Abstract
Purpose
Cannabinoid subtype 1 (CB1) receptors are found in nearly every organ in the body, may be involved in several neuropsychiatric and metabolic disorders, and are therefore an active target for pharmacotherapy and biomarker development. We recently reported brain imaging of CB1 receptors with two PET radioligands: 11C-MePPEP and 18F-FMPEP-d 2. Here we describe the biodistribution and dosimetry estimates for these two radioligands.
Methods
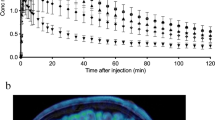
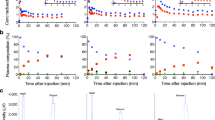
Seven healthy subjects (four men and three women) underwent whole-body PET scans for 120 min after injection with 11C-MePPEP. Another seven healthy subjects (two men and five women) underwent whole-body PET scans for 300 min after injection with 18F-FMPEP-d 2. Residence times were acquired from regions of interest drawn on tomographic images of visually identifiable organs for both radioligands and from radioactivity excreted in urine for 18F-FMPEP-d 2.
Results
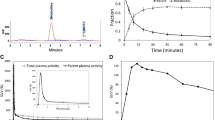
The effective doses of 11C-MePPEP and 18F-FMPEP-d 2 are 4.6 and 19.7 μSv/MBq, respectively. Both radioligands demonstrated high uptake of radioactivity in liver, lung, and brain shortly after injection and accumulated radioactivity in bone marrow towards the end of the scan. After injection of 11C-MePPEP, radioactivity apparently underwent hepatobiliary excretion only, while radioactivity from 18F-FMPEP-d 2 showed both hepatobiliary and urinary excretion.
Conclusion
11C-MePPEP and 18F-FMPEP-d2 yield an effective dose similar to other PET radioligands labeled with either 11C or 18F. The high uptake in brain confirms the utility of these two radioligands to image CB1 receptors in brain, and both may also be useful to image CB1 receptors in the periphery.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piomelli D. The molecular logic of endocannabinoid signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci 2003;4:873–84.
Glickfeld LL, Scanziani M. Self-administering cannabinoids. Trends Neurosci 2005;28:341–3.
Basavarajappa BS. The endocannabinoid signaling system: a potential target for next-generation therapeutics for alcoholism. Mini Rev Med Chem 2007;7:769–79.
Eggan SM, Hashimoto T, Lewis DA. Reduced cortical cannabinoid 1 receptor messenger RNA and protein expression in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2008;65:772–84.
Kunos G, Osei-Hyiaman D, Batkai S, Sharkey KA, Makriyannis A. Should peripheral CB(1) cannabinoid receptors be selectively targeted for therapeutic gain? Trends Pharmacol Sci 2009;30:1–7.
Caraceni P, Domenicali M, Giannone F, Bernardi M. The role of the endocannabinoid system in liver diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;23:65–77.
Mukhopadhyay P, Mohanraj R, Bátkai S, Pacher P. CB1 cannabinoid receptor inhibition: promising approach for heart failure? Congest Heart Fail 2008;14:330–4.
Donohue SR, Krushinski JH, Pike VW, Chernet E, Phebus L, Chesterfield AK, et al. Synthesis, ex vivo evaluation, and radiolabeling of potent 1, 5-diphenylpyrrolidin-2-one cannabinoid subtype-1 receptor ligands as candidates for in vivo imaging. J Med Chem 2008;51:5833–42.
Terry GE, Liow J-S, Zoghbi SS, Hirvonen J, Farris AG, Lerner A, et al. Quantitation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in healthy human brain using positron emission tomography and an inverse agonist radioligand. Neuroimage 2009;48:362–70.
Terry GE, Hirvonen J, Liow J-S, Zoghbi SS, Gladding R, Tauscher JT, et al. Imaging and quantitation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in human and monkey brains using (18)F-labeled inverse agonist radioligands. J Nucl Med 2010;51:112–20.
Sprague DR, Chin FT, Liow JS, Fujita M, Burns HD, Hargreaves R, et al. Human biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the tachykinin NK1 antagonist radioligand [18F]SPA-RQ: comparison of thin-slice, bisected, and 2-dimensional planar image analysis. J Nucl Med 2007;48:100–7.
ICRP. ICRP publication 89: Basic anatomical and physiological data for use in radiological protection: reference values. A report of age- and gender-related differences in the anatomical and physiological characteristics of reference individuals. Oxford: Pergamon; 2002.
ICRP. ICRP publication 23: Report of the Task Group on Reference Man. Oxford: Pergamon; 1975.
ICRP. ICRP publication 30 part 1: Limits for intakes of radionuclides by workers. Oxford: Pergamon; 1979.
Stabin MG, Sparks RB, Crowe E. OLINDA/EXM: the second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med 2005;46:1023–7.
Brown AK, Fujita M, Fujimura Y, Liow JS, Stabin M, Ryu YH, et al. Radiation dosimetry and biodistribution in monkey and man of 11C-PBR28: a PET radioligand to image inflammation. J Nucl Med 2007;48:2072–9.
Patinkin D, Milman G, Breuer A, Fride E, Mechoulam R. Endocannabinoids as positive or negative factors in hematopoietic cell migration and differentiation. Eur J Pharmacol 2008;595:1–6.
Galiegue S, Mary S, Marchand J, Dussossoy D, Carriere D, Carayon P, et al. Expression of central and peripheral cannabinoid receptors in human immune tissues and leukocyte subpopulations. Eur J Biochem 1995;232:54–61.
Do Y, McKallip RJ, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti PS. Activation through cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 on dendritic cells triggers NF-kappaB-dependent apoptosis: novel role for endogenous and exogenous cannabinoids in immunoregulation. J Immunol 2004;173:2373–82.
Vesselle H, Grierson J, Peterson LM, Muzi M, Mankoff DA, Krohn KA. 18F-Fluorothymidine radiation dosimetry in human PET imaging studies. J Nucl Med 2003;44:1482–8.
Brown WD, Oakes TR, DeJesus OT, Taylor MD, Roberts AD, Nickles RJ, et al. Fluorine-18-fluoro-L-DOPA dosimetry with carbidopa pretreatment. J Nucl Med 1998;39:1884–91.
Bátkai S, Jarai Z, Wagner JA, Goparaju SK, Varga K, Liu J, et al. Endocannabinoids acting at vascular CB1 receptors mediate the vasodilated state in advanced liver cirrhosis. Nat Med 2001;7:827–32.
Teixeira-Clerc F, Julien B, Grenard P, Tran Van Nhieu J, Deveaux V, Li L, et al. CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonism: a new strategy for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Nat Med 2006;12:671–6.
Oesch S, Walter D, Wachtel M, Pretre K, Salazar M, Guzmán M, et al. Cannabinoid receptor 1 is a potential drug target for treatment of translocation-positive rhabdomyosarcoma. Mol Cancer Ther 2009;8:1838–45.
Van Laere K, Koole M, Sanabria Bohorquez SM, Goffin K, Guenther I, Belanger MJ, et al. Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the human cannabinoid type-1 receptor ligand 18F-MK-9470 in healthy subjects. J Nucl Med 2008;49:439–45.
Acknowledgements
We thank Maria D. Ferraris Araneta, William C. Kreisl, Barbara Scepura, Gerald Hodges, Amanda Farris, and Leah Dickstein for subject recruitment and care; Robert Gladding for his assistance in image processing; the NIH PET Department for imaging; and PMOD Technologies for providing its image analysis and modeling software. This research was supported by a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement with Eli Lilly and by the Intramural Program of NIMH (projects # Z01-MH-002852-04 and #Z01-MH-002793-06). Jussi Hirvonen was supported by personal grants from The Academy of Finland, The Finnish Cultural Foundation, The Finnish Foundation for Alcohol Studies, The Finnish Medical Foundation, The Instrumentarium Foundation, The Jalmari and Rauha Ahokas Foundation, The Paulo Foundation, The Research Foundation of Orion Corporation, and The Yrjö Jahnsson Foundation.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terry, G.E., Hirvonen, J., Liow, JS. et al. Biodistribution and dosimetry in humans of two inverse agonists to image cannabinoid CB1 receptors using positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37, 1499–1506 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1411-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-010-1411-7