Abstract
Rationale
Cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptor antagonists are reportedly effective in reducing food intake both preclinically and clinically. This may be due in part to their effects on monoamine release in the brain. The level of central CB1 receptor occupancy underlying these neurobiological effects is unclear.
Objectives
We explored the relationship between in vivo CB1 receptor occupancy in the frontal cortex and changes in both monoamine release in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and feeding behavior in rats in response to two orally administered CB1 receptor antagonists presently in clinical trials, SR141716A (rimonabant) and SLV319.
Methods
CB1 receptor occupancy was measured using [3H] SR141716A, and these occupancies were related to potencies to mediate increases in dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine (NE) release measured with microdialysis and decreases in consumption of a highly palatable diet (HP).
Results
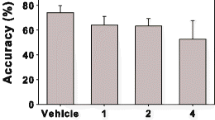
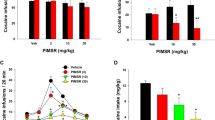
High receptor occupancy levels (>65%) were required to detect increases in monoamine release that were achieved with 3 and 10 mg/kg of SR141716A and 10 mg/kg of SLV319 for DA and 10 mg/kg of SR141716A for NE. Decreases in HP consumption were seen at occupancies higher than 65% for SR141716A that were achieved with 3 and 10 mg/kg. In contrast, decreases in HP consumption were seen at relatively low CB1 receptor occupancies (11%) for SLV319.
Conclusions
The occupancy method described here is an effective tool for interrelating central CB1 receptor occupancy with neurobiological actions of CB1 receptor antagonists and for furthering our understanding of the role of CB1 receptors in central nervous system physiology and pathology.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel E (1971) Effects of marihuana on the solution of anagrams, memory, and appetite. Nature 231:260–261
Arnone M, Maruani J, Chaperon F, Thiebot M, Poncelet MH, Soubrie P, Le Fur G (1997) Selective inhibition of sucrose and ethanol intake by SR141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 132:104–106
Breivogel CS, Griffin G, Di Marzo V, Martin BR (2001) Evidence for a new G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor in mouse brain. Mol Pharmacol 60:155–163
Cani P, Montoya M, Neyrinck A, Delzenne N, Lambert D (2004) Potential modulation of plasma ghrelin and glucagon-like peptide-1 by anorexigenic cannabinoid compounds, SR141716A (rimonabant) and oleoylethanolamide. Br J Nutr 92:757–761
Cohen C, Perrault G, Voltz C, Steinberg R, Soubrie P (2002) SR141716, a central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor antagonist, blocks the motivational and dopamine-releasing effects of nicotine in rats. Behav Pharmacol 13:451–463
Cosenza M, Gifford A, Gatley S, Pyatt B, Liu Q, Makriyannis A, Volkow N (2000) Locomotor activity and occupancy of brain cannabinoid CB1 receptors by the antagonist/inverse agonist AM281. Synapse 38:477–482
De Fronseca F, Del Arco I, Martin-Calderon J, Gorriti M, Navarro M (1998) Role of the endogenous cannabinoid system in the regulation of motor activity. Neurobiol Dis 5:483–501
Deroche-Gamonet V, Le Moal M, Piazza P, Soubrie P (2001) SR141716, a CB1 receptor antagonist, decreases the sensitivity to the reinforcing effects of electrical brain stimulation in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 157:254–259
Devane W, Dysarc F, Johnson M, Mevin L, Howlett A (1988) Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol 34:605–613
Devane W, Hanus L, Breuer A, Pertwee R, Stevenson L, Griffin G, Gibson D, Mandelbaum A, Etinger A, Mechoulam R (1992) Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 258:1946–1949
Di Marzo V, Goparaju S, Wang L, Liu J, Batkai S, Jarai Z, Fezza F, Miura G, Palmiter R, Sugiura T, Kunos G (2001) Leptin-regulated endocannabinoids are involved in maintaining food intake. Nature 410:822–825
Durcan M, Denner G, White J, Johnston J, Gonzales D, Niaura R, Rigotti N, Sachs D (2002) The effect of bupropion sustained-release on cigarette craving after smoking cessation. Clin Ther 24:540–551
Gallant A (1987) Nonlinear statistical models. Wiley, New York
Gaoni Y, Mechoulam R (1964) Isolation, structure and partial synthesis of an active component of hashish. J Am Chem Soc 86:1646–1647
Goeders N, Kuhar M (1985) Benzodiazepine receptor binding in vivo with [3H]-Ro 15-1788. Life Sci 37:345–355
Gomez R, Navarro M, Ferrer B, Trigo J, Bilbao A, Del Arco I, Cippitelli A, Nava F, Piomelli D, Rodriguez de Fonseca F (2002) A peripheral mechanism for CB1 cannabinoid receptor-dependent modulation of feeding. J Neurosci 22:9612–9617
Grundy R (2002) The therapeutic potential of the cannabinoids in neuroprotection. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 11:1365–1374
Haller J, Varga B, Ledent C, Freund T (2004) CB1 cannabinoid receptors mediate anxiolytic effects: convergent genetic and pharmacological evidence with CB1-specific agents. Behav Pharmacol 15:299–304
Lange J, Coolen H, van Stuivenberg H, Dijksman J, Herremans A, Ronken E, Keizer H, Hiskias G, Tipker K, McCreary A, Veerman W, Wals H, Stork B, Verveer P, den Hartog A, de Jong N, Adolfs T, Hoogendoorn J, Kruse C (2004) Synthesis, biological properties, and molecular modeling investigations of novel 3,4-diarylpyrazolines as potent and selective CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 47:627–643
Li S, Perry K, Wong D (2002) Influence of fluoxetine on the ability of bupropion to modulate extracellular dopamine and norepinephrine concentrations in three mesocorticolimbic areas of rats. Neuropharmacology 42:181–190
Lichtman A (2000) SR141716A enhances spatial memory as assessed in a radial-arm maze task in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 404:175–179
Matsuda L, Lolait S, Brownstein M, Young A, Bonner T (1990) Structure of cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 346:561–564
Mechoulam R, Ben-Shabat S, Hanus L, Ligumsky M, Kaminski N et al (1995) Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 50:83–90
Mechoulam R, Fride E, Hanus L, Sheskin T, Bisogno T, Di Marzo V, Bayewitch M, Vogel Z (1997) Anandamide may mediate sleep induction. Nature 389:25–26
Monory K, Tzavara ET, Lexime J, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Borsodi A, Hanoune J (2002) Novel, not adenylyl cyclase-coupled cannabinoid binding site in cerebellum of mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 292:231–235
Munro S, Thomas K, Abu-Shaar M (1993) Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 365:61–65
Navarro M, Carrera M, Fratta W, Valverde O, Cossu G, Fattore L, Chowen J, Gomez R, Del Arco I, Villanua M, Maldonado R, Koub G, Rodriguez de Foncesca F (2001) Functional interaction between opioid and cannabinoid receptors in drug self-administration. J Neurosci 21:5344–5350
Nunez E, Benito C, Pazos M, Barbachano A, Fajardo O, Gonzalez S, Tolon R, Romero J (2004) Cannabinoid CB2 receptors are expressed by perivascular microglial cells in the human brain: an immunohistochemical study. Synapse 53:208–213
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Perry K, Fuller R (1997) Fluoxetine increases norepinephrine release in rat hypothalamus as measured by tissue levels of MHPG-SO4 and microdialysis in conscious rats. J Neural Transm 104:953–966
Plasse T, Gorter R, Krasnow S, Lane M, Shepard K, Wadleigh R (1991) Recent clinical experience with dronabinol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40:695–700
Poncelet M, Maruani J, Calassi R, Soubrie P (2003) Overeating, alcohol and sucrose consumption decrease in CB1 receptor deleted mice. Neurosci Lett 343:216–218
Ravinet Trillou C, Delgorge C, Menet C, Arnone M, Soubrie P (2004) CB1 cannabinoid receptor knockout in mice leads to leanness, resistance to diet-induced obesity and enhanced leptin sensitivity. Int J Obes 28:640–648
Rinaldi-Carmona M, Barth F, Heaulme M, Shire D, Calandra B et al (1994) SR141716A, a potent and selective antagonist of the brain cannabinoid receptor. FEBS Lett 350:240–244
Robinson L, Riedel G (2004) Cannabinoid function in spatial learning: an update. Curr Neuropharmacol 2:125–143
Santucci V, Storme J, Soubrie P, Le Fur G (1996) Arousal-enhancing properties of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR 141716A in rats as assessed by electroencephalographic spectral and sleep-waking cycle analysis. Life Sci 58:PL103–110
Simiand J, Keane M, Keane PE, Soubrie P (1998) SR141716, a CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist, selectively reduces sweet food intake in marmoset. Behav Pharmacol 9:179–181
Smith R, Fathi Z (2005) Recent advances in the research and development of CB(1) antagonists. IDrugs 8:53–66
Tataranni P, Gautier JF, Chen K, Uecker A, Bandy D, Salbe A, Pratley R, Lawson M, Reiman E, Ravussin E (1999) Neuroanatomical correlates of hunger and satiation in humans using positron emission tomography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:4569–4574
Tsou K, Brown S, Sanudo-Pena M, Mackie K, Walker J (1998) Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 83:393–411
Tzavara E, Davis R, Perry K, Li X, Salhoff C, Bymaster F, Witkin J, Nomikos GG (2003) The CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A selectively increases monoaminergic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex: implications for therapeutic actions. Br J Pharmacol 138:544–553
Van Gaal LF, Rissanen AM, Scheen AJ, Ziegler O, Rössner S (2005) Effects of the cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker rimonabant on weight reduction and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight patients: 1-year experience from the RIO-Europe study. Lancet 365:1389–1397
Verty A, McGregor I, Mallet P (2004) Consumption of high carbohydrate, high fat, and normal chow is equally suppressed by a cannabinoid receptor antagonist in non-deprived rats. Neurosci Lett 354:217–220
Walker M, Huang S (2002) Cannabinoid analgesia. Pharmacol Ther 95:127–135
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Need, A.B., Davis, R.J., Alexander-Chacko, J.T. et al. The relationship of in vivo central CB1 receptor occupancy to changes in cortical monoamine release and feeding elicited by CB1 receptor antagonists in rats. Psychopharmacology 184, 26–35 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0234-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0234-x