Abstract
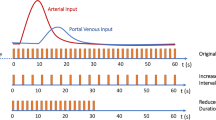
Perfusion imaging allows for the quantitative extraction of physiological perfusion parameters of the liver microcirculation at levels far below the spatial the resolution of CT and MR imaging. Because of its peculiar structure and architecture, perfusion imaging is more challenging in the liver than in other organs. Indeed, the liver is a mobile organ and significantly deforms with respiratory motion. Moreover, it has a dual vascular supply and the sinusoidal capillaries are fenestrated in the normal liver. Using extracellular contrast agents, perfusion imaging has shown its ability to discriminate patients with various stages of liver fibrosis. The recent introduction of hepatobiliary contrast agents enables quantification of both the liver perfusion and the hepatocyte transport function using advanced perfusion models. The purpose of this review article is to describe the characteristics of liver perfusion imaging to assess chronic liver disease, with a special focus on CT and MR imaging.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman SL (2003) Liver fibrosis – from bench to bedside. J Hepatol 38 Suppl 1:S38-53
Tacke F (2017) Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases. J Hepatol 66 (6):1300-1312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.026
Itai Y, Matsui O (1997) Blood flow and liver imaging. Radiology 202 (2):306-314. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.202.2.9015047
Pandharipande PV, Krinsky GA, Rusinek H, Lee VS (2005) Perfusion imaging of the liver: current challenges and future goals. Radiology 234 (3):661-673. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2343031362
Beck GM, De Becker J, Jones AC, von Falkenhausen M, Willinek WA, Gieseke J (2008) Contrast-enhanced timing robust acquisition order with a preparation of the longitudinal signal component (CENTRA plus) for 3D contrast-enhanced abdominal imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 27 (6):1461-1467. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21393
Chandarana H, Block TK, Rosenkrantz AB, Lim RP, Kim D, Mossa DJ, Babb JS, Kiefer B, Lee VS (2011) Free-breathing radial 3D fat-suppressed T1-weighted gradient echo sequence: a viable alternative for contrast-enhanced liver imaging in patients unable to suspend respiration. Invest Radiol 46 (10):648-653. https://doi.org/10.1097/rli.0b013e31821eea45
Leporq B, Daire JL, Pastor CM, Deltenre P, Sempoux C, Schmidt S, Van Beers BE (2018) Quantification of hepatic perfusion and hepatocyte function with dynamic gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI in patients with chronic liver disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 132 (7):813-824. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20171131
Saranathan M, Rettmann DW, Hargreaves BA, Clarke SE, Vasanawala SS (2012) DIfferential Subsampling with Cartesian Ordering (DISCO): a high spatio-temporal resolution Dixon imaging sequence for multiphasic contrast enhanced abdominal imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 35 (6):1484-1492. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.23602
Hedderich DM, Weiss K, Spiro JE, Giese D, Beck GM, Maintz D, Persigehl T (2018) Clinical Evaluation of Free-Breathing Contrast-Enhanced T1w MRI of the Liver using Pseudo Golden Angle Radial k-Space Sampling. Rofo 190 (7):601-609. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0044-101263
Materne R, Smith AM, Peeters F, Dehoux JP, Keyeux A, Horsmans Y, Van Beers BE (2002) Assessment of hepatic perfusion parameters with dynamic MRI. Magn Reson Med 47 (1):135-142
Leporq B, Dumortier J, Pilleul F, Beuf O (2012) 3D-liver perfusion MRI with the MS-325 blood pool agent: a noninvasive protocol to asses liver fibrosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 35 (6):1380-1387. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.23594
Sourbron S, Sommer WH, Reiser MF, Zech CJ (2012) Combined quantification of liver perfusion and function with dynamic gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 263 (3):874-883. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12110337
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161 (2):401-407. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.161.2.3763909
Roberts C, Issa B, Stone A, Jackson A, Waterton JC, Parker GJ (2006) Comparative study into the robustness of compartmental modeling and model-free analysis in DCE-MRI studies. J Magn Reson Imaging 23 (4):554-563. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.20529
Thng CH, Koh TS, Collins DJ, Koh DM (2010) Perfusion magnetic resonance imaging of the liver. World J Gastroenterol 16 (13):1598-1609
Annet L, Peeters F, Abarca-Quinones J, Leclercq I, Moulin P, Van Beers BE (2007) Assessment of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in liver fibrosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 25 (1):122-128. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.20771
Tofts PS, Brix G, Buckley DL, Evelhoch JL, Henderson E, Knopp MV, Larsson HB, Lee TY, Mayr NA, Parker GJ, Port RE, Taylor J, Weisskoff RM (1999) Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced T(1)-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: standardized quantities and symbols. J Magn Reson Imaging 10 (3):223-232
Langen KM, Jones DT (2001) Organ motion and its management. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50 (1):265-278
Heacock L, Gao Y, Heller SL, Melsaether AN, Babb JS, Block TK, Otazo R, Kim SG, Moy L (2017) Comparison of conventional DCE-MRI and a novel golden-angle radial multicoil compressed sensing method for the evaluation of breast lesion conspicuity. J Magn Reson Imaging 45 (6):1746-1752. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25530
Weiss J, Ruff C, Grosse U, Grozinger G, Horger M, Nikolaou K, Gatidis S (2019) Assessment of Hepatic Perfusion Using GRASP MRI: Bringing Liver MRI on a New Level. Invest Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1097/rli.0000000000000586
Chandarana H, Feng L, Ream J, Wang A, Babb JS, Block KT, Sodickson DK, Otazo R (2015) Respiratory Motion-Resolved Compressed Sensing Reconstruction of Free-Breathing Radial Acquisition for Dynamic Liver Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Invest Radiol 50 (11):749-756. https://doi.org/10.1097/rli.0000000000000179
Feng L, Grimm R, Block KT, Chandarana H, Kim S, Xu J, Axel L, Sodickson DK, Otazo R (2014) Golden-angle radial sparse parallel MRI: combination of compressed sensing, parallel imaging, and golden-angle radial sampling for fast and flexible dynamic volumetric MRI. Magn Reson Med 72 (3):707-717. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24980
Jajamovich GH, Dyvorne H, Donnerhack C, Taouli B (2014) Quantitative liver MRI combining phase contrast imaging, elastography, and DWI: assessment of reproducibility and postprandial effect at 3.0 T. PLoS One 9 (5):e97355. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097355
Goh V, Halligan S, Bartram CI (2007) Quantitative tumor perfusion assessment with multidetector CT: are measurements from two commercial software packages interchangeable? Radiology 242 (3):777-782. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2423060279
Heye T, Davenport MS, Horvath JJ, Feuerlein S, Breault SR, Bashir MR, Merkle EM, Boll DT (2013) Reproducibility of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Part I. Perfusion characteristics in the female pelvis by using multiple computer-aided diagnosis perfusion analysis solutions. Radiology 266 (3):801-811. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12120278
Heye T, Merkle EM, Reiner CS, Davenport MS, Horvath JJ, Feuerlein S, Breault SR, Gall P, Bashir MR, Dale BM, Kiraly AP, Boll DT (2013) Reproducibility of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Part II. Comparison of intra- and interobserver variability with manual region of interest placement versus semiautomatic lesion segmentation and histogram analysis. Radiology 266 (3):812-821. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12120255
Leach MO, Morgan B, Tofts PS, Buckley DL, Huang W, Horsfield MA, Chenevert TL, Collins DJ, Jackson A, Lomas D, Whitcher B, Clarke L, Plummer R, Judson I, Jones R, Alonzi R, Brunner T, Koh DM, Murphy P, Waterton JC, Parker G, Graves MJ, Scheenen TW, Redpath TW, Orton M, Karczmar G, Huisman H, Barentsz J, Padhani A, Experimental Cancer Medicine Centres Imaging Network Steering C (2012) Imaging vascular function for early stage clinical trials using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol 22 (7):1451-1464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2446-x
. https://qibawiki.rsna.org/images/1/12/DCE-MRI_Quantification_Profile_v1.0.pdf. Accessed July 12 2019
Miles KA, Hayball MP, Dixon AK (1993) Functional images of hepatic perfusion obtained with dynamic CT. Radiology 188 (2):405-411. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.188.2.8327686
Blomley MJ, Coulden R, Dawson P, Kormano M, Donlan P, Bufkin C, Lipton MJ (1995) Liver perfusion studied with ultrafast CT. J Comput Assist Tomogr 19 (3):424-433
Van Beers BE, Leconte I, Materne R, Smith AM, Jamart J, Horsmans Y (2001) Hepatic perfusion parameters in chronic liver disease: dynamic CT measurements correlated with disease severity. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176 (3):667-673. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.176.3.1760667
Ronot M, Asselah T, Paradis V, Michoux N, Dorvillius M, Baron G, Marcellin P, Van Beers BE, Vilgrain V (2010) Liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: differentiating minimal from intermediate fibrosis with perfusion CT. Radiology 256 (1):135-142. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10091295
Van Beers BE, Materne R, Annet L, Hermoye L, Sempoux C, Peeters F, Smith AM, Jamart J, Horsmans Y (2003) Capillarization of the sinusoids in liver fibrosis: noninvasive assessment with contrast-enhanced MRI in the rabbit. Magn Reson Med 49 (4):692-699. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.10420
Zhou L, Chen TW, Zhang XM, Yang Z, Tang HJ, Deng D, Zeng NL, Wang LY, Chen XL, Li H, Li CP, Li L, Xie XY, Hu J (2013) Liver dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for staging liver fibrosis in a piglet model. J Magn Reson Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24248
Annet L, Materne R, Danse E, Jamart J, Horsmans Y, Van Beers BE (2003) Hepatic flow parameters measured with MR imaging and Doppler US: correlations with degree of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Radiology 229 (2):409-414. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2292021128
Baxter S, Wang ZJ, Joe BN, Qayyum A, Taouli B, Yeh BM (2009) Timing bolus dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI assessment of hepatic perfusion: Initial experience. J Magn Reson Imaging 29 (6):1317-1322. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21795
Hagiwara M, Rusinek H, Lee VS, Losada M, Bannan MA, Krinsky GA, Taouli B (2008) Advanced liver fibrosis: diagnosis with 3D whole-liver perfusion MR imaging–initial experience. Radiology 246 (3):926-934. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2463070077
Van Beers BE, Garteiser P, Leporq B, Rautou PE, Valla D (2017) Quantitative Imaging in Diffuse Liver Diseases. Semin Liver Dis 37 (3):243-258. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1603651
Van Beers BE, Pastor CM, Hussain HK (2012) Primovist, Eovist: what to expect? J Hepatol 57 (2):421-429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2012.01.031
Giraudeau C, Leporq B, Doblas S, Lagadec M, Pastor CM, Daire JL, Van Beers BE (2017) Gadoxetate-enhanced MR imaging and compartmental modelling to assess hepatocyte bidirectional transport function in rats with advanced liver fibrosis. Eur Radiol 27 (5):1804-1811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4536-7
Lagadec M, Doblas S, Giraudeau C, Ronot M, Lambert SA, Fasseu M, Paradis V, Moreau R, Pastor CM, Vilgrain V, Daire JL, Van Beers BE (2015) Advanced fibrosis: Correlation between pharmacokinetic parameters at dynamic gadoxetate-enhanced MR imaging and hepatocyte organic anion transporter expression in rat liver. Radiology 274 (2):379-386. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14140313
Ba-Ssalamah A, Bastati N, Wibmer A, Fragner R, Hodge JC, Trauner M, Herold CJ, Bashir MR, Van Beers BE (2017) Hepatic gadoxetic acid uptake as a measure of diffuse liver disease: Where are we? J Magn Reson Imaging 45 (3):646-659. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25518
Feier D, Balassy C, Bastati N, Stift J, Badea R, Ba-Ssalamah A (2013) Liver fibrosis: histopathologic and biochemical influences on diagnostic efficacy of hepatobiliary contrast-enhanced MR imaging in staging. Radiology 269 (2):460-468. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13122482
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Kang HJ, Ahn SJ, Yang H, Kim E, Okuaki T, Han JK (2019) Quantitative Assessment of Liver Function by Using Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MRI: Hepatocyte Uptake Ratio. Radiology 290 (1):125-133. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2018180753
Noren B, Forsgren MF, Dahlqvist Leinhard O, Dahlstrom N, Kihlberg J, Romu T, Kechagias S, Almer S, Smedby O, Lundberg P (2013) Separation of advanced from mild hepatic fibrosis by quantification of the hepatobiliary uptake of Gd-EOB-DTPA. Eur Radiol 23 (1):174-181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2583-2
Kim H, Park SH, Kim EK, Kim MJ, Park YN, Park HJ, Choi JY (2014) Histogram analysis of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI for quantitative hepatic fibrosis measurement. PLoS One 9 (12):e114224. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114224
Yasaka K, Akai H, Kunimatsu A, Abe O, Kiryu S (2018) Liver Fibrosis: Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Staging by Using Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced Hepatobiliary Phase MR Images. Radiology 287 (1):146-155. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017171928
Ulloa JL, Stahl S, Yates J, Woodhouse N, Kenna JG, Jones HB, Waterton JC, Hockings PD (2013) Assessment of gadoxetate DCE-MRI as a biomarker of hepatobiliary transporter inhibition. NMR Biomed 26 (10):1258-1270. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.2946
Bonnaventure P, Cusin F, Pastor CM (2019) Hepatocyte Concentrations of Imaging Compounds Associated with Transporter Inhibition: Evidence in Perfused Rat Livers. Drug Metab Dispos 47 (4):412-418. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.118.084624
Luciani A, Vignaud A, Cavet M, Nhieu JT, Mallat A, Ruel L, Laurent A, Deux JF, Brugieres P, Rahmouni A (2008) Liver cirrhosis: intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging–pilot study. Radiology 249 (3):891-899. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2493080080
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Baek JH, Shin CI, Kiefer B, Han JK, Choi BI (2014) Evaluation of hepatic fibrosis using intravoxel incoherent motion in diffusion-weighted liver MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr 38 (1):110-116. https://doi.org/10.1097/rct.0b013e3182a589be
Chow AM, Gao DS, Fan SJ, Qiao Z, Lee FY, Yang J, Man K, Wu EX (2012) Liver fibrosis: an intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) study. J Magn Reson Imaging 36 (1):159-167. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.23607
Zhang Y, Jin N, Deng J, Guo Y, White SB, Yang GY, Omary RA, Larson AC (2013) Intra-voxel incoherent motion MRI in rodent model of diethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis. Magn Reson Imaging 31 (6):1017-1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2013.03.007
Lee JT, Liau J, Murphy P, Schroeder ME, Sirlin CB, Bydder M (2012) Cross-sectional investigation of correlation between hepatic steatosis and IVIM perfusion on MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 30 (4):572-578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2011.12.013
Guiu B, Petit JM, Capitan V, Aho S, Masson D, Lefevre PH, Favelier S, Loffroy R, Verges B, Hillon P, Krause D, Cercueil JP (2012) Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 3.0-T MR study. Radiology 265 (1):96-103. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12112478
Joo I, Lee JM, Yoon JH, Jang JJ, Han JK, Choi BI (2014) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging-an experimental study in a rabbit model. Radiology 270 (1):131-140. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13122506
Martirosian P, Pohmann R, Schraml C, Schwartz M, Kuestner T, Schwenzer NF, Scheffler K, Nikolaou K, Schick F (2019) Spatial-temporal perfusion patterns of the human liver assessed by pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling MRI. Z Med Phys 29 (2):173-183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.zemedi.2018.08.004
Cox EF, Palaniyappan N, Aithal GP, Guha IN, Francis ST (2019) Using MRI to study the alterations in liver blood flow, perfusion, and oxygenation in response to physiological stress challenges: Meal, hyperoxia, and hypercapnia. J Magn Reson Imaging 49 (6):1577-1586. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26341
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ronot, M., Leporq, B., Van Beers, B.E. et al. CT and MR perfusion techniques to assess diffuse liver disease. Abdom Radiol 45, 3496–3506 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02338-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02338-z