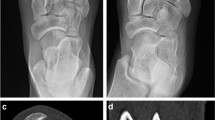
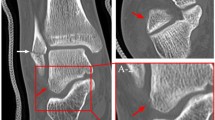
Abstract
Purpose
To prospectively evaluate a dedicated extremity cone-beam CT (CBCT) scanner in cases with and without orthopedic hardware by (1) comparing its imaging duration and image quality to those of radiography and multidetector CT (MDCT) and (2) comparing its radiation dose to that of MDCT.
Materials and methods
Written informed consent was obtained for all subjects for this IRB-approved, HIPAA-compliant study. Fifty subjects with (1) fracture of small bones, (2) suspected intraarticular fracture, (3) fracture at the site of complex anatomy, or (4) a surgical site difficult to assess with radiography alone were recruited and scanned on an extremity CBCT scanner prior to FDA approval. Same-day radiographs were performed in all subjects. Some subjects also underwent MDCT within 1 month of CBCT. Imaging duration and image quality were compared between CBCT and radiographs. Imaging duration, effective radiation dose, and image quality were compared between CBCT and MDCT.
Results
Fifty-one CBCT scans were performed in 50 subjects. Average imaging duration was shorter for CBCT than radiographs (4.5 min vs. 6.6 min, P = 0.001, n = 51) and MDCT (7.6 min vs. 10.9 min, P = 0.01, n = 7). Average estimated effective radiation dose was less for CBCT than MDCT (0.04 mSv vs. 0.13 mSv, P = 0.02, n = 7). CBCT images yielded more diagnostic information than radiographs in 23/51 cases and more diagnostic information than MDCT in 1/7 cases, although radiographs were superior for detecting hardware complications.
Conclusion
CBCT performs high-resolution imaging of the extremities using less imaging time than radiographs and MDCT and lower radiation dose than MDCT.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mozzo P, Procacci C, Tacconi A, Martini PT, Andreis IA. A new volumetric CT machine for dental imaging based on the cone-beam technique: preliminary results. Eur Radiol. 1998;8:1558–64.
De Cock J, Mermuys K, Goubau J, Van Petegem S, Houthoofd B, Casselman JW. Cone-beam computed tomography: a new low dose, high resolution imaging technique of the wrist, presentation of three cases with technique. Skeletal Radiol. 2012;41:93–6.
Kapila S, Conley RS, Harrell Jr WE. The current status of cone beam computed tomography imaging in orthodontics. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2011;40:24–34.
Jung Y-H, Cho B-H. Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography. Imaging Sci Dent. 2012;42:219–24.
Miracle AC, Mukherji SK. Conebeam CT of the head and neck, part 2: clinical applications. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30:1285–92.
De Vos W, Casselman J, Swennen GRJ. Cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) imaging of the oral and maxillofacial region: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;38:609–25.
Guerrero ME, Jacobs R, Loubele M, Schutyser F, Suetens P, van Steenberghe D. State-of-the-art on cone beam CT imaging for preoperative planning of implant placement. Clin Oral Investig. 2006;10:1–7.
Okano T, Harata Y, Sugihara Y, Sakaino R, Tsuchida R, Iwai K, et al. Absorbed and effective doses from cone beam volumetric imaging for implant planning. Dento-Maxillo-Facial Radiol. 2009;38:79–85.
Gracco A, Incerti Parenti S, Ioele C, Alessandri Bonetti G, Stellini E. Prevalence of incidental maxillary sinus findings in Italian orthodontic patients: a retrospective cone-beam computed tomography study. Korean J Orthod. 2012;42:329–34.
Ruivo J, Mermuys K, Bacher K, Kuhweide R, Offeciers E, Casselman JW. Cone beam computed tomography, a low-dose imaging technique in the postoperative assessment of cochlear implantation. Otol Neurotol. 2009;30:299–303.
Faccioli N, Barillari M, Guariglia S, Zivelonghi E, Rizzotti A, Cerini R, et al. Radiation dose saving through the use of cone-beam CT in hearing-impaired patients. Radiol Med. 2009;114:1308–18.
Vu T, Bayome M, Kook Y-A, Han SH. Evaluation of the palatal soft tissue thickness by cone-beam computed tomography. Korean J Orthod. 2012;42:291–6.
de Souza KRS, Oltramari-Navarro PVP, de Lima Navarro R, de Castro Ferreira Conti AC, de Almeida MR. Reliability of a method to conduct upper airway analysis in cone-beam computed tomography. Braz Oral Res. 2013;27:48–54.
Faccioli N, Foti G, Barillari M, Atzei A, Mucelli RP. Finger fractures imaging: accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography and multislice computed tomography. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39:1087–95.
Koskinen SK, Haapamäki VV, Salo J, Lindfors NC, Kortesniemi M, Seppälä L, et al. CT arthrography of the wrist using a novel, mobile, dedicated extremity cone-beam CT (CBCT). Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42:649–57.
Kröpil P, Hakimi AR, Jungbluth P, Riegger C, Rubbert C, Miese F, et al. Cone beam CT in assessment of tibial bone defect healing: an animal study. Acad Radiol. 2012;19:320–5.
Tuominen EKJ, Kankare J, Koskinen SK, Mattila KT. Weight-bearing CT imaging of the lower extremity. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200:146–8.
Hirschmann A, Pfirrmann CWA, Klammer G, Espinosa N, Buck FM. Upright Cone CT of the hindfoot: Comparison of the non-weight-bearing with the upright weight-bearing position. Eur Radiol. 2013.
Carrino JA, Al Muhit A, Zbijewski W, Thawait GK, Stayman JW, Packard N, et al. Dedicated cone-beam CT system for extremity imaging. Radiology. 2014;270:816–24.
Joemai RMS, Zweers D, Obermann WR, Geleijns J. Assessment of patient and occupational dose in established and new applications of MDCT fluoroscopy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192:881–6.
Finkenstaedt T, Morsbach F, Calcagni M, Vich M, Pfirrmann CWA, Alkadhi H, et al. Metallic artifacts from internal scaphoid fracture fixation screws: comparison between C-arm flat-panel, cone-beam, and multidetector computed tomography. Invest Radiol. 2014;49:532–9.
Sprawls P. AAPM tutorial. CT image detail and noise. RadioGraphics. 1992;12:1041–6.
Blokhuis TJ, de Bruine JH, Bramer JA, den Boer FC, Bakker FC, Patka P, et al. The reliability of plain radiography in experimental fracture healing. Skeletal Radiol. 2001;30:151–6.
Panjabi MM, Lindsey RW, Walter SD, White AA. The clinician’s ability to evaluate the strength of healing fractures from plain radiographs. J Orthop Trauma. 1989;3:29–32.
Schnarkowski P, Rédei J, Peterfy CG, Weidenmaier W, Mutschler W, Arand M, et al. Tibial shaft fractures: assessment of fracture healing with computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1995;19:777–81.
Holberg C, Steinhäuser S, Geis P, Rudzki-Janson I. Cone-beam computed tomography in orthodontics: benefits and limitations. J Orofac Orthop. 2005;66:434–44.
Huda W, Gkanatsios N. Radiation dosimetry for extremity radiographs. Health Phys. 1998;75:492–9.
Koivisto J, Kiljunen T, Wolff J, Kortesniemi M. Assessment of effective radiation dose of an extremity CBCT, MSCT and conventional X ray for knee area using MOSFET dosemeters. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2013;157:515–24.
United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, Vol. 1: Sources, vol. 1. New York: United Nations Publishing; 2000.
Coppenrath E, Draenert F, Lechel U, Veit R, Meindl T, Reiser M. et al [Cross-sectional imaging in dentomaxillofacial diagnostics: dose comparison of dental MSCT and NewTom 9000 DVT]. Röfo. 2008;180:396–401.
Roberts JA, Drage NA, Davies J, Thomas DW. Effective dose from cone beam CT examinations in dentistry. Br J Radiol. 2009;82:35–40.
Koong B. Cone beam imaging: is this the ultimate imaging modality? Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21:1201–8.
Tsiklakis K, Donta C, Gavala S, Karayianni K, Kamenopoulou V, Hourdakis CJ. Dose reduction in maxillofacial imaging using low dose Cone Beam CT. Eur J Radiol. 2005;56:413–7.
Li T, Li X, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Heron DE, Huq MS. Simultaneous reduction of radiation dose and scatter for CBCT by using collimators. Med Phys. 2013;40:121913.
Boas FE, Fleischmann D. CT artifacts: causes and reduction techniques. Imag Med. 2012;4:229–40.
Alsufyani NA, Noga ML, Finlay WH, Major PW. Topical contrast agents to improve soft-tissue contrast in the upper airway using cone beam CT: a pilot study. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2013;42:20130022.
Endo M, Tsunoo T, Nakamori N, Yoshida K. Effect of scattered radiation on image noise in cone beam CT. Med Phys. 2001;28:469.
Schulze R, Heil U, Gross D, Bruellmann DD, Dranischnikow E, Schwanecke U, et al. Artefacts in CBCT: a review. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2011;40:265–73.
Meilinger M, Schmidgunst C, Schütz O, Lang EW. Metal artifact reduction in cone beam computed tomography using forward projected reconstruction information. Z Med Phys. 2011;21:174–82.
Wang Q, Li L, Zhang L, Chen Z, Kang K. A novel metal artifact reducing method for cone-beam CT based on three approximately orthogonal projections. Phys Med Biol. 2013;58:1–17.
Li X, Li T, Yang Y, Heron DE, Huq MS. A novel image-domain-based cone-beam computed tomography enhancement algorithm. Phys Med Biol. 2011;56:2755–66.
Zhu L, Wang J, Xing L. Noise suppression in scatter correction for cone-beam CT. Med Phys. 2009;36:741–52.
Stuehmer C, Essig H, Bormann K-H, Majdani O, Gellrich N-C, Rücker M. Cone beam CT imaging of airgun injuries to the craniomaxillofacial region. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;37:903–6.
Luckow M, Deyhle H, Beckmann F, Dagassan-Berndt D, Müller B. Tilting the jaw to improve the image quality or to reduce the dose in cone-beam computed tomography. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80:e389–93.
Kataoka ML, Hochman MG, Rodriguez EK, Lin P-JP, Kubo S, Raptopolous VD. A review of factors that affect artifact from metallic hardware on multi-row detector computed tomography. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2010;39:125–36.
Gupta R, Cheung AC, Bartling SH, Lisauskas J, Grasruck M, Leidecker C, et al. Flat-panel volume CT: fundamental principles, technology, and applications. Radiographics. 2008;28:2009–22.
Dixon RL, Boone JM. Stationary table CT dosimetry and anomalous scanner-reported values of CTDIvol. Med Phys. 2014;41:011907.
American Association of Physicists in Medicine. Report of AAPM Task Group 111: The Future of CT Dosimetry. Comprehensive Methodology for the Evaluation of Radiation Dose in X-Ray Computed Tomography. AAPM; 2010.
Zbijewski W, De Jean P, Prakash P, Ding Y, Stayman JW, Packard N, et al. A dedicated cone-beam CT system for musculoskeletal extremities imaging: design, optimization, and initial performance characterization. Med Phys. 2011;38:4700–13.
Schulze D, Heiland M, Thurmann H, Adam G. Radiation exposure during midfacial imaging using 4- and 16-slice computed tomography, cone beam computed tomography systems and conventional radiography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2004;33:83–6.
Braak SJ, van Strijen MJL, van Es HW, Nievelstein RAJ, van Heesewijk JPM. Effective dose during needle interventions: cone-beam CT guidance compared with conventional CT guidance. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;22:455–61.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Marie Verlicco and Patricia Giorgio, registered radiologic technologists, for undergoing training in the operation of the Verity CBCT scanner and for recruiting subjects for the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, A.J., Chang, C.Y., Thomas, B.J. et al. Using cone-beam CT as a low-dose 3D imaging technique for the extremities: initial experience in 50 subjects. Skeletal Radiol 44, 797–809 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2105-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2105-9