Abstract
Purpose
[18F]MK-9470 is an inverse agonist for the type 1 cannabinoid (CB1) receptor allowing its use in PET imaging. We characterized the kinetics of [18F]MK-9470 and evaluated its ability to quantify CB1 receptor availability in the rat brain.
Methods
Dynamic small-animal PET scans with [18F]MK-9470 were performed in Wistar rats on a FOCUS-220 system for up to 10 h. Both plasma and perfused brain homogenates were analysed using HPLC to quantify radiometabolites. Displacement and blocking experiments were done using cold MK-9470 and another inverse agonist, SR141716A. The distribution volume (V T) of [18F]MK-9470 was used as a quantitative measure and compared to the use of brain uptake, expressed as SUV, a simplified method of quantification.
Results
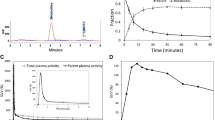
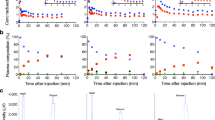
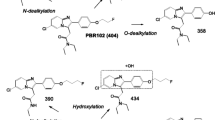
The percentage of intact [18F]MK-9470 in arterial plasma samples was 80 ± 23 % at 10 min, 38 ± 30 % at 40 min and 13 ± 14 % at 210 min. A polar radiometabolite fraction was detected in plasma and brain tissue. The brain radiometabolite concentration was uniform across the whole brain. Displacement and pretreatment studies showed that 56 % of the tracer binding was specific and reversible. V T values obtained with a one-tissue compartment model plus constrained radiometabolite input had good identifiability (≤10 %). Ignoring the radiometabolite contribution using a one-tissue compartment model alone, i.e. without constrained radiometabolite input, overestimated the [18F]MK-9470 V T, but was correlated. A correlation between [18F]MK-9470 V T and SUV in the brain was also found (R 2 = 0.26–0.33; p ≤ 0.03).
Conclusion
While the presence of a brain-penetrating radiometabolite fraction complicates the quantification of [18F]MK-9470 in the rat brain, its tracer kinetics can be modelled using a one-tissue compartment model with and without constrained radiometabolite input.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howlett AC, Barth F, Bonner TI, Cabral G, Casellas P, Devane WA, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:161–202.
Di Marzo V, Bifulco M, De Petrocellis L. The endocannabinoid system and its therapeutic exploitation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:771–84.
Parolaro D, Realini N, Vigano D, Guidali C, Rubino T. The endocannabinoid system and psychiatric disorders. Exp Neurol. 2010;224:3–14.
Scotter EL, Abood ME, Glass M. The endocannabinoid system as a target for the treatment of neurodegenerative disease. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;160:480–98.
Katona I, Freund TF. Endocannabinoid signaling as a synaptic circuit breaker in neurological disease. Nat Med. 2008;14:923–30.
Bahr BA, Karanian DA, Makanji SS, Makriyannis A. Targeting the endocannabinoid system in treating brain disorders. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006;15:351–65.
Charalambous A, Marciniak G, Shiue CY, Dewey SL, Schlyer DJ, Wolf AP, et al. PET studies in the primate brain and biodistribution in mice using (-)-5'-18F-delta 8-THC. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991;40:503–7.
Horti AG, Fan H, Kuwabara H, Hilton J, Ravert HT, Holt DP, et al. 11C-JHU75528: a radiotracer for PET imaging of CB1 cannabinoid receptors. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:1689–96.
Terry G, Liow JS, Chernet E, Zoghbi SS, Phebus L, Felder CC, et al. Positron emission tomography imaging using an inverse agonist radioligand to assess cannabinoid CB1 receptors in rodents. Neuroimage. 2008;41:690–8.
Yasuno F, Brown AK, Zoghbi SS, Krushinski JH, Chernet E, Tauscher J, et al. The PET radioligand [11C]MePPEP binds reversibly and with high specific signal to cannabinoid CB1 receptors in nonhuman primate brain. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:259–69.
Terry GE, Liow JS, Zoghbi SS, Hirvonen J, Farris AG, Lerner A, et al. Quantitation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in healthy human brain using positron emission tomography and an inverse agonist radioligand. Neuroimage. 2009;48:362–70.
Terry GE, Hirvonen J, Liow JS, Seneca N, Tauscher JT, Schaus JM, et al. Biodistribution and dosimetry in humans of two inverse agonists to image cannabinoid CB1 receptors using positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:1499–506.
Terry GE, Hirvonen J, Liow JS, Zoghbi SS, Gladding R, Tauscher JT, et al. Imaging and quantitation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in human and monkey brains using (18)F-labeled inverse agonist radioligands. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:112–20.
Burns HD, Van Laere K, Sanabria-Bohorquez S, Hamill TG, Bormans G, Eng WS, et al. [18F]MK-9470, a positron emission tomography (PET) tracer for in vivo human PET brain imaging of the cannabinoid-1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:9800–5.
Wong DF, Kuwabara H, Horti AG, Raymont V, Brasic J, Guevara M, et al. Quantification of cerebral cannabinoid receptors subtype 1 (CB1) in healthy subjects and schizophrenia by the novel PET radioligand [11C]OMAR. Neuroimage. 2010;52:1505–13.
Addy C, Wright H, Van Laere K, Gantz I, Erondu N, Musser BJ, et al. The acyclic CB1R inverse agonist taranabant mediates weight loss by increasing energy expenditure and decreasing caloric intake. Cell Metab. 2008;7:68–78.
Van Laere K, Goffin K, Casteels C, Dupont P, Mortelmans L, de Hoon J, et al. Gender-dependent increases with healthy aging of the human cerebral cannabinoid-type 1 receptor binding using [(18)F]MK-9470 PET. Neuroimage. 2008;39:1533–41.
Van Laere K, Goffin K, Bormans G, Casteels C, Mortelmans L, de Hoon J, et al. Relationship of type 1 cannabinoid receptor availability in the human brain to novelty-seeking temperament. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66:196–204.
Van Laere K, Casteels C, Dhollander I, Goffin K, Grachev I, Bormans G, et al. Widespread decrease of type 1 cannabinoid receptor availability in Huntington disease in vivo. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1413–7.
Gérard N, Pieters G, Goffin K, Bormans G, Van Laere K. Brain type 1 cannabinoid receptor availability in patients with anorexia and bulimia nervosa. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;70:777–84.
Van Laere K, Casteels C, Lunskens S, Goffin K, Grachev ID, Bormans G, et al. Regional changes in type 1 cannabinoid receptor availability in Parkinson's disease in vivo. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33:620.e1–8.
Goffin K, Van Paesschen W, Van Laere K. In vivo activation of endocannabinoid system in temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Brain. 2011;134:1033–40.
Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J, Fujita M, Gjedde A, Gunn RN, et al. Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27:1533–9.
Need AB, Davis RJ. Alexander-Chacko JT, Eastwood B, Chernet E, Phebus LA, et al. The relationship of in vivo central CB1 receptor occupancy to changes in cortical monoamine release and feeding elicited by CB1 receptor antagonists in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006;184:26–35.
Boellaard R, van Lingen A, Lammertsma AA. Experimental and clinical evaluation of iterative reconstruction (OSEM) in dynamic PET: quantitative characteristics and effects on kinetic modeling. J Nucl Med. 2001;42:808–17.
Hoekzema E, Rojas S, Herance R, Pareto D, Abad S, Jimenez X, et al. [(11)C]-DASB microPET imaging in the aged rat: frontal and meso-thalamic increases in serotonin transporter binding. Exp Gerontol. 2011;46:1020–5.
Sanabria-Bohorquez SM, Hamill TG, Goffin K, De Lepeleire I, Bormans G, Burns HD, et al. Kinetic analysis of the cannabinoid-1 receptor PET tracer [(18)F]MK-9470 in human brain. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:920–33.
Celen S, Koole M, De Angelis M, Sannen I, Chitneni SK, Alcazar J, et al. Preclinical evaluation of 18F-JNJ41510417 as a radioligand for PET imaging of phosphodiesterase-10A in the brain. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1584–91.
Casteels C, Vermaelen P, Nuyts J, Van Der Linden A, Baekelandt V, Mortelmans L, et al. Construction and evaluation of multitracer small-animal PET probabilistic atlases for voxel-based functional mapping of the rat brain. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:1858–66.
Tai YC, Ruangma A, Rowland D, Siegel S, Newport DF, Chow PL, et al. Performance evaluation of the microPET focus: a third-generation microPET scanner dedicated to animal imaging. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:455–63.
Thie JA. Understanding the standardized uptake value, its methods, and implications for usage. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:1431–4.
Thie JA, Hubner KF, Isidoro FP, Smith GT. A weight index for the standardized uptake value in 2-deoxy-2-[F-18]fluoro-D-glucose-positron emission tomography. Mol Imaging Biol. 2007;9:91–8.
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Little MD, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, de Costa BR, et al. Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87:1932–6.
Fujita M, Seibyl JP, Verhoeff NP, Ichise M, Baldwin RM, Zoghbi SS, et al. Kinetic and equilibrium analyses of [(123)I]epidepride binding to striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D(2) receptors. Synapse. 1999;34:290–304.
Hirst RA, Almond SL, Lambert DG. Characterisation of the rat cerebella CB1 receptor using SR141716A, a central cannabinoid receptor antagonist. Neurosci Lett. 1996;220:101–4.
Zoghbi SS, Shetty HU, Ichise M, Fujita M, Imaizumi M, Liow JS, et al. PET imaging of the dopamine transporter with 18F-FECNT: a polar radiometabolite confounds brain radioligand measurements. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:520–7.
Dewar KM, Montreuil B, Grondin L, Reader TA. Dopamine D2 receptors labeled with [3H]raclopride in rat and rabbit brains. Equilibrium binding, kinetics, distribution and selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989;250:696–706.
Khawaja X, Evans N, Reilly Y, Ennis C, Minchin MC. Characterisation of the binding of [3H]WAY-100635, a novel 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor antagonist, to rat brain. J Neurochem. 1995;64:2716–26.
Vandenbroucke A, Foudray AM, Olcott PD, Levin CS. Performance characterization of a new high resolution PET scintillation detector. Phys Med Biol. 2010;55:5895–911.
Acknowledgements
Merck & Co is acknowledged for making available the [18F]MK-9470 precursor. The authors thank Peter Vermaelen, Ann Van Santvoort, Nathalie Gérard, Ivan Sannen and Julie Cornelis for their assistance in data acquisition, as well as the Leuven PET radiopharmacy team for tracer preparation. Financial support of the Research Council of the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (OT/05/58), the Fund for Scientific Research, Flanders, Belgium (FWO/G.0548.06), and the K.U.Leuven In Vivo Molecular Imaging (IMIR) Consortium (KUL PF/10/017) is gratefully acknowledged. Cindy Casteels is a postdoctoral fellow and Koen Van Laere a senior clinical investigator of the Flemish Fund for Scientific Research.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casteels, C., Koole, M., Celen, S. et al. Preclinical evaluation and quantification of [18F]MK-9470 as a radioligand for PET imaging of the type 1 cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39, 1467–1477 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-012-2163-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-012-2163-3