., Lotti, P. et al. On the P-induced behavior of the zeolite phillipsite: an in situ single-crystal synchrotron X-ray diffraction study. Phys Chem Minerals 44, 1–20 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-016-0832-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-016-0832-7